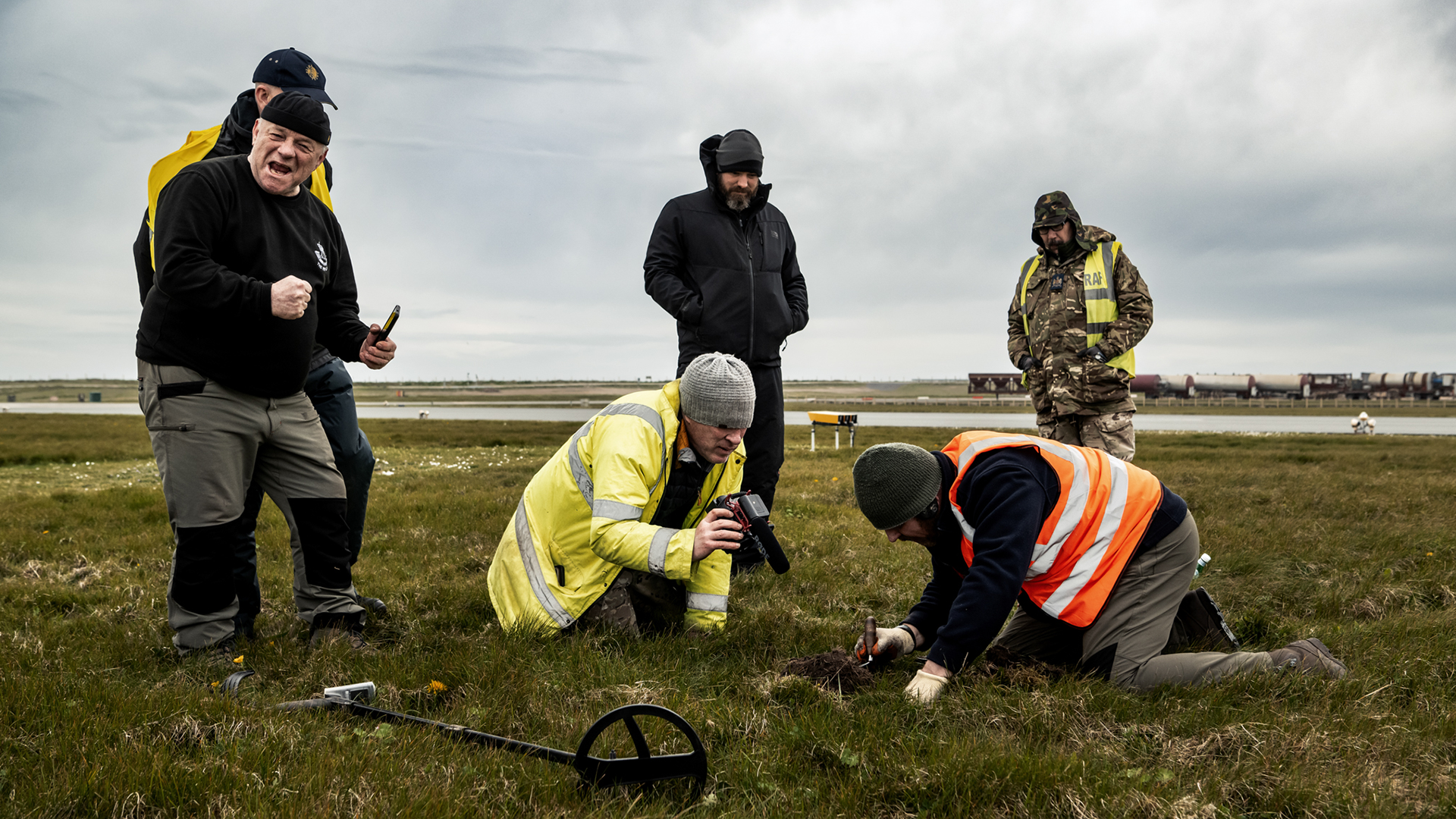
Military personnel and veterans at RAF Valley in Anglesey on the island of Anglesey, Wales, have uncovered sensational Iron Age treasures.
