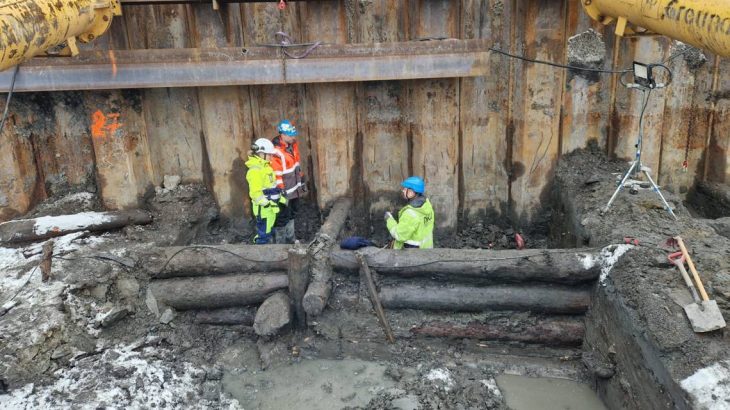
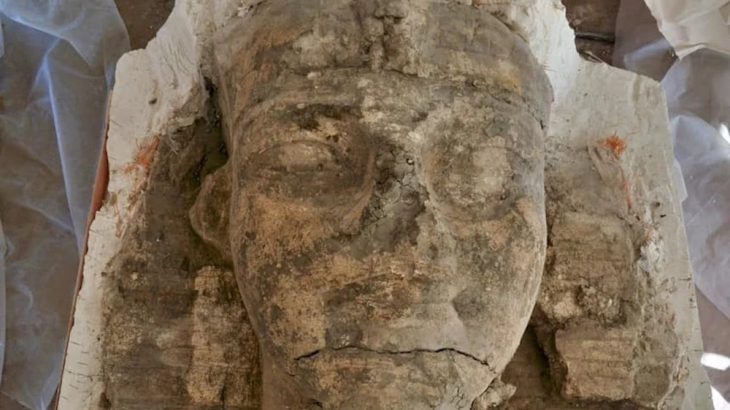
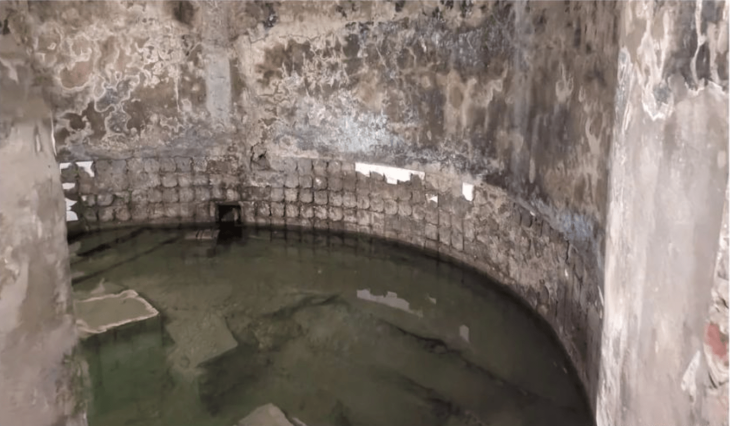
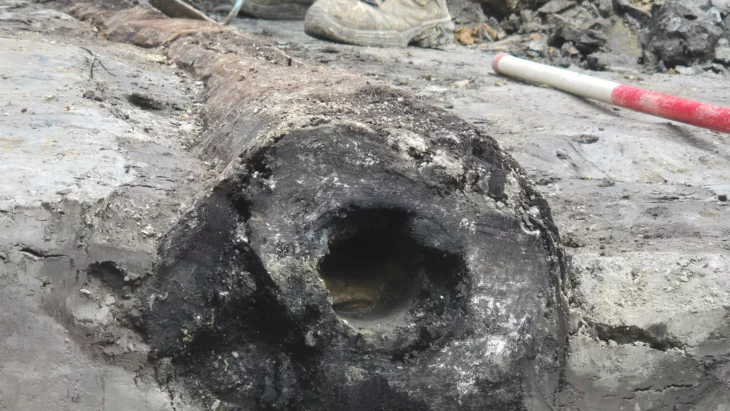
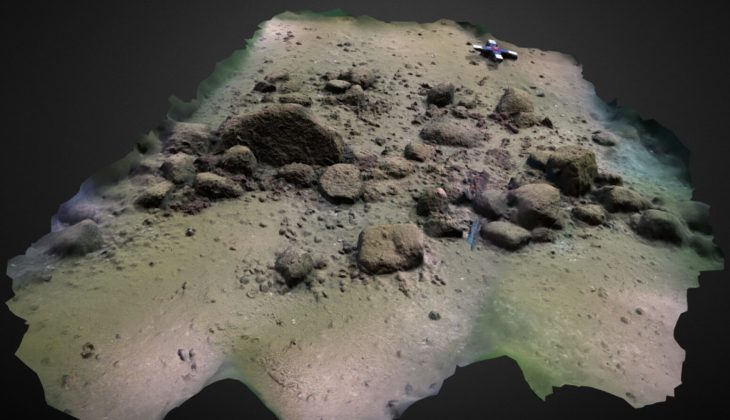
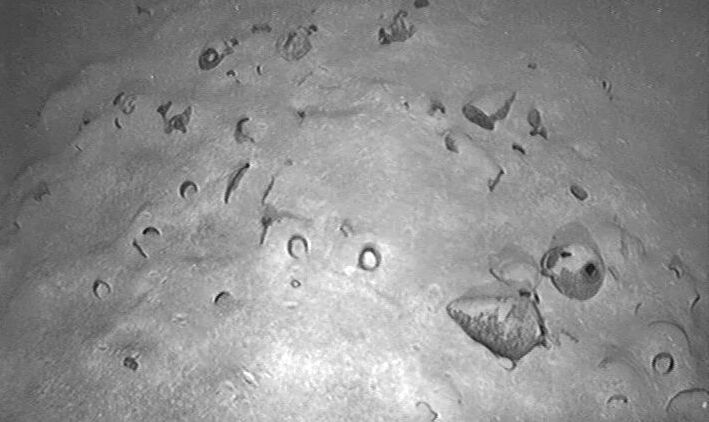
Archaeological excavations at the ancient city of Kerkenes (Pteria) in central Anatolia have revealed burial features that may be linked to Proto-Turkic or steppe-related traditions, according to early reports from the research team. The discovery could provide new insight into cultural interactions in Anatolia during the late Iron Age, around 2,600 years ago.
The discovery was made during excavations led by Prof. Dr. Şevket Dönmez, one of Türkiye’s leading Iron Age experts and the head of the Department of Turkish-Islamic Archaeology at Istanbul University. The project is conducted under the “Heritage for the Future” initiative by the Turkish Ministry of Culture and Tourism, with the participation of scholars from Istanbul University, Bozok University, Muğla Sıtkı Koçman University, and Amasya University.
