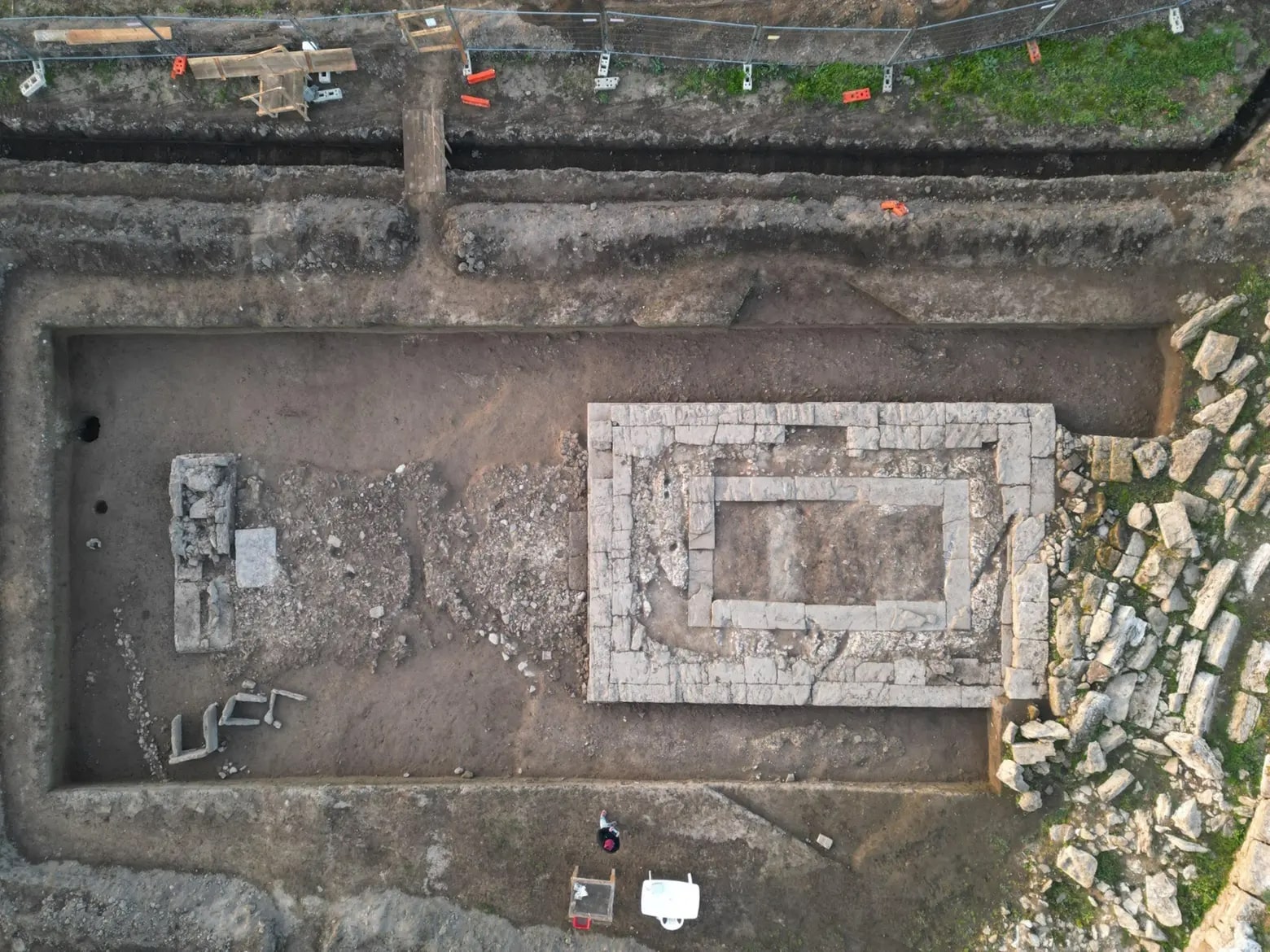
Archaeologists have made a series of extraordinary discoveries that may fundamentally alter the understanding of the past of the ancient city of Magna Graecia thanks to the delicate restoration work done on the Greek temple discovered in 2019 along the walls of the ancient city Poseidonia, present-day Paestum.