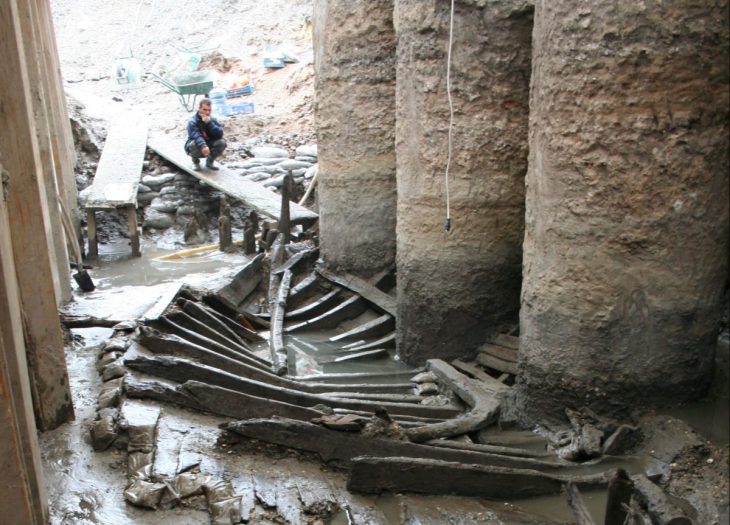
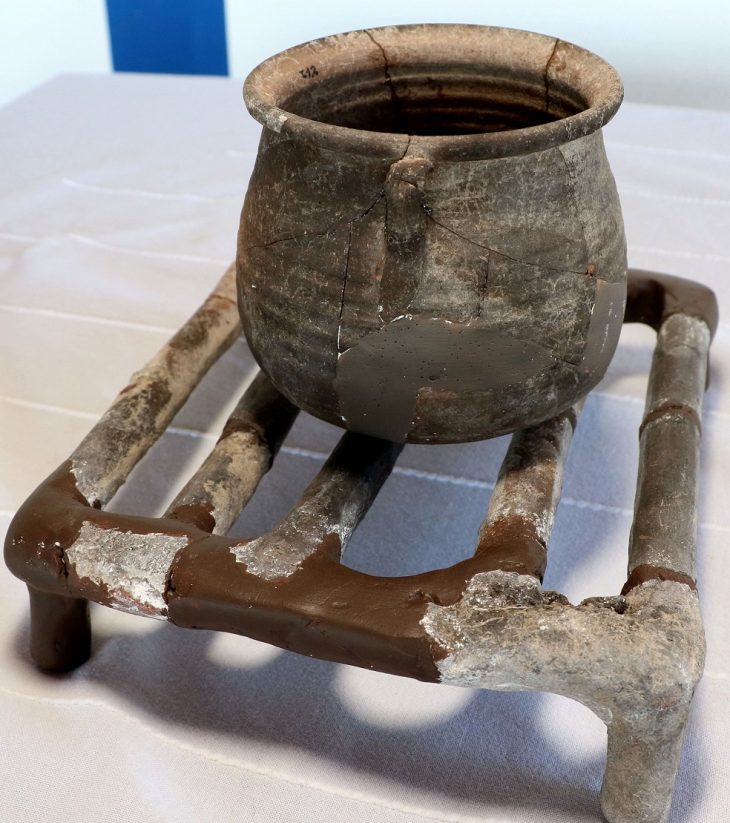
A team of military personnel and veterans has unearthed remarkable artifacts, including parts of a Celtic chariot, a terret ring, and a bridle-bit for a horse, all dating back approximately 2,000 years. These invaluable discoveries have been officially designated as national treasures and will soon be incorporated into the collections at Amgueddfa Cymru – Museum Wales.