Excavations at the Heart of Ancient Pteria
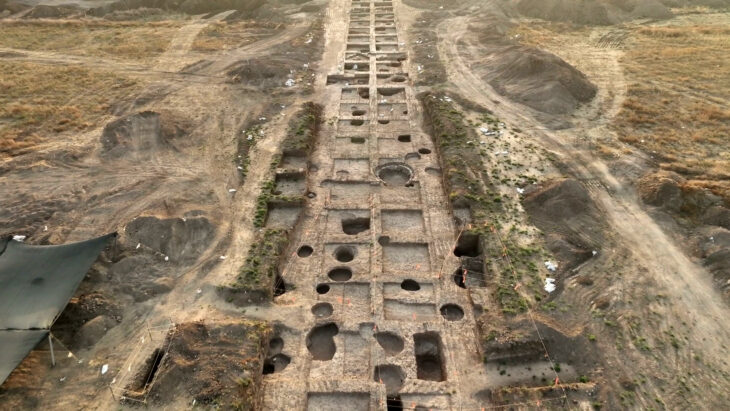
Kerkenes, located near Şahmuratlı Village in Yozgat’s Sorgun district, is one of the largest Iron Age sites in Anatolia. Identified with the ancient city of Pteria—mentioned by the Greek historian Herodotus as a major stronghold destroyed by the Persians in the 6th century BCE—the site covers an area of about 2.5 square kilometers on the Kerkenes Plateau.
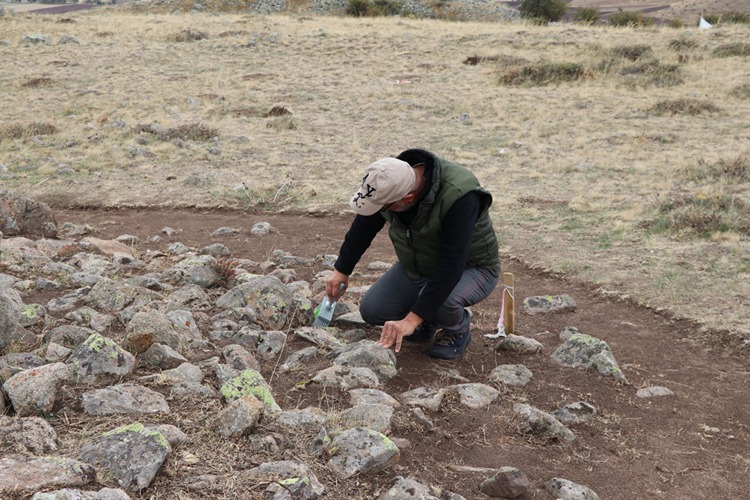
The current excavations focus on two main areas: Keykavus Fortress and a nearby zone locally known as the “Türkmen Cemetery” or “Şehitlik Mevkii.” The latter has drawn particular attention after the discovery of disturbed burial mounds and open-air sacred spaces associated with ancient funerary practices.
