Mysterious Proto-Sinaitic inscriptions may point to Moses and Joseph as historical figures, sparking global scholarly controversy.
A groundbreaking proto-thesis by independent scholar Michael S. Bar-Ron suggests exactly that. After eight years of rigorous epigraphic analysis, Bar-Ron argues that two inscriptions found at Serabit el-Khadim, an ancient turquoise mining site on Egypt’s Sinai Peninsula, contain the Semitic phrase “This is from MŠ” — a possible early rendering of the name Moses (Moshe).
The inscriptions, dated to Egypt’s late 12th Dynasty during the reign of Pharaoh Amenemhat III, are written in Proto-Sinaitic, considered one of the world’s earliest alphabetic scripts. According to Bar-Ron, this writing system reflects an early Northwest Semitic dialect remarkably close to Biblical Hebrew, but with traces of Aramaic structure.
“If correct, this could be the first inscriptional evidence of Moses as a historical individual,” Bar-Ron states. “And the implications for our understanding of the Exodus traditions are enormous.”

A Message from Moses?
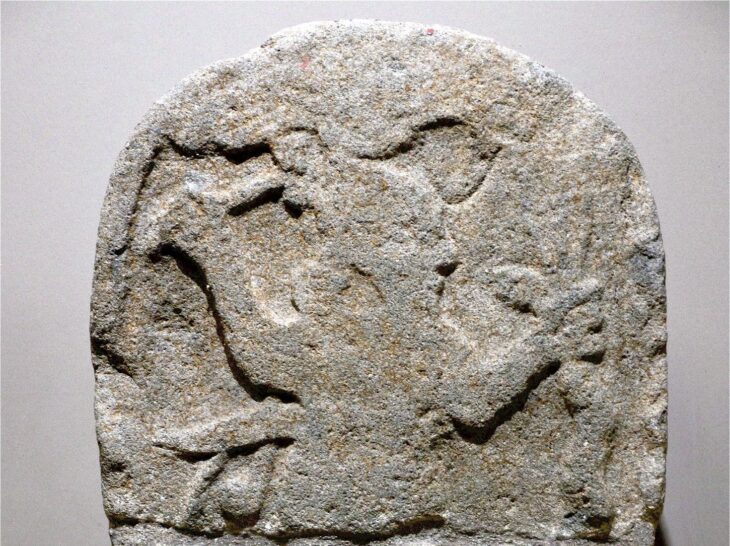
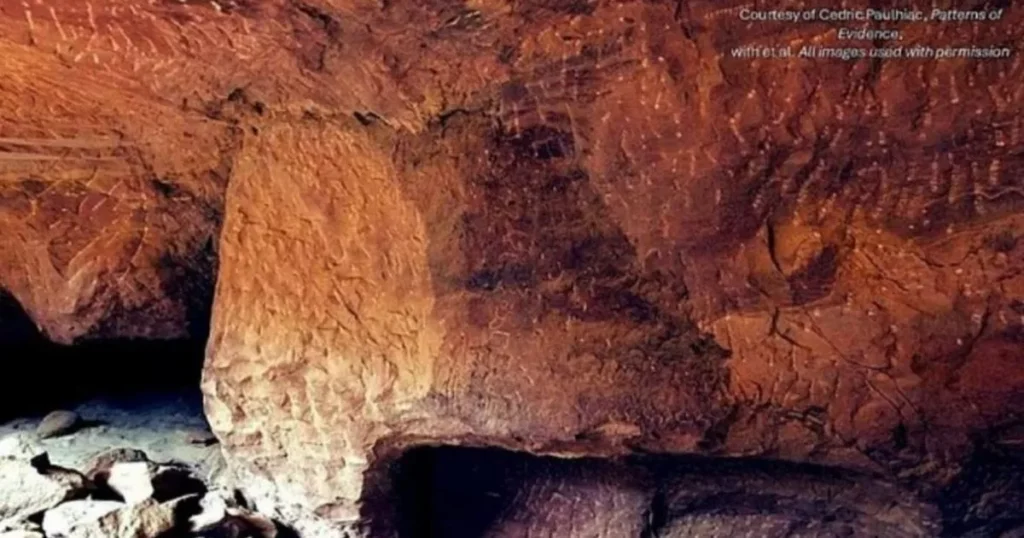
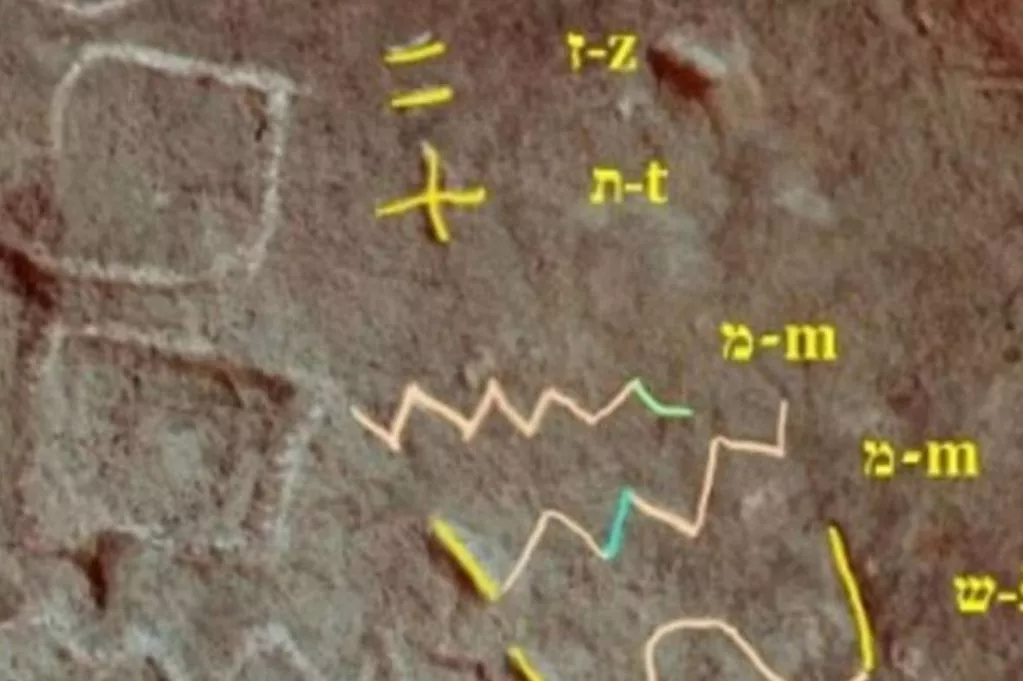
Two inscriptions — Sinai 357 and 361 — bear the characters M-Š in configurations that Bar-Ron interprets as personal authorship marks: “ZT MMŠ” (This is from MŠ) and “NʾUM MŠ” (A saying of MŠ). These inscriptions, he claims, appear alongside others that share linguistic style, personal tone, and even poetic structure — all pointing to a single Semitic scribe with elite Egyptian training, consistent with the biblical tradition of Moses being raised in Pharaoh’s palace.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