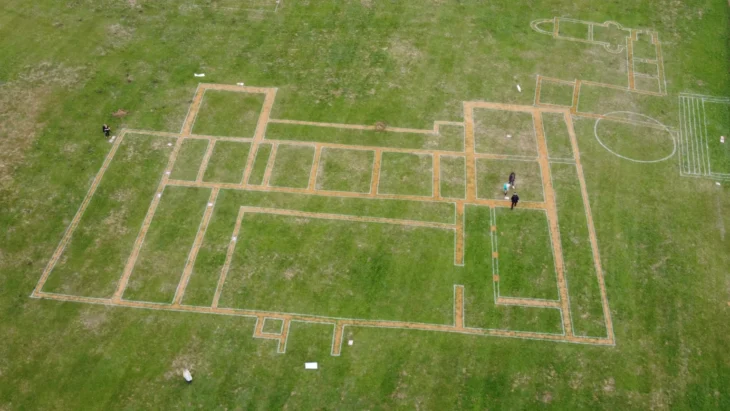
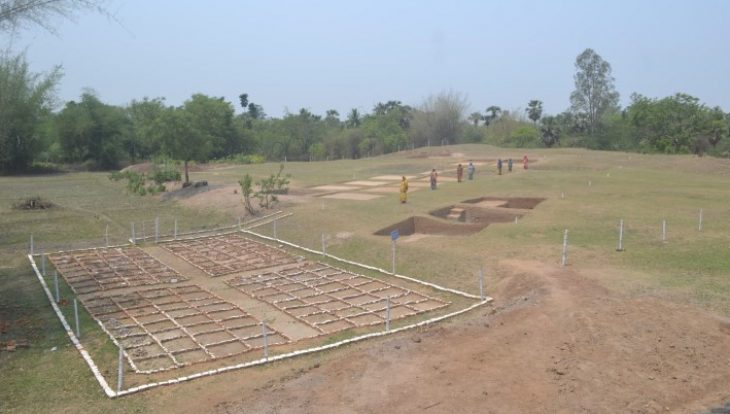
In April, an archaeological dig led by the Defence Infrastructure Organisation (DIO) brought together military personnel and veterans from Operation Nightingale, an initiative designed to support the health and wellbeing of veterans. This project provided a unique opportunity for these individuals to actively participate in the excavation, contributing to both their personal development and the discovery of significant historical artifacts.
Richard Osgood, a senior archaeologist with the Defence Infrastructure Organisation (DIO), expressed enthusiasm about the recent discoveries at RAF Valley, stating that they are “extremely exciting for all involved.” He emphasized the national significance of the Llyn Cerrig Bach hoard for both Wales and the United Kingdom. Osgood noted that these new findings have validated the earlier suspicions of archaeologists regarding the potential for additional artifacts from this particular hoard.
The Llyn Cerrig Bach hoard, initially discovered in the 1940s during the expansion of airfields to accommodate American bombers in World War II, stands as one of the United Kingdom’s most significant collections of Iron Age artifacts. This hoard comprises over 150 iron and bronze items, which date from approximately 300 BCE to 100 CE, and were interred in a sacred lake by early inhabitants of the region, reflecting the cultural and ritualistic practices of Iron Age societies.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
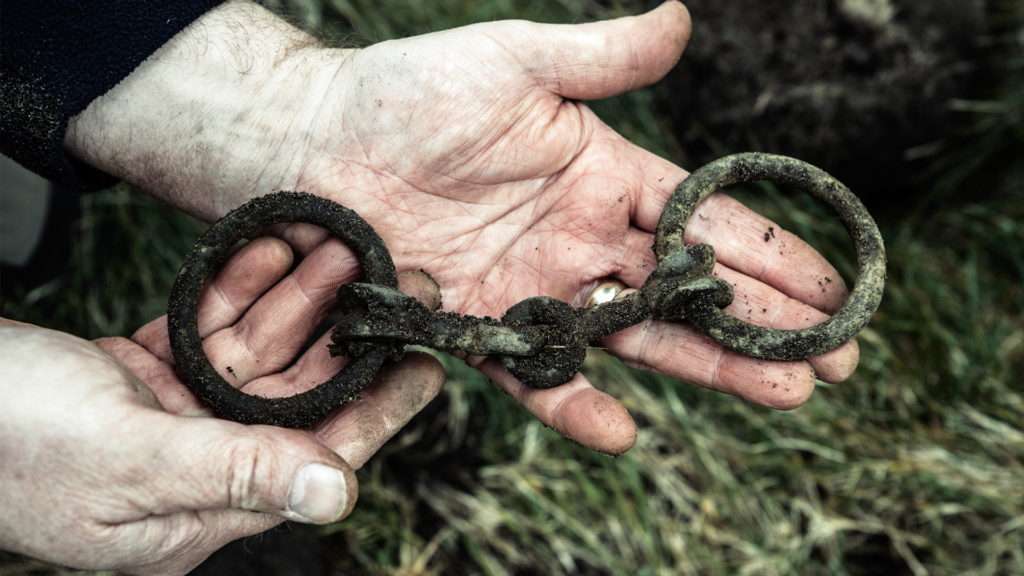

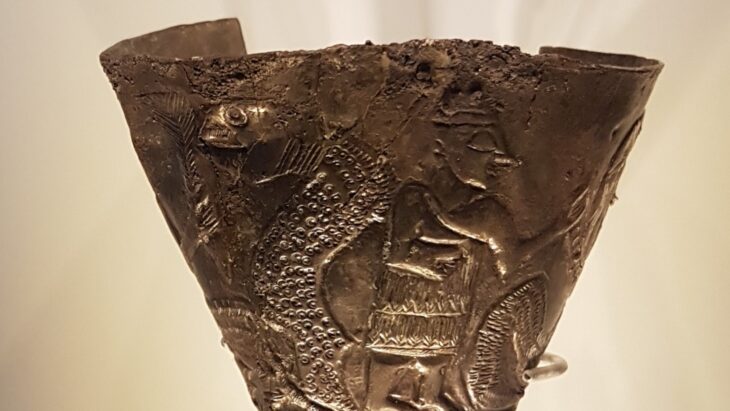
Among the newly uncovered artifacts is a terret ring, a crucial component used for guiding chariot reins, which features a rare red inlay. This particular terret ring is noteworthy as it is one of only three known examples in Wales, highlighting its exceptional craftsmanship and the technological sophistication of the period. The item was unearthed by retired RAF Squadron Leader David Ulke, whose involvement underscores the collaborative efforts between military personnel and archaeologists in uncovering and preserving the region’s rich historical heritage.