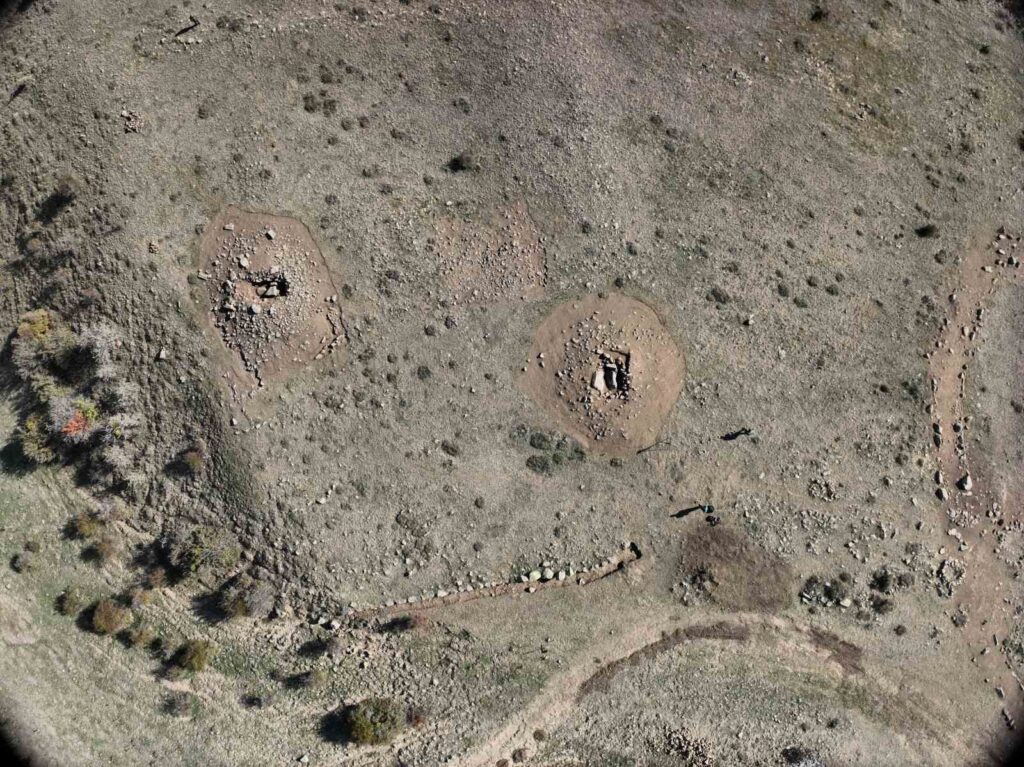

Possible Link to Proto-Turkic Kurgan Traditions
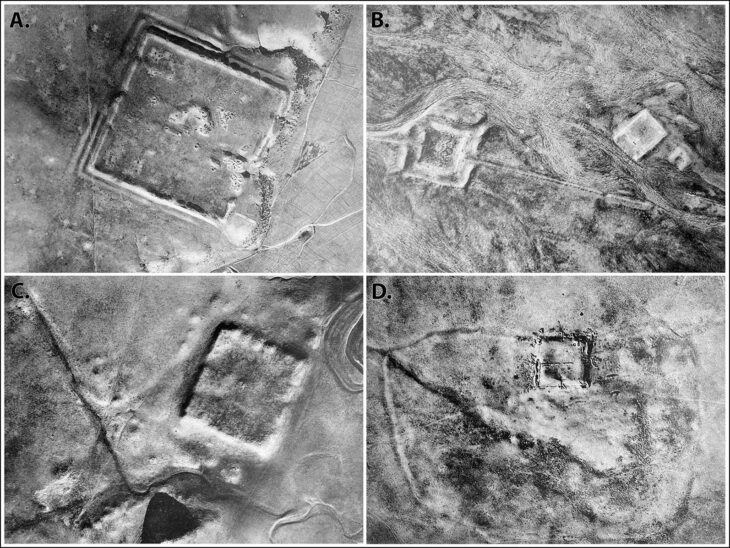
According to Prof. Dönmez, initial findings suggest that some of the burial structures may be connected to kurgan-type tombs—earthen or stone mounds commonly associated with Scythian and early Turkic (Proto-Turkic) cultures of the Eurasian steppe.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“We have identified a large circular structure about 60 meters in diameter, which we describe as a geoglyph—a monumental design made with stones visible from above,” said Dönmez.
