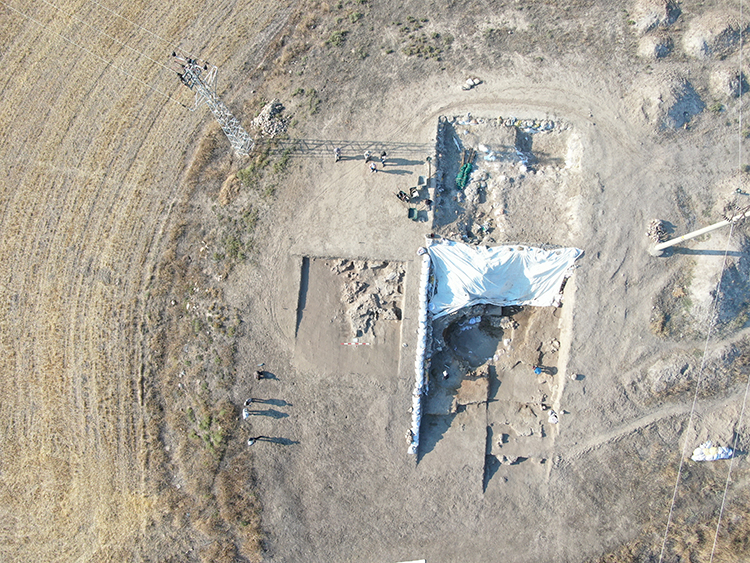
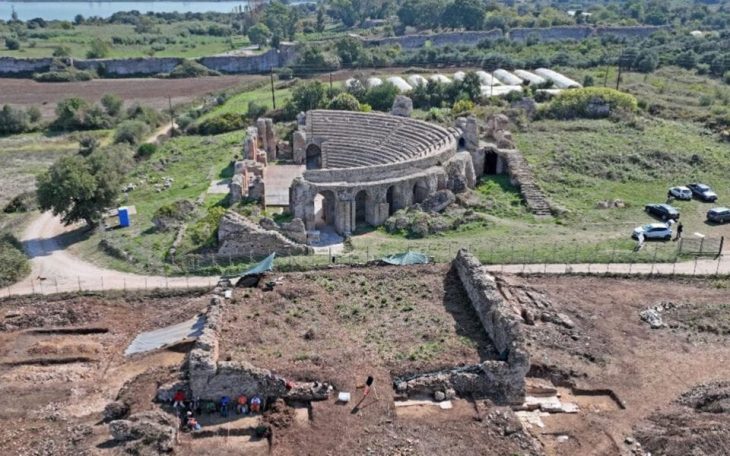
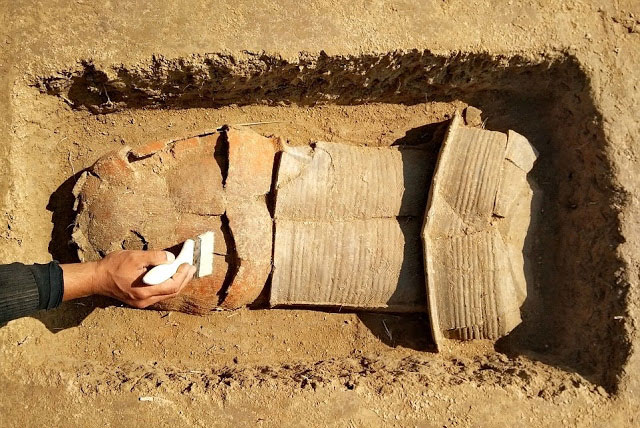
Archaeologists excavating at Üçhöyük in Bolvadin, Afyonkarahisar (western Türkiye) have uncovered remarkable new evidence that may help identify the long-lost capital of the kingdom of Purušhanda, a powerful Anatolian city-state from the early second millennium BC.