Located in the Italian province of Salerno, Paestum was a large ancient Greek city on the coast of the Tyrrhenian Sea in Magna Graecia (southern Italy). It is now famous for three Doric-order Greek temples dating from around 550 to 450 BC.
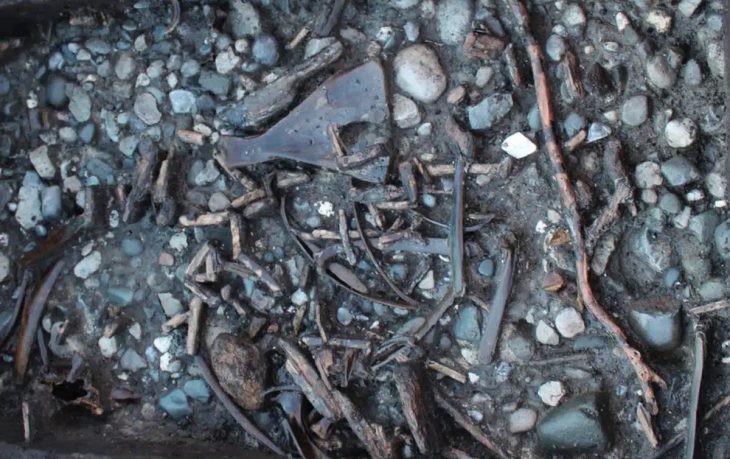
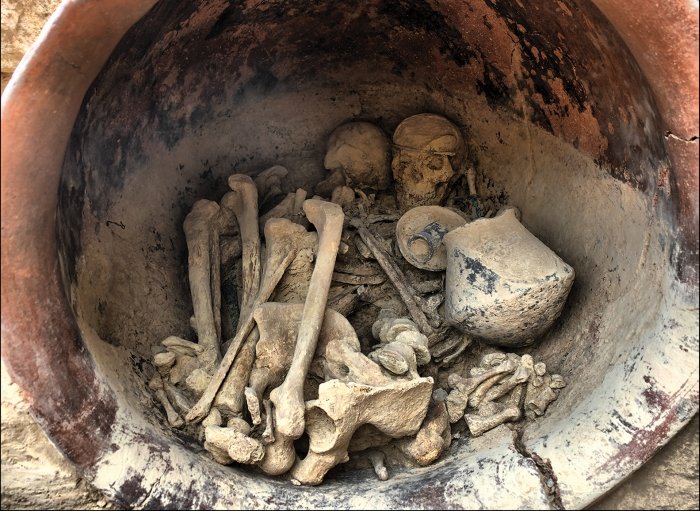
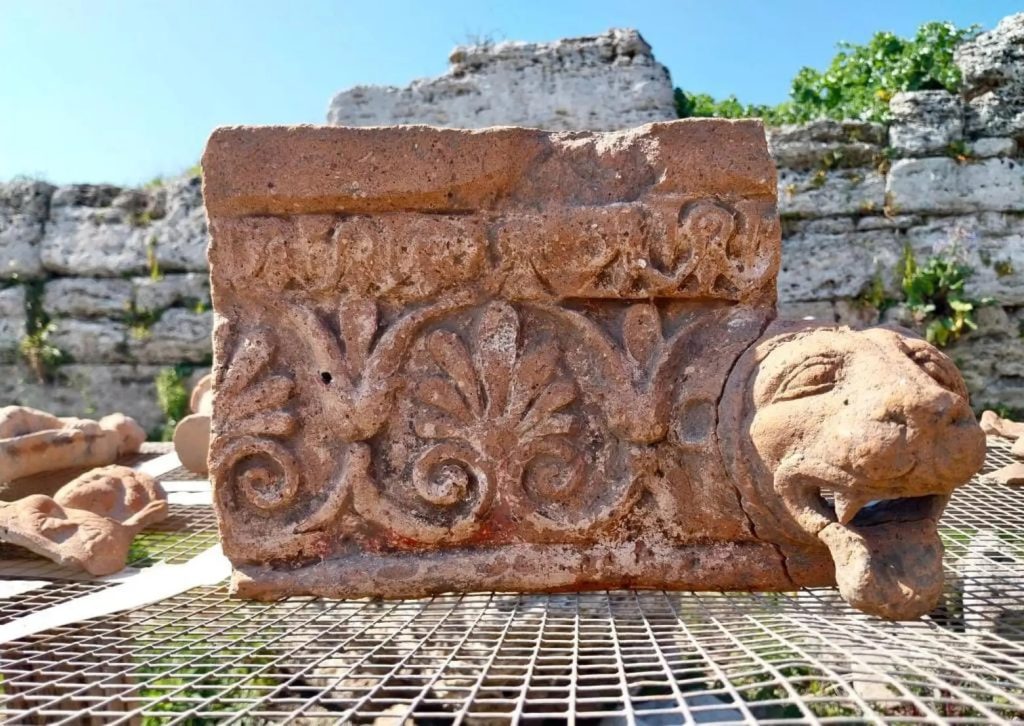
The ruins of another temple were found in 2019 during excavations. More artifacts have been found as a result of the ongoing excavation, including a stone pedestal with steps, colored terracotta roof decorations with lion-shaped dripstones, an extraordinary gorgon, and an impactful representation of Aphrodite.
