Researchers from the London Archaeological Museum (MOLA) determined that an Iron Age comb they found during an archaeological dig that ended in 2018 was made from a human skull and was most likely used as a talisman rather than styling hair.
The accessory, dubbed the Bar Hill Comb was among 280,000 items of interest collected between 2016 and 2018 during the A14 improvement scheme.
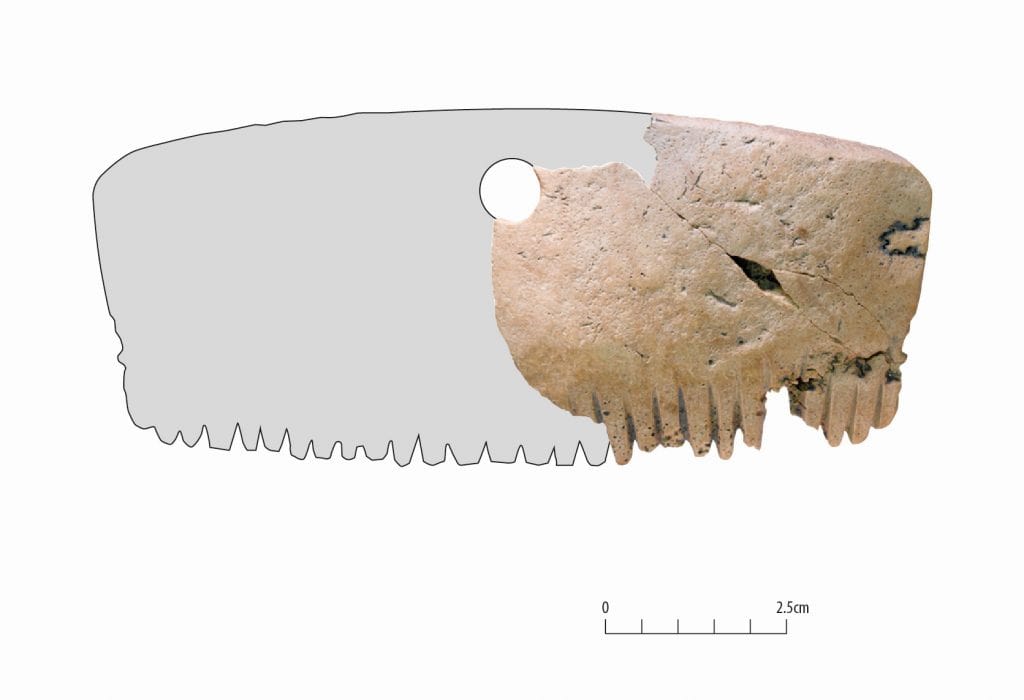
The comb is around 2 inches long with a curved top and teeth carved into the bottom.
The reconstruction drawing created by the MOLA researchers suggests that the comb was originally rectangular with a circle carved out in the middle for attaching to clothing.
“The Bar Hill Comb may have been a highly symbolic and powerful object for members of the local community,” Michael Marshall, a prehistoric and Roman finds specialist at MOLA said in a statement.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
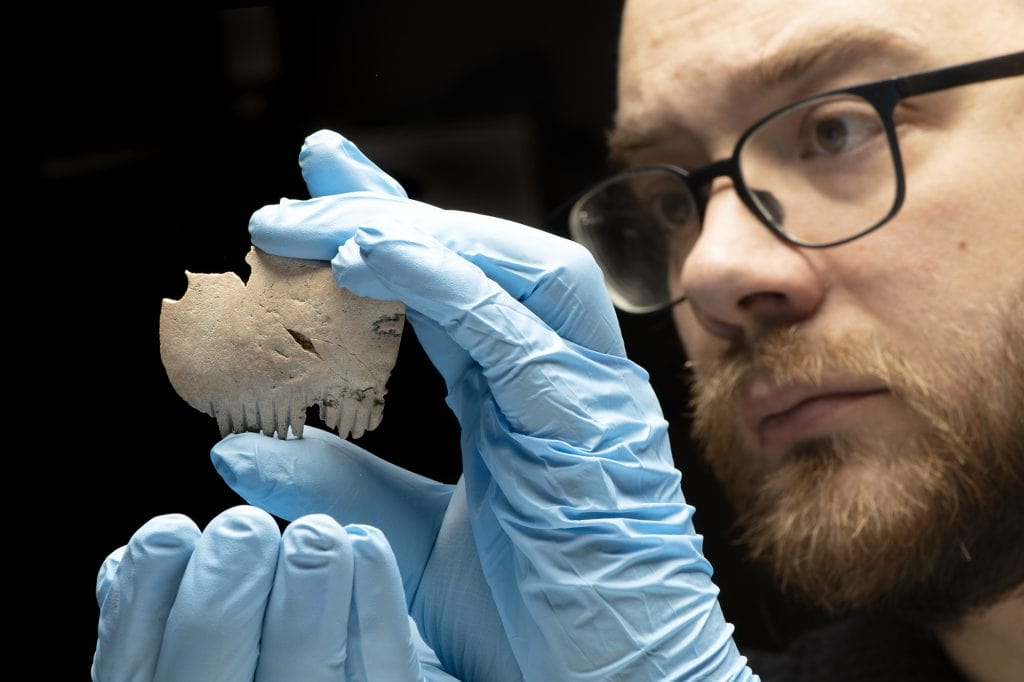

“It is possible it was carved from the skull of an important member of Iron Age society, whose presence was in some way preserved and commemorated through their bones.”
He said only two other comparable examples have ever been found in Britain – both within 15 miles (24km) of the Bar Hill Comb.
The lack of wear on the comb’s teeth distinguishes this bone from other finds, suggesting that it was possibly worn as an amulet rather than used to brush hair at all.
Many people in the British Isles during the Iron Age revered human skulls, according to historians. Both carved stone heads and skulls served as talismans, as evidenced in ritual practices documented by archaeologists and in folklore. The comb’s tines show no signs of use or deterioration, and traces of a hole that was drilled into its top indicate that it was once attached to a string for wearing.
Cover Photo: Reconstruction of Bar Hill Comb. Photo: © MOLA.