“This combination of a kurgan and a sacred ‘kut’ area resembles examples found in Central Asia, particularly from the Scythian and Göktürk periods. Such a pattern appearing in Anatolia around 550 BCE suggests that Proto-Turkic groups may have been active in this region much earlier than previously thought.”
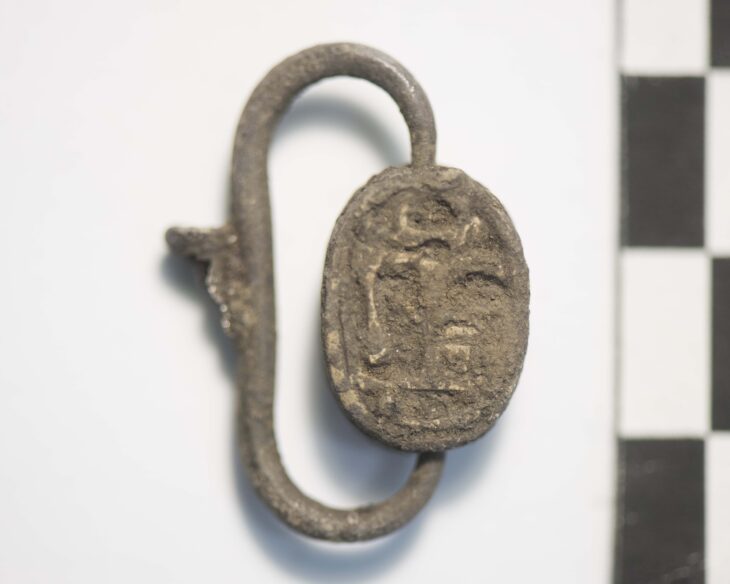
Although the graves were heavily damaged by looters in earlier years, ongoing analysis aims to clarify their chronology and cultural context through scientific dating methods and comparative architectural studies.
Rewriting Early Turkish Presence in Anatolia
If confirmed, the findings could significantly reshape the understanding of Turkish cultural origins in Anatolia, extending their architectural and ritual traditions back to the late Iron Age—long before the Seljuk and Byzantine periods typically associated with Turkish settlement.
“Our current evidence points to a Proto-Turkic presence in central Anatolia dating back 2,600 years,” Dönmez noted. “However, a definitive conclusion will depend on the results of radiocarbon dating and further archaeological data.”
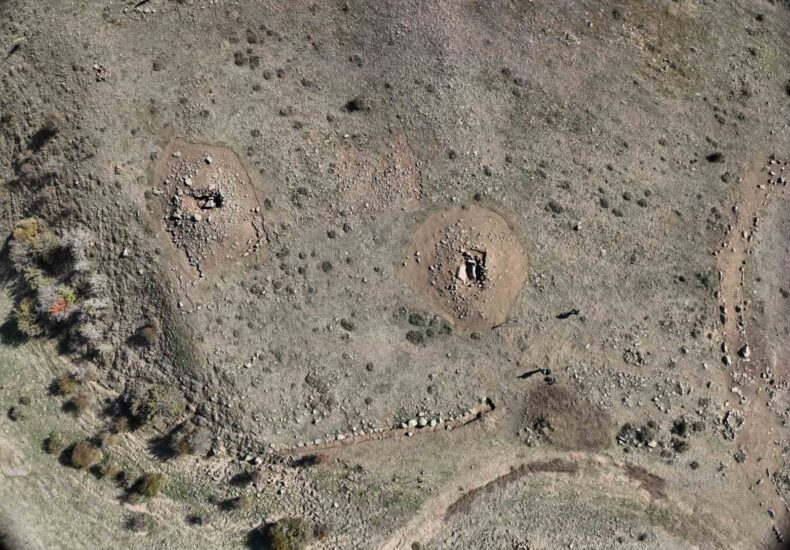

Kerkenes: A Site of National and Global Significance
The Kerkenes excavations have long been recognized as one of Türkiye’s most important archaeological projects. Beyond its historical ties to the Phrygians, Lydians, and Persians, the site now appears to offer a unique window into Eurasian steppe cultures and their interactions with Anatolia during the Iron Age.
Local authorities, including the Yozgat Museum Directorate and Sorgun Municipality, have expressed strong support for the project, emphasizing its potential to transform the region into a significant archaeological and cultural tourism hub.
As research continues, Kerkenes stands not only as a key to Anatolia’s multi-layered past but also as a focal point in the ongoing exploration of Proto-Turkic history and its far-reaching influence across continents.
Cover Image Credit: Sait Çelik/AA