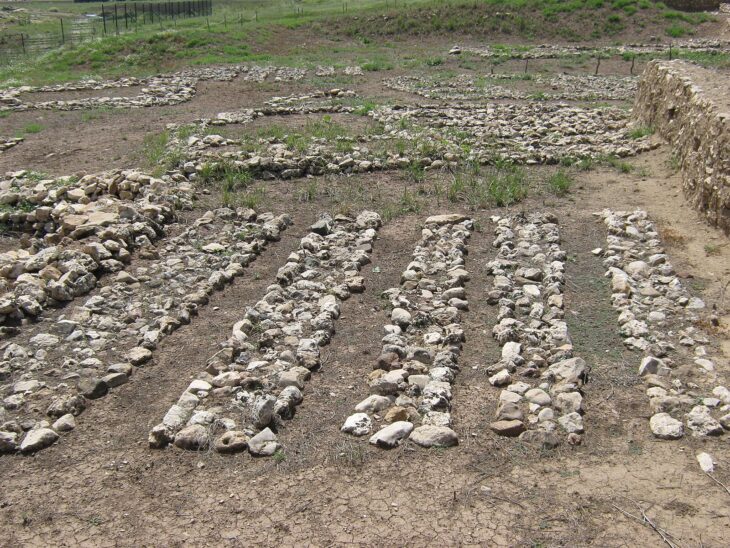
During the latest season of excavations, the team discovered three mudbrick-built ovens and two hearths, pointing to large-scale, organized production activities rather than ordinary domestic use. Experts believe these facilities may have been linked to palace or elite-controlled workshops.
Organized Production in Bronze Age Anatolia
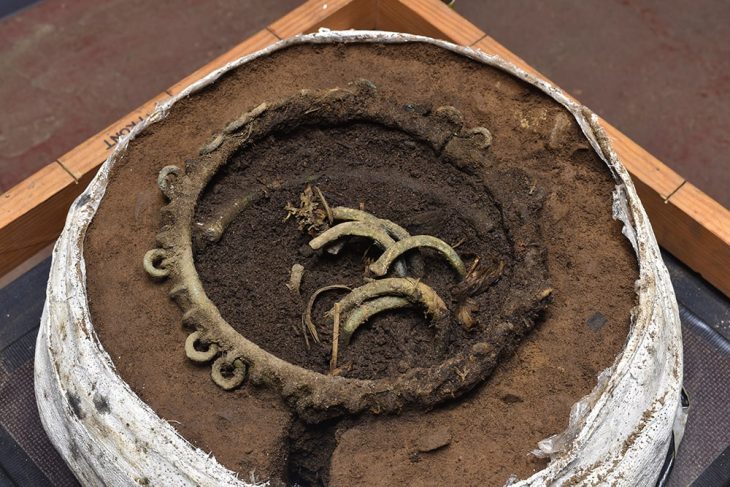
Excavations at Üçhöyük began in 2020 and have continued under a presidential decree since 2024, directed by Prof. Dr. Özdemir Koçak of Selçuk University. The project, supported by the Governorship of Afyonkarahisar, Bolvadin Municipality, and Japanese scholars, has already produced important finds such as seals, spindle whorls, copper and lead pins, figurines, and storage jars.
Prof. Koçak emphasized the importance of the ovens and hearths:
“These were not simple domestic structures. They reflect a form of organized, large-scale production. Üçhöyük seems to have functioned as a ‘cargo center,’ producing goods for distribution across the region.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
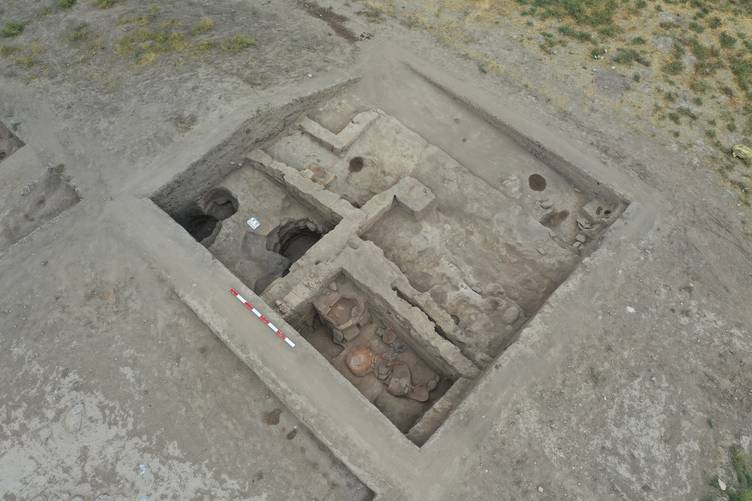

Purušhanda: A Forgotten Anatolian Power
The name Purušhanda (also spelled Purushanda) appears frequently in Old Assyrian merchant tablets from Kültepe (Kanesh), one of the largest trade hubs in Bronze Age Anatolia. Around 2000–1700 BC, Purušhanda was described as a major commercial and political power controlling trade routes across central Anatolia.
