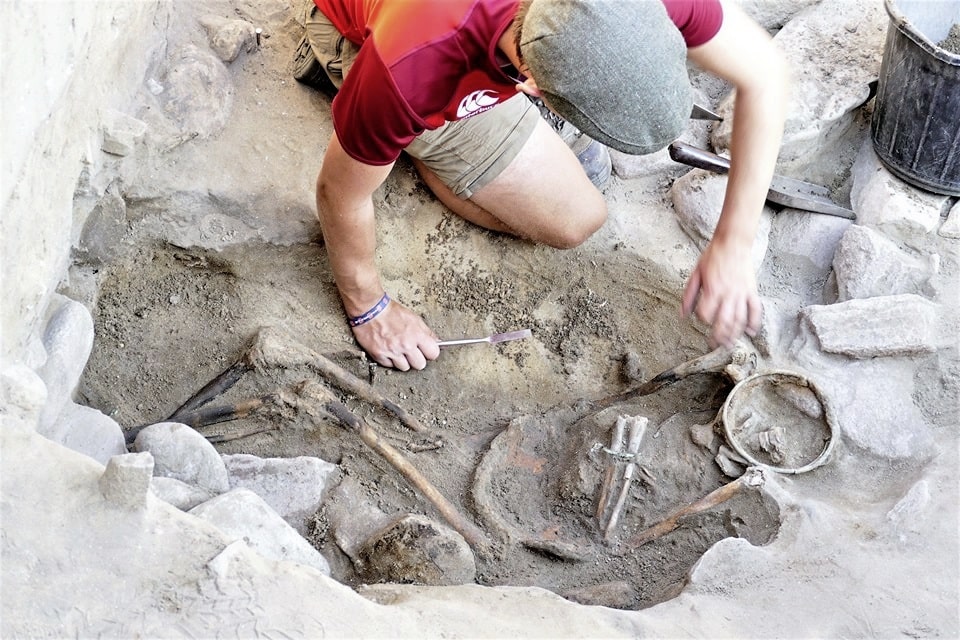
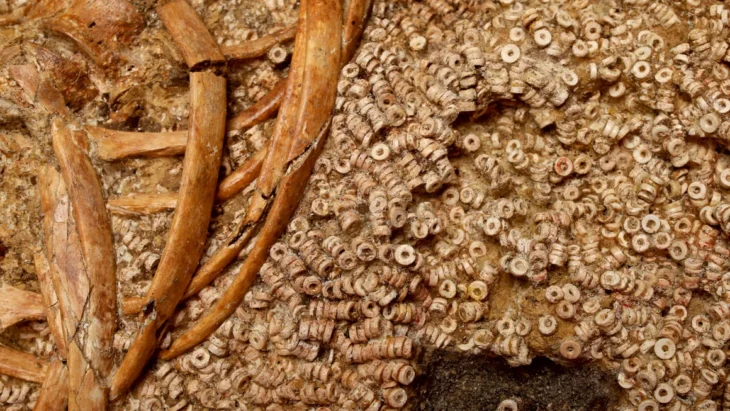
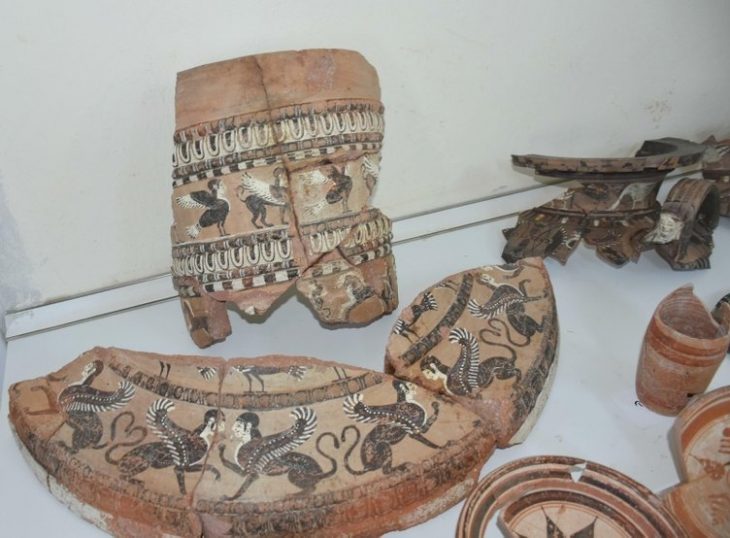
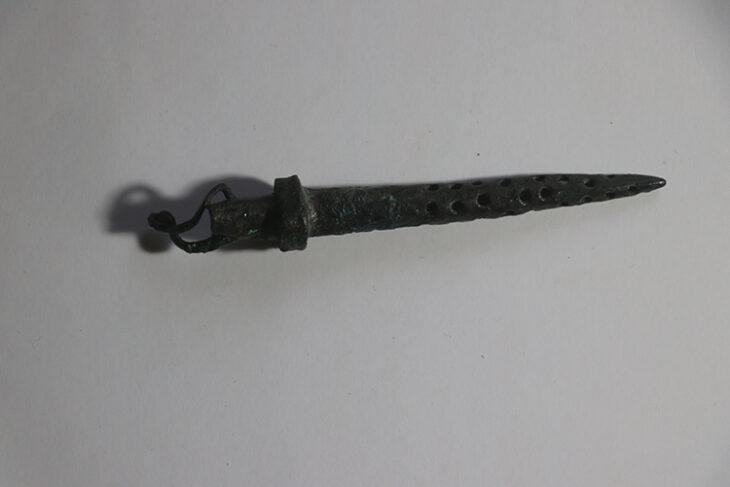