High-resolution photographs, 3D scans, and direct study of casts at Harvard’s Museum of the Ancient Near East were used to substantiate the claim. Epigraphic features like the letter mem (מ) and certain unique formations were tracked across multiple inscriptions to support the idea of a single authorial hand.

The Joseph Connection
In addition to Moses, Bar-Ron puts forward another startling theory: that the Egyptian vizier Ankhu, known from other archaeological records, could be the historical basis for the biblical Joseph.
One key inscription, Sinai 350, bears a hybrid Egyptian-Semitic cartouche and references to the deity El, associated with early Hebrew worship. Its refined execution suggests the author was not a slave, but rather a Semitic official in high standing, possibly working under Amenemhat III. This scenario fits closely with the Joseph narrative in the Book of Genesis.
Bar-Ron’s thesis proposes that a Semitic elite class, possibly including Joseph, rose to influence during this era, only to be later enslaved — a transformation echoed in Exodus.
Religious Conflict in Stone
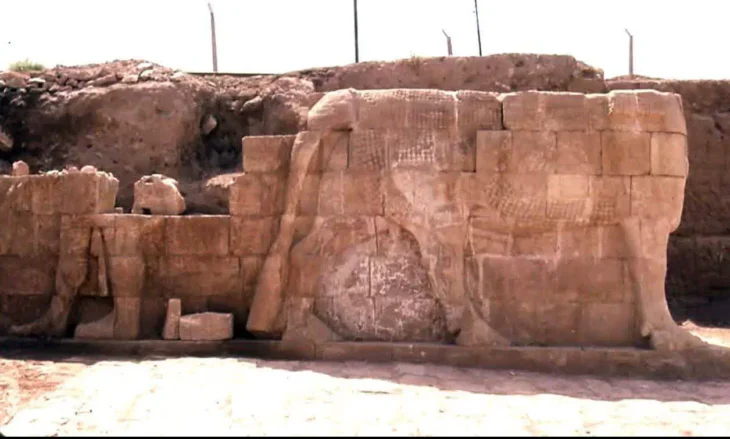
More than a linguistic puzzle, the inscriptions also tell a story of religious strife. Bar-Ron categorizes the 22 inscriptions into five clades, with some praising Baʿalat (the Canaanite goddess linked to Hathor), and others showing signs of deliberate defacement — often by later scribes loyal to El, the god of the Hebrews.
“We see worshipful inscriptions lauding Baʿalat, only to have later scribes hack them — scratching out cultic fish symbols and replacing them with praises to El,” Bar-Ron told Patterns of Evidence. “This is ground zero for theological rebellion.”
