The workers working on a routine road construction project near Shahr-e Belqeys (City of Belqeys) in northeast Iran made an unexpected discovery.
Shahr-e Belqeys is a castle located in Esfarayen County in North Khorasan Province, Iran. The fortress dates back to the Sasanian Empire. It is the second largest adobe fort in Iran after the UNESCO-registered Bam Fortress. Belqeys archaeological site has an area of over 51,000 square.
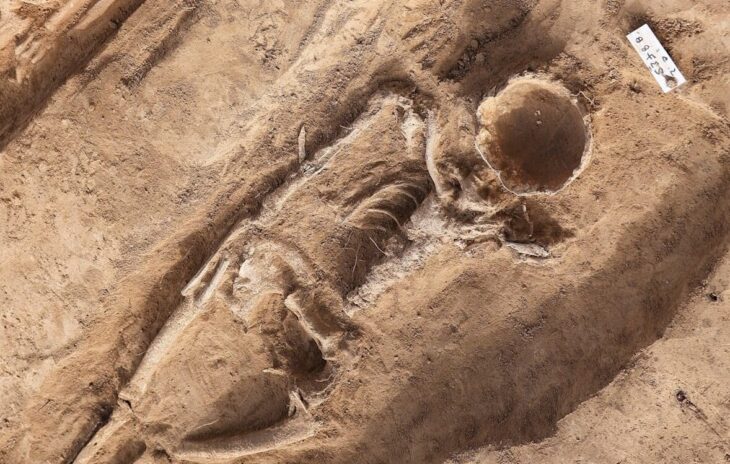
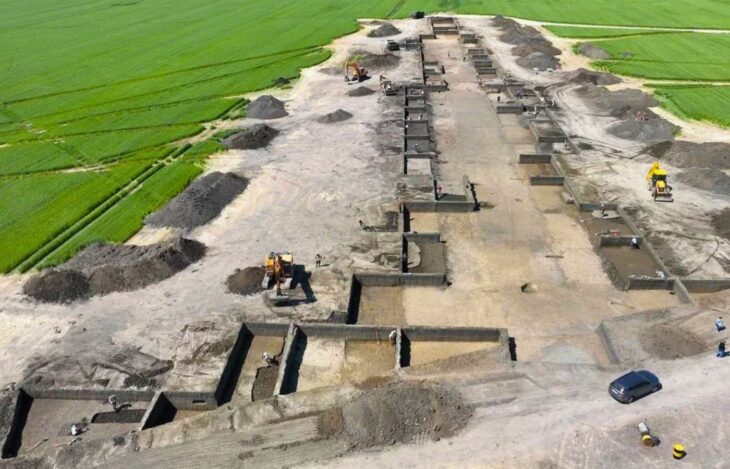
“Remains of ancient underground corridors were discovered a few days ago during a road construction project in Bam village of Esfarayen county,” an expert with Belqeys archaeological site said on Monday.
“The total length of those corridors is 18 km, and there is a bathroom and a mill on the way, which has not been opened yet,” the expert said. “Last years, traces of this underground city had been discovered but to protect it, these remains were blocked by the local cultural heritage directorate. Now we reached these ancient structures from another place, which confirms the statements of the local people,” the expert explained. “The ruins have yielded potteries estimated to belong to the Seljuk period, IlKhanid, and even earlier periods. However, an extensive archaeological excavation is needed to delve into its secrets.”

Shahr-e Belqeys was prosperous during a period from the late Sassanid era to early Islamic times. Historical evidence, including a book on the history of Nishabur (Middle Persian: Nev-Shapur), suggests that Shahr-e Belqeys won special attention by Sassanid monarchs of the time.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Archaeological excavations at nearby mounts and hilltops put the antiquity of Belqeys in some 6,000 years.
These Medieval subterranean corridors in Iran are not a first. Nooshabad, known as Ouyi to locals, is an underground city with many passages and chambers in Isfahan Province in central Iran.
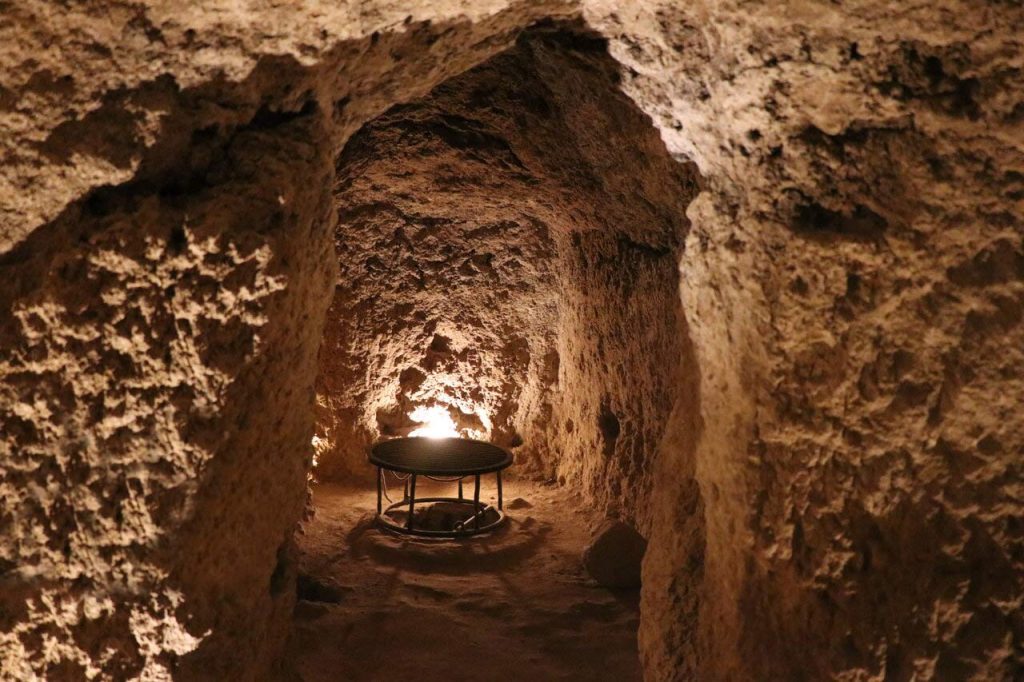

Nooshabad, which was discovered by chance during a construction project, was initially built to protect city dwellers against invasion and plundering, particularly during the Mongol invasion of Iran.
Construction of this man-made subterranean city, called Ouee (or Ouyi), dates back to the Sasanian (or Neo-Persian) Empire that ruled from 224 to 651. Inhabitants would dig underground chambers as hideout spots for women, children, and the elderly in the event of an attack by foreign invaders.
The fact that these newly found underground tunnels were built in the same way reveals their intended use. In the future, it will be possible to have more information about the tunnels if the Iranian government allows the excavation works.