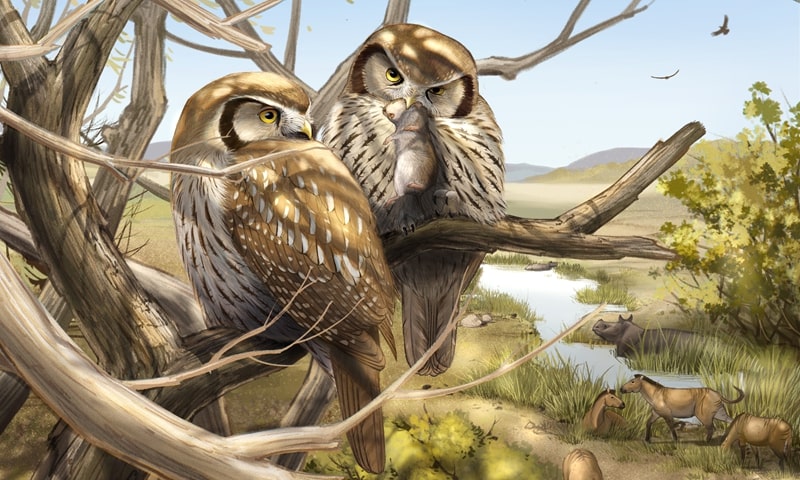
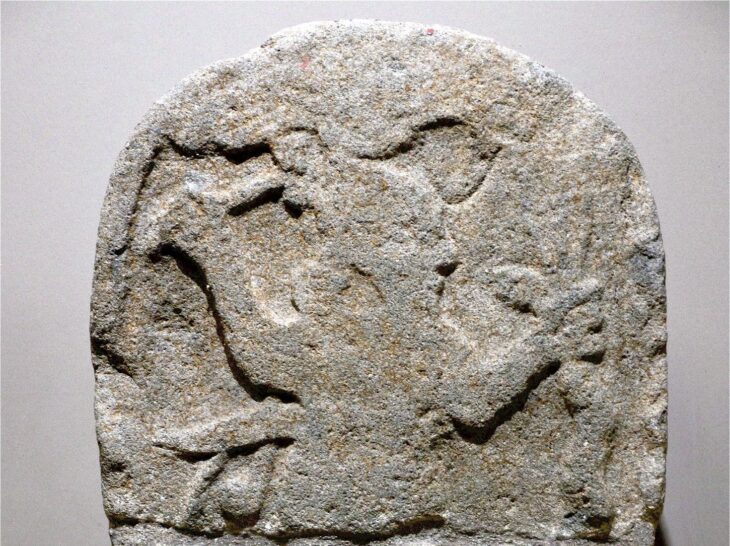
The incredibly well-preserved fossil skeleton of an extinct owl that lived was discovered on the edge of the Tibetan Plateau, in the Linxia Basin of China’s Gansu province, at an altitude of about 2,100 meters.
A species of diurnal owls was identified from a piece of fossil found giving clues on how the diurnal birds evolved in the mostly nocturnal species. Most owls living today are nocturnal.
Detailed analysis of the skeleton’s fossilised eye bones by researchers at the Chinese Academy of Sciences reveals that, unlike most modern owls, this species was active in the daytime, not the night.
A study published today in the journal PNAS traces an “evolutionary reversal” in one of the largest living groups of owls and presents “the first fossil evidence for diurnal behavior” among the birds, according to the abstract.
The research focuses on a well-preserved skeleton from northern China’s Ma Liushu Formation. Measuring about 12 inches from head to toe, Miosurnia diurna is estimated to be 6 to 10 million years old and is related to modern diurnal species such as burrowing owls and Northern hawk owls. The extinct owl belongs to the clade Surniini which contains most living diurnal owl species.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
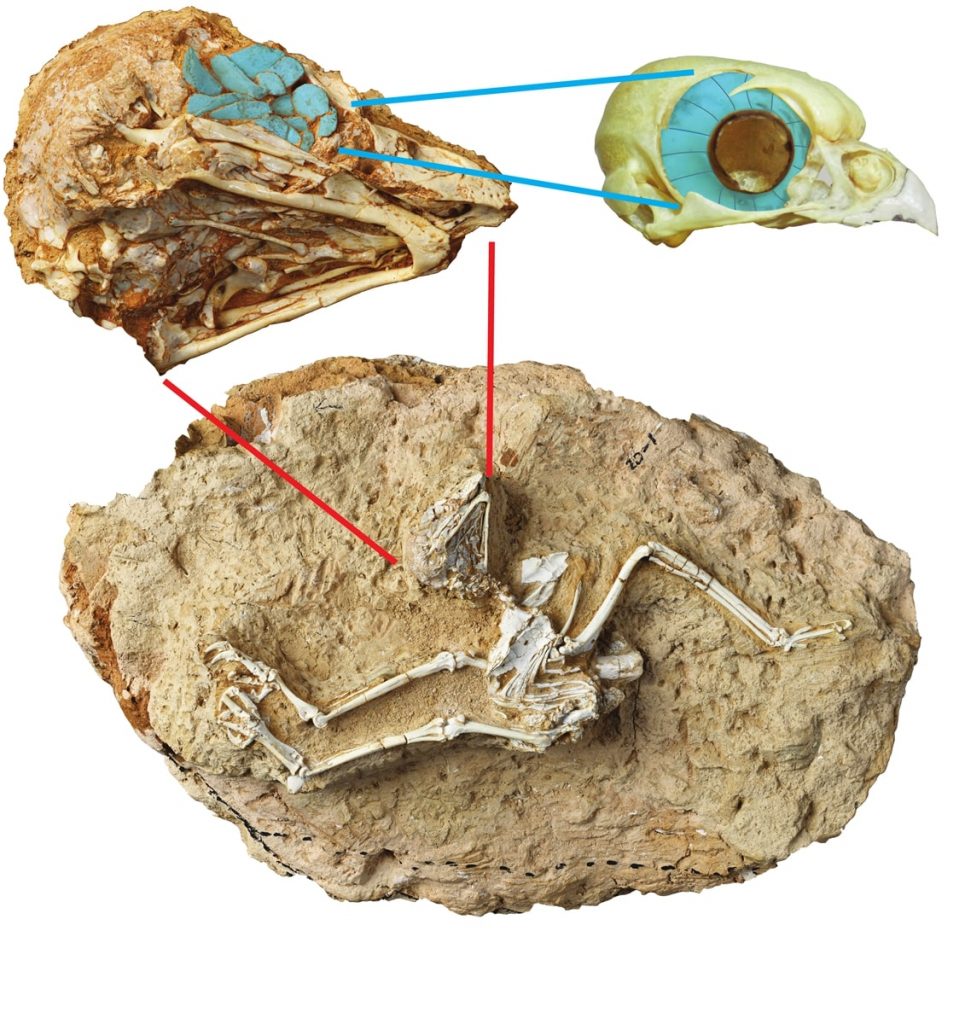
The researchers named the species Miosurnia diurna in reference to its close living relative, the diurnal Northern Hawk Owl (Surnia ulula).
