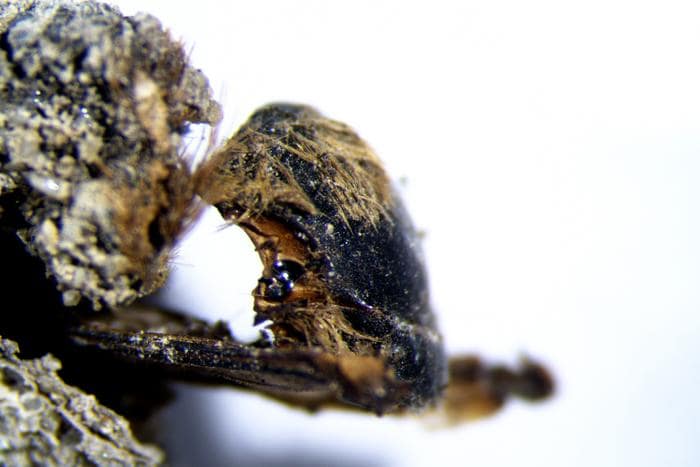
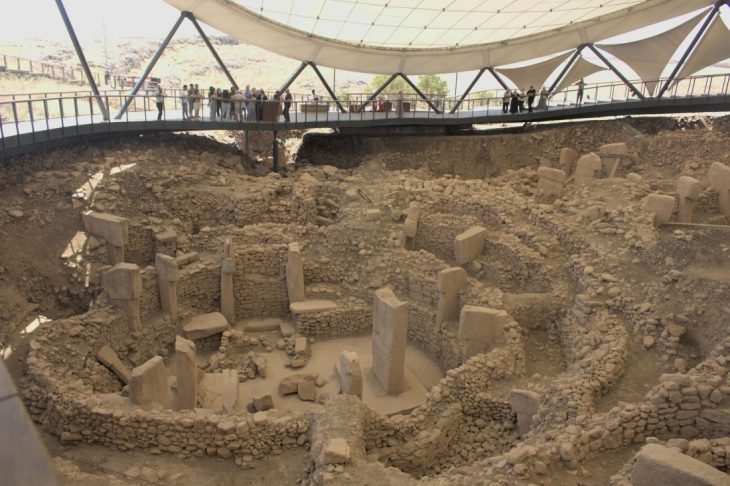
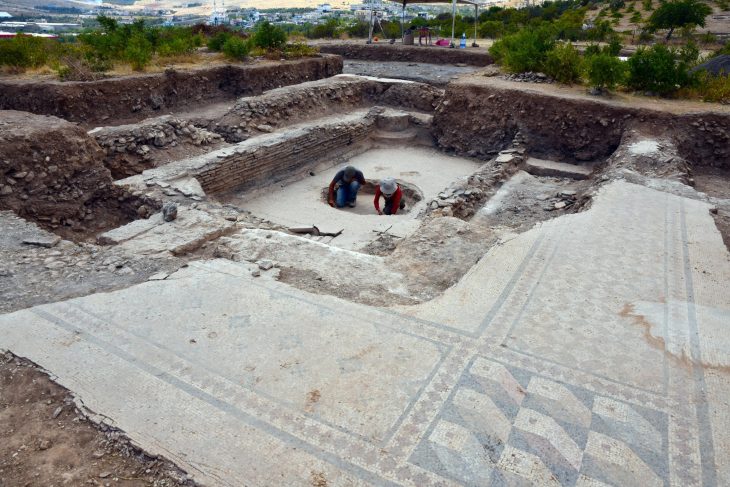
The UNESCO World Heritage Site of Boğazköy-Hattuša, once the capital of the Hittite Empire during the late Bronze Age (circa 1650 to 1200 BC), is now at the forefront of digital humanities research. This ancient site, located in northern Türkiye, has yielded a wealth of cuneiform tablets that represent one of the largest collections of texts from the ancient Near East, including thousands of documents in Hittite and other Anatolian languages, as well as Sumerian, Akkadian, and Hurrian texts.
Since its launch in 2023, the Thesaurus Linguarum Hethaeorum Digitalis (TLHdig 0.1) has provided researchers and students with unprecedented online access to these historical sources through the Hethitologie-Portal Mainz platform. The tool has quickly gained popularity among Hittitologists, recording over 100,000 accesses per month.
The latest version, TLHdig 0.2, has significantly expanded its capabilities, now encompassing more than 98% of all published sources—approximately 22,000 XML text documents, many containing multiple rejoined fragments. The current corpus boasts nearly 400,000 transliterated lines, with plans for TLHdig 1.0, expected in late 2025, to provide complete coverage of all published texts.
Researchers can now browse and search texts in both transliteration and cuneiform, utilizing various filters for more complex queries. TLHdig is seamlessly integrated within the Hethitologie-Portal Mainz infrastructure, connecting users to a range of digital catalog tools, media databases, and text editions.
TLHdig is not just a tool; it is a community-driven research platform. The TLHdig team has compiled the corpus using both digital and analogue resources developed by generations of Hittitologists, including contributions from various digital text edition projects on the Hethitologie-Portal Mainz.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The platform also features an online submission pipeline, allowing scholars to publish new Hittite cuneiform texts easily. Users can input their transliterations into the creator interface and follow a step-by-step manual for guidance, ensuring a smooth submission process.
This collaborative and dynamic approach ensures that TLHdig will continue to evolve alongside the field of Hittite studies, enhancing both the quantity and quality of available data. It serves as a foundational resource for text editions and supports a wide array of research methodologies, including innovative AI applications.
The development of TLHdig has been funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) and is led by a team of esteemed scholars: Professor Gerfrid Müller from the Mainz Academy of Sciences and Literature and the University of Würzburg, Professor Doris Prechel from the University of Mainz, Professor Elisabeth Rieken from the University of Marburg, and Professor Daniel Schwemer from the University of Würzburg.
As the digital landscape continues to transform the study of ancient texts, TLHdig stands as a testament to the power of collaboration and innovation in the pursuit of knowledge about the Hittite Empire and its rich historical legacy.
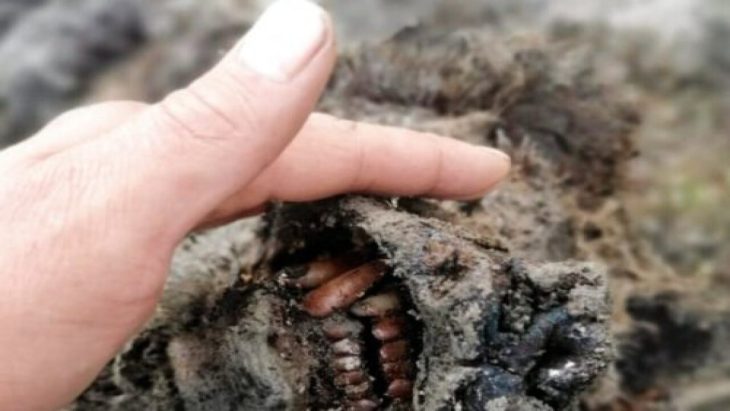
Cover Image Credit: From cuneiform to code: section of a Hittite cuneiform text found in Boğazköy-Hattuša in 2024 (photo and XML text). Image Credit: Daniel Schwemer / Universität Würzburg
If this news piqued your interest, we also recommend checking out our article titled “Turkish Researchers Use Artificial Intelligence to Read Cuneiform Hittite Tablets.”
TLHdig on Hethitologie-Portal Mainz: https://www.hethport.uni-wuerzburg.de/TLHdig/