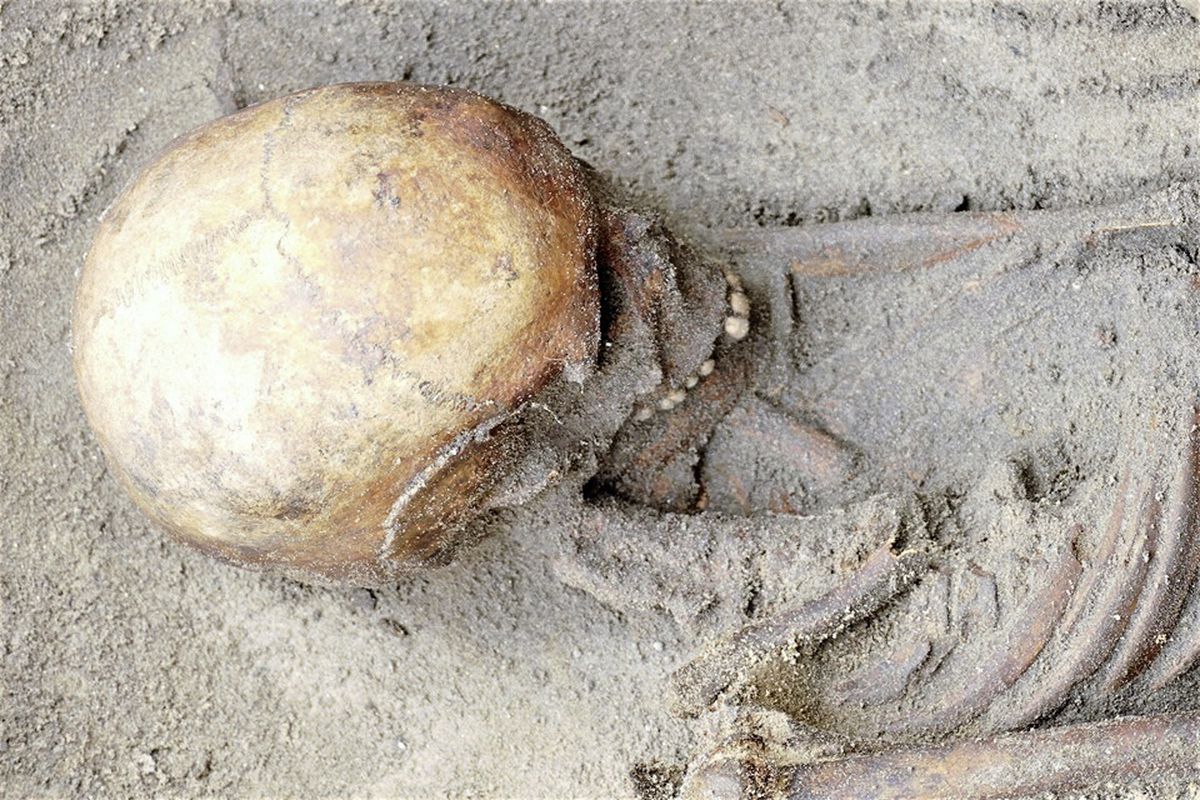
Well-preserved skeletons from the late Iron Age and Roman periods were found in Alderney, one of the channel islands.