A comparison of sclera bones of the Miocene diurna and 55 reptiles and 360 birds, including many owls, showed the ancient bird’s eyes are less open to light and enable it to see things clear during the day, according to a statement by the institute. Scleral ossicles are small bones that form a ring around the pupil and iris in the outer region of the eye.
Nocturnal animals require overall larger eyes and bigger pupils to see in low-light conditions, but diurnal animals have smaller eyes and pupils.
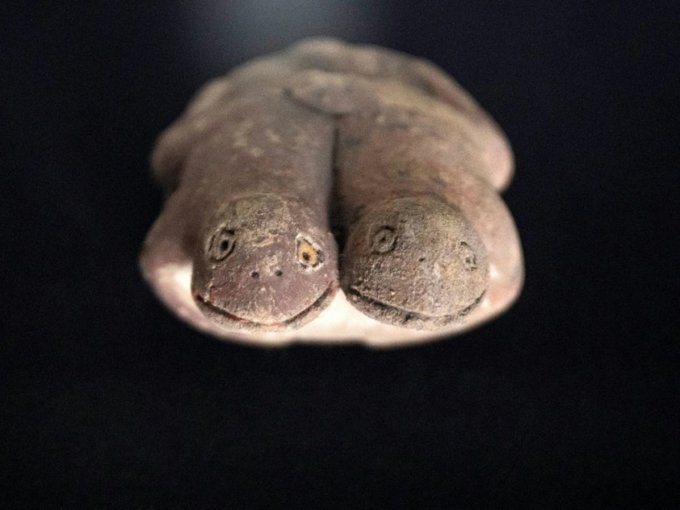
In the Miosurnia diurna fossil, the soft parts of the eye had decayed long ago, leaving the small trapezoidal scleral ossicles randomly collapsed into the owl’s eye socket.
‘It is the amazing preservation of the bones of the eye in this fossil skull that allows us to see that this owl preferred the day and not the night,’ said Dr. LI, first author of the study.
This extinct species is the first record of an ancient owl being ‘diurnal’, or active during the day.
In contrast with other ancient owls, whose senses of sight, sound, and even smell were suited to the darkness, Miosurnia diurna seemed to be better adapted for daytime, with large eyes and less-tubular ears that match the traits in grassland owls today. As such, the extinct owl’s environment might have been the main driver behind its behavioral shift: The study goes so far to attribute the night-to-day switch to “steppe habitat expansion and climate cooling in the late Miocene.”
The fossil and associated analyses of the eye and behavioral evolution also point to a long evolutionary history of nonnocturnal behavior among owls that has yet to be studied in detail.
Cover Photo: Miosurnia diurna, an extinct owl found in a Chinese fossil formation, probably looked similar to some of the diurnal owls today. Zheng Qiuyang