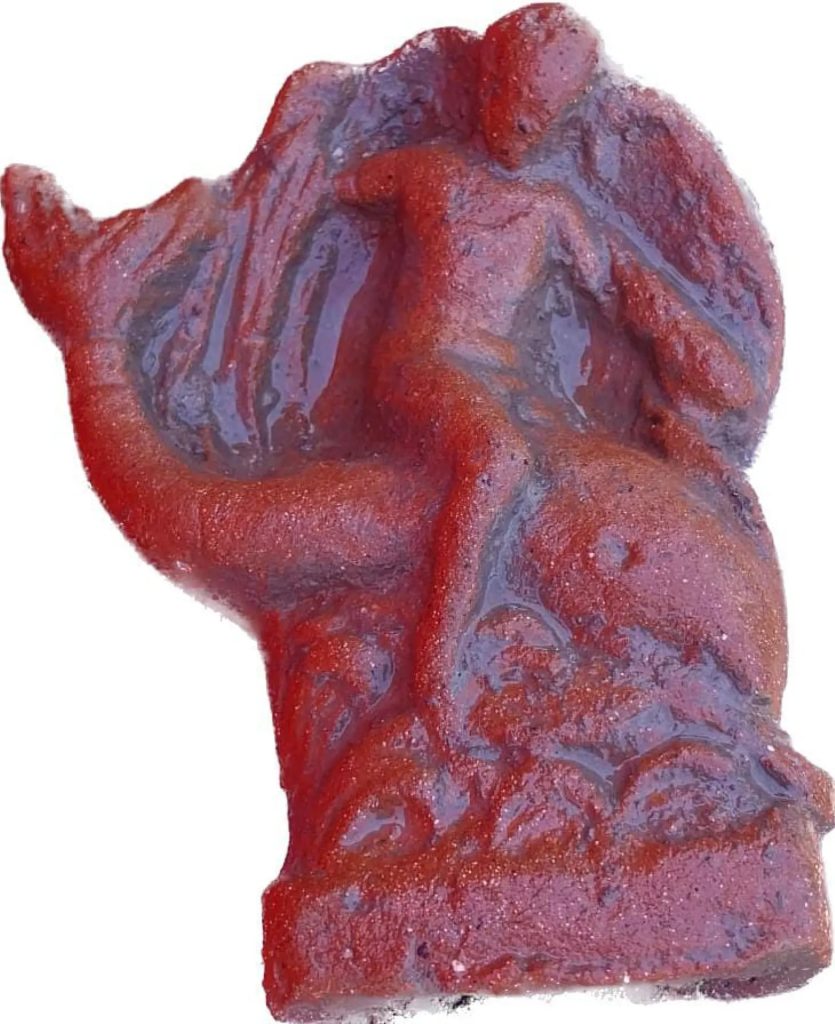
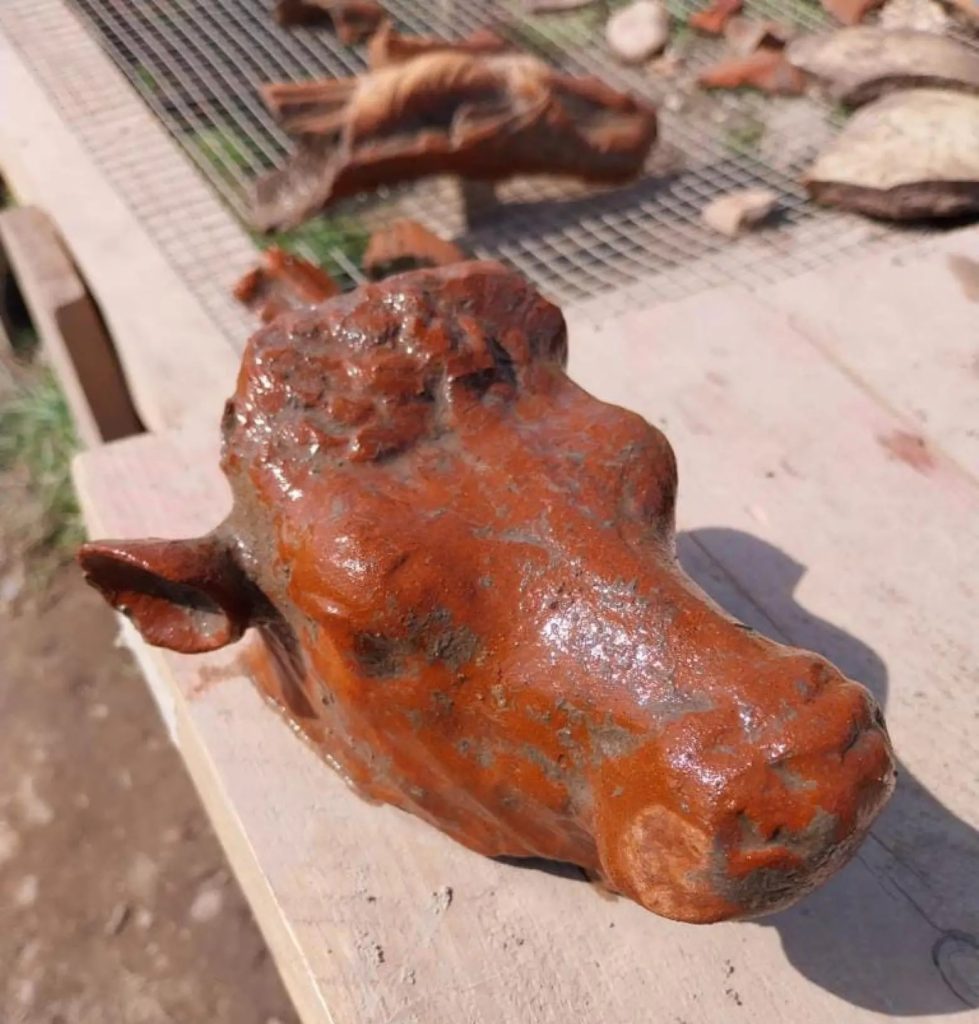
In addition, an altar with groves in the stones to catch the blood from sacrifices and seven bullheads are present. Votive offerings that have been uncovered depict Eros riding a dolphin and proceeding in the direction of Poseidon, the god who is responsible for the city’s name.

Findings which, as confirmed by the director Tiziana D’Angelo herself, could “change the known history of ancient Poseidonia”.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Tiziana D’Angelo, the Director of the Paestum archaeological site, told ANSA the dig was set to “change the recorded history of ancient Poseidonia”.
It’s almost like looking through a window into the city’s 500-year history. Founded by Greeks from Sybaris in 600 BC, it was later conquered by Lucanians before becoming a Roman colony.
The new temple is the smaller Doric peripteral temple that we know before the Hellenistic age, the first building in Paestum that fully expresses the Doric canon.

The ‘little temple’ (tempietto) is a structure that measures 15.6 meters by 7.5 meters and has four columns in front and seven on the sides. It is in the Doric order, like the others, but it is distinguished by the purity of its shapes.
The analysis of the clay decorations allowed the foundation to be dated to the first quarter of the fifth century BC. Some of the most important monumental buildings still standing today were constructed during this time period, including the Temple of Hera, which was constructed between 560 and 520 BC, and the Temple of Athena, which dates back to 500 BC. The Temple of Neptune, on the other hand, was not finished until 460 BC.

The little temple is very significant because it partially exemplifies the community’s artistic and cultural autonomy. It further disproves those who have always believed that the colonies limited themselves to copying the works of the motherland.
Cover Photo: Archaeological Park of Paestum and Velia