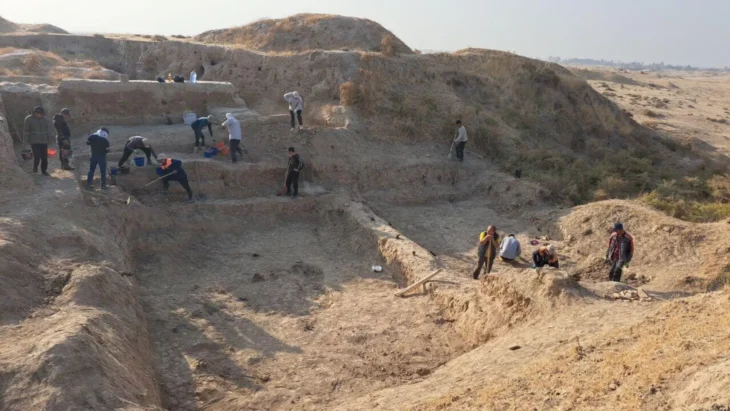
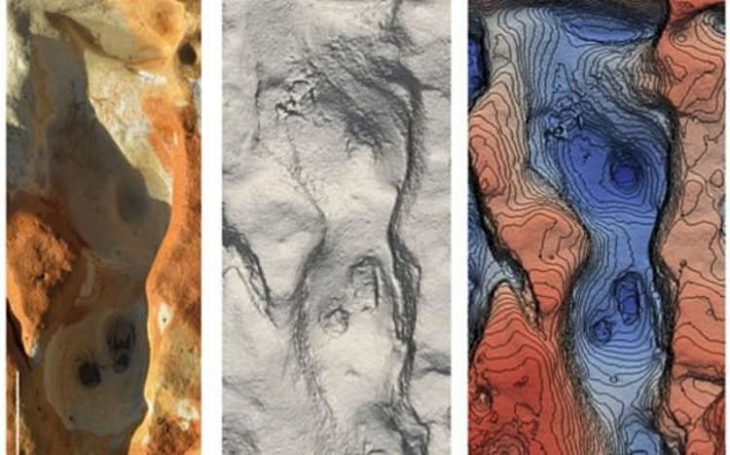
The site on Longis Common in Alderney, according to States archaeologist Phil de Jersey, is one of the most exciting archaeological sites in the Channel Islands since the two meters of sand over the graves has helped preserve the bones and prevent the site from being disturbed.
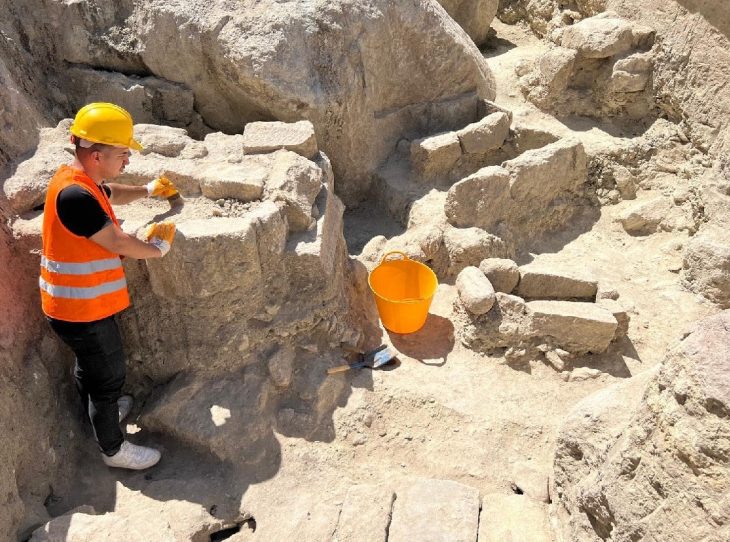
Human bones were discovered during the installation of an electricity cable on Rue des Mielles, near Longis Bay, in 2017. It prompted the Guernsey Museum and the Alderney Society to investigate. Eight of the bones have now been radiocarbon dated, five from the service trench along the Rue des Mielles and three from a paddock field excavation.
They date from about 750BC up to 238AD.