According to cuneiform sources, Assyrian traders paid special attention to Purušhanda because of its strategic role in long-distance trade. Even Sargon of Akkad (24th century BC) claimed to have campaigned against its ruler, underscoring the city’s prominence.
By the 17th century BC, however, the Hittite kingdom expanded its power over central Anatolia, absorbing Purušhanda and other independent city-states into its growing empire. This transition marks a crucial moment in Anatolia’s early history—when local kingdoms gave way to Hittite imperial dominance.
Üçhöyük: A Candidate for the Lost Capital
The exact location of Purušhanda has long remained uncertain, with several competing theories among scholars. Yet the discoveries at Üçhöyük, located in today’s Afyonkarahisar province, strengthen the argument that it may indeed be the lost capital.
Finds such as seals, industrial installations, and storage facilities suggest that Üçhöyük was not a rural settlement but a major production and trade center in the 1600s BC. If future excavations uncover written tablets or royal inscriptions, Üçhöyük could be conclusively identified as the seat of Purušhanda’s rulers.
Afyonkarahisar’s Provincial Director of Culture and Tourism, Yusuf Altın, highlighted the significance of the excavations:
“The evidence strongly suggests Üçhöyük could be the heart of the lost kingdom of Purušhanda. A discovery of inscriptions would allow us to confirm this beyond doubt.”
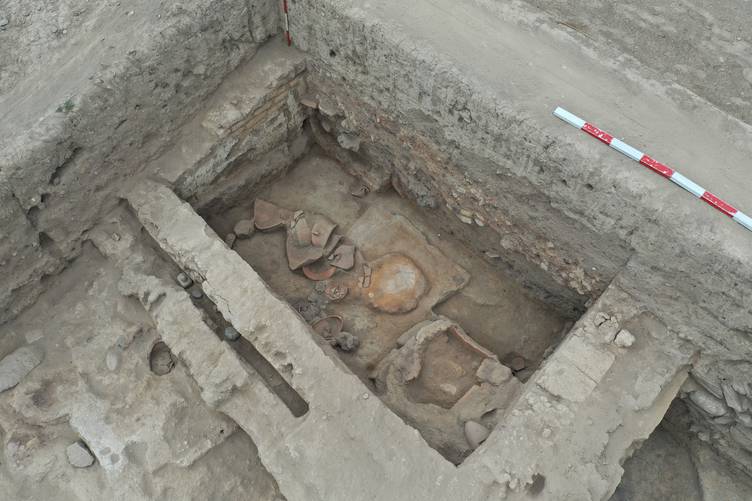

Future Prospects: Heritage and Tourism
The excavation team plans to restore the mudbrick ovens and hearths for preservation and eventual public display. If Üçhöyük is confirmed as Purušhanda, it would not only solve one of Anatolia’s enduring archaeological mysteries but also transform the site into a major cultural heritage attraction for Türkiye.
With each season of discoveries, Üçhöyük is moving closer to rewriting the history of Bronze Age Anatolia and possibly revealing the long-lost kingdom of Purušhanda.
Cover Image Credit: AA