Another notable discovery from the excavation is a horse bridle-bit, dating to approximately 60 CE, which was found by RAF Flight Sergeant Graham Moore. This artifact shares a similar shape with examples from a hoard located at Polden Hill in Somerset. Moore described the challenging search, stating, “The search for the lost hoard was hard work, and we had a huge area to cover. It wasn’t until the final day—just 10 minutes before we finished—that I discovered the horse bridle-bit. Initially, the team thought I was joking, but they quickly realized I had found something special.”
The excavation underscores the site’s historical continuity over the centuries. Group Captain Gez Currie, the Station Commander at RAF Valley, emphasized the importance of the location, stating that it serves as a reminder of its significance in Welsh history. He noted that the preparations at RAF Valley in the 1940s, aimed at preventing invasion, revealed the site’s historical relevance and its connections to an earlier Roman invasion.
The significance of the Llyn Cerrig Bach hoard extends beyond its material value; it provides critical insights into the social, economic, and spiritual life of Iron Age communities in Britain. The artifacts serve as a testament to the advanced metallurgical skills of the time and offer a glimpse into the trade networks and cultural exchanges that existed across the region. Ongoing research and analysis of these findings will undoubtedly contribute to a deeper understanding of Iron Age Britain and its historical context.
Cover Image Credit: Personnel and veterans in action on Operation Nightingale. Credit: Harvey Mills