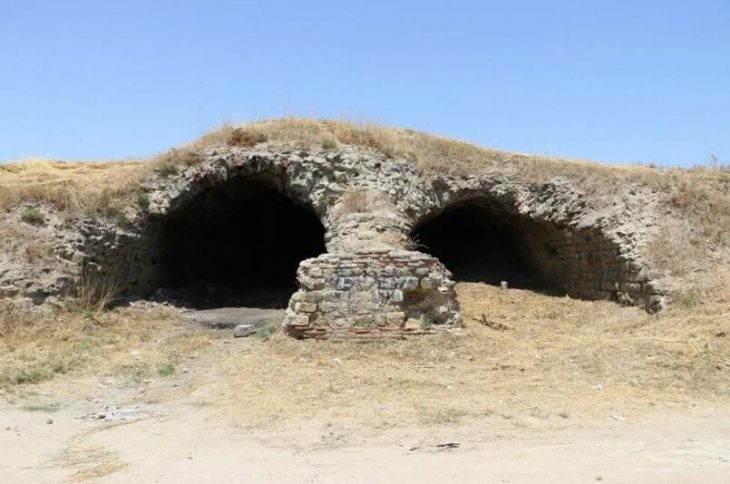
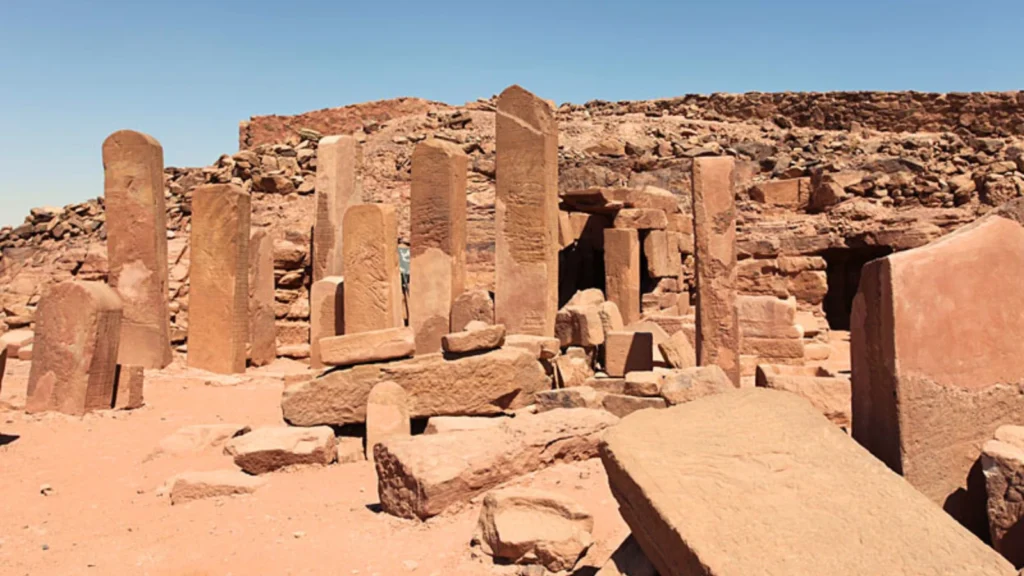
The remains of a burnt temple to Baʿalat at Serabit el-Khadim align with Bar-Ron’s theory of a violent religious purge, potentially led by followers of El — perhaps even Moses himself. Combined with phrases like nimosh (“let us depart”), these writings suggest a proto-Exodus narrative recorded in real-time.

Controversy and Skepticism
Not all academics are convinced. Dr. Thomas Schneider, Egyptologist at the University of British Columbia, labeled the claims “completely unproven and misleading,” criticizing what he sees as arbitrary letter identifications and theological bias.
Nonetheless, the inscriptions — first unearthed in the early 1900s and long considered undecipherable — are receiving renewed attention. Even skeptics acknowledge that they provide a unique glimpse into the cultural, linguistic, and religious world of Semitic laborers in ancient Egypt.
A History Waiting to Be Rewritten?
If Bar-Ron’s interpretations hold under further academic scrutiny, it could mark a turning point in biblical archaeology, offering tangible evidence that the Exodus narrative may have roots in real history.
As debate swirls in scholarly circles, one thing is clear: the mystery of Serabit el-Khadim has not yet given up all its secrets.
Bar-Ron, M. S. (2025). Presenting critical readings of 22 complex P-S inscriptions across five proposed clades, the Stele of Reniseneb, a seal of an Asiatic Egyptian high official and their implications for early Biblical traditions: A proto-thesis summarizing eight years of critical Proto-Sinaitic research (Unpublished proto-thesis). Johannes Gutenberg University of Mainz.
