Dr de Jersey said they had expected the bones to be from the late Iron Age, based on the pottery finds, but the surprise was the wide timespan covered.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
‘It does imply that the site was used for a long time – hundreds of years,’ he said.
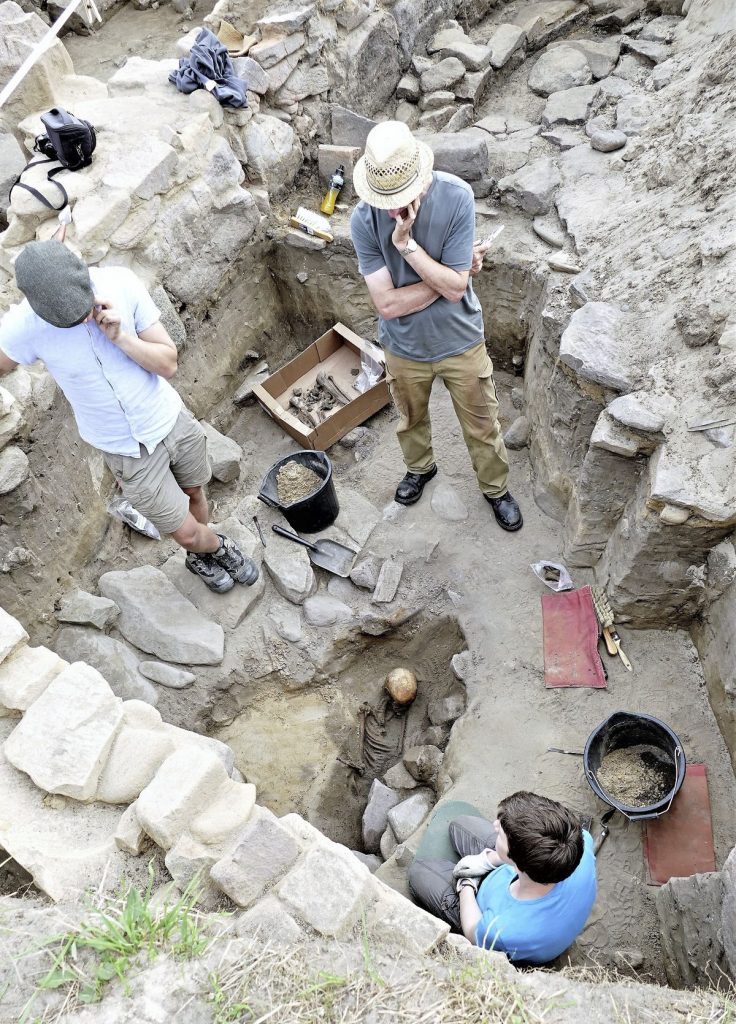

A settlement from around the same era was excavated up the hill from the site in the 1970s and Dr de Jersey said the inhabitants possibly lived on the hill and buried their dead at its foot. Among the bone finds was a female, who was likely to be from between 590 and 380BC. The iron and bronze torc around her neck corresponds well with these dates.
Another adult female was found, but she was most likely between 170BC and AD90. The pot buried at her head is typical of the late Iron Age, which corresponds to the period between the second century BC and the turn of the millennium.
Dr de Jersey said the date range was very wide and indicated that the burials were over a much larger area than they had expected.
He would like to do a large-scale dig, but the Guernsey archaeology department has a very small budget, and the region poses difficulties. The sand that protects the bones makes drilling down two meters is difficult because the sides of the trenches are impossible to stabilize, necessitating the excavation of huge holes.
‘You can’t dig small trenches! So logistically it’s a very challenging site to dig. And we just don’t have the resources” said Dr de Jersey.
There is, though, a reason to be optimistic. If a university took on the project it would have students to help with excavating the dig, although travel restrictions due to Covid and the ordinary challenges with getting to Alderney would make it difficult.
An individual in the UK has secured a grant to carry out a ground-penetrating radar scan of the common, which would help determine the scale of the cemetery. Dr de Jersey said they were conscious there are also Second World War graves on the common, but the scan would not disturb them.
With the current travel restrictions, it is not clear when this can take place.
Dr de Jersey said when they finally dig the site, it was important to do it right.
‘I would rather not dig it than dig it badly,’ he said.
‘It can only ever be dug once, as digging is very destructive, so we need to make sure we do a good job of it.’
Fortunately, there is time to ensure it is done right.
Source: Guernsey Press
Cover Photo: David Nash