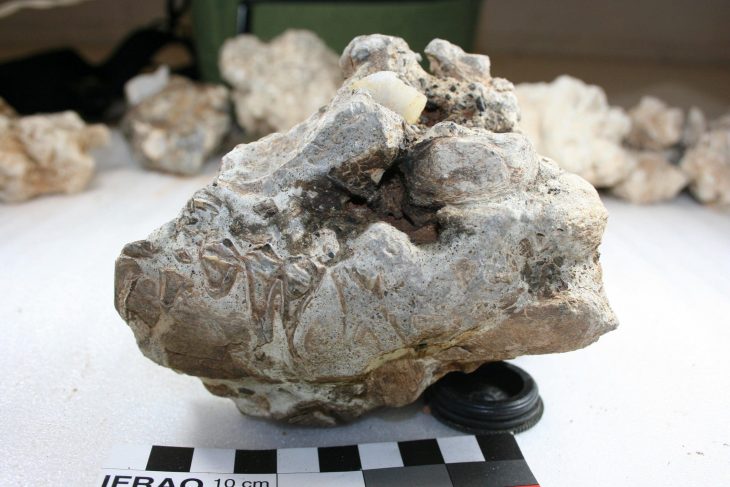
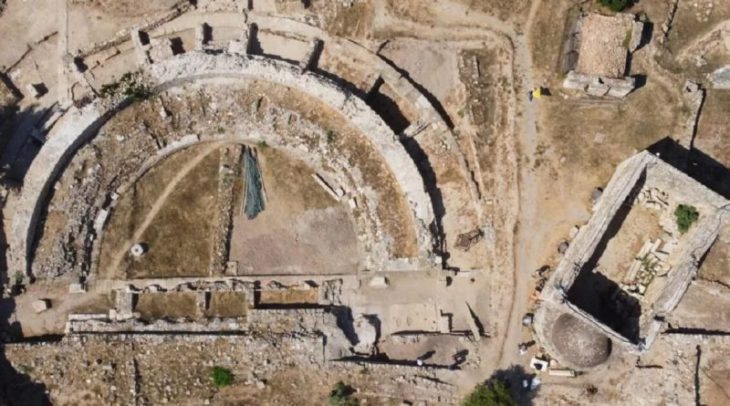
In a discovery that may reshape our understanding of how ancient Romans perceived the natural world, archaeologists have uncovered a fossilized trilobite intentionally modified and likely worn as an amulet at a Roman-era site in northwestern Spain.
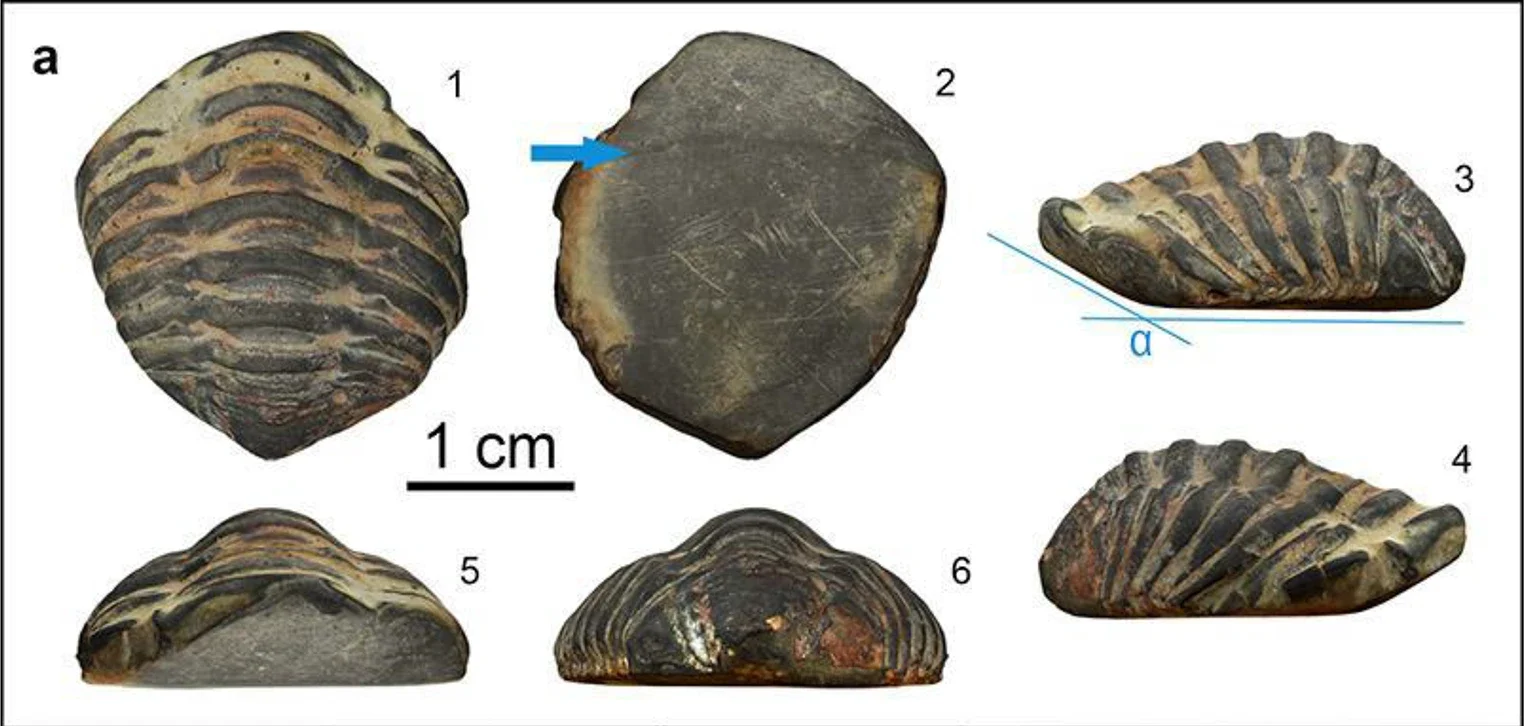
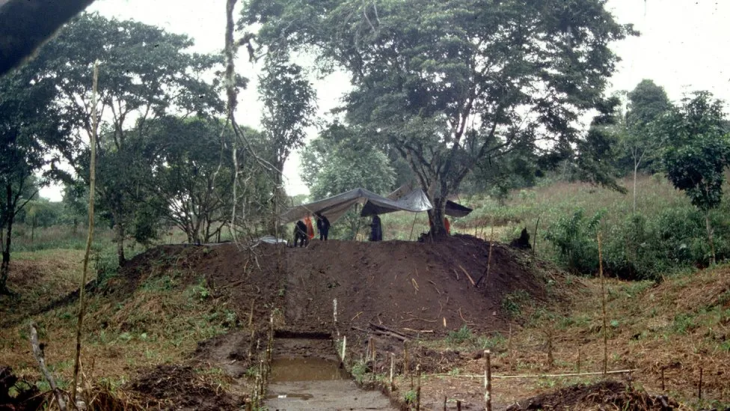
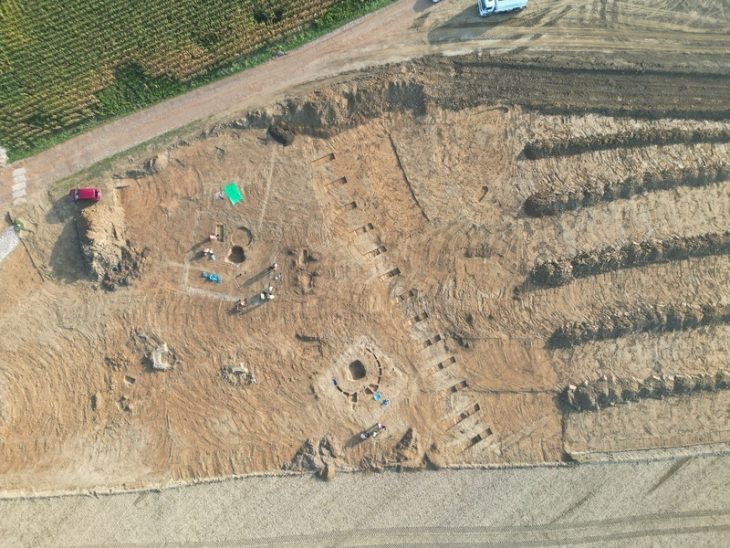
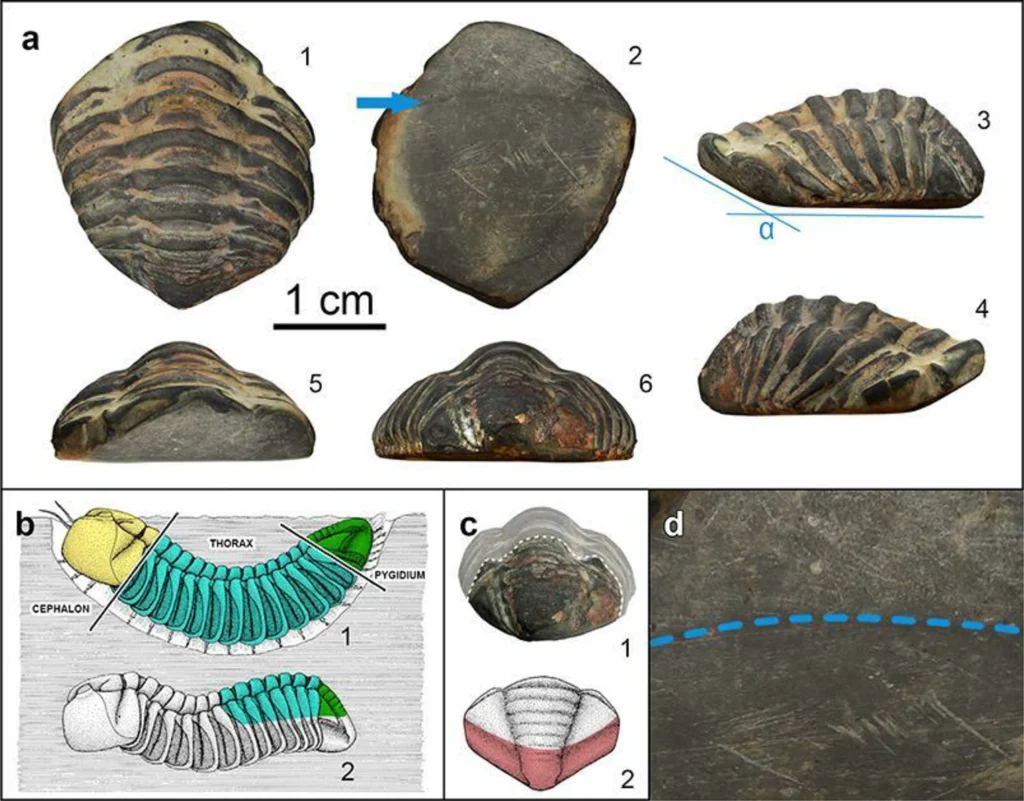
The fossil—identified as an Ordovician trilobite (Colpocoryphe)—was found during excavations at the settlement of A Cibdá de Armea, near the modern-day town of Allariz, Galicia. Dating to between the 1st and 3rd centuries CE, the object represents the first known example of a trilobite fossil being used in Roman material culture, and among the rarest fossil artifacts found in archaeological contexts globally.
A Fossil from Deep Time in a Roman Context
Trilobites, marine arthropods that lived more than 400 million years ago, are long extinct. Yet this particular specimen was found not in a museum or scientific collection, but within the remains of a Roman domus, surrounded by pottery, coins, glass shards, and animal bones.
What sets this fossil apart is its clear anthropogenic modification. Seven distinct facets on the fossil’s ventral (underside) surface indicate that it was deliberately ground down—possibly to be worn against the skin as an amulet, pendant, or component of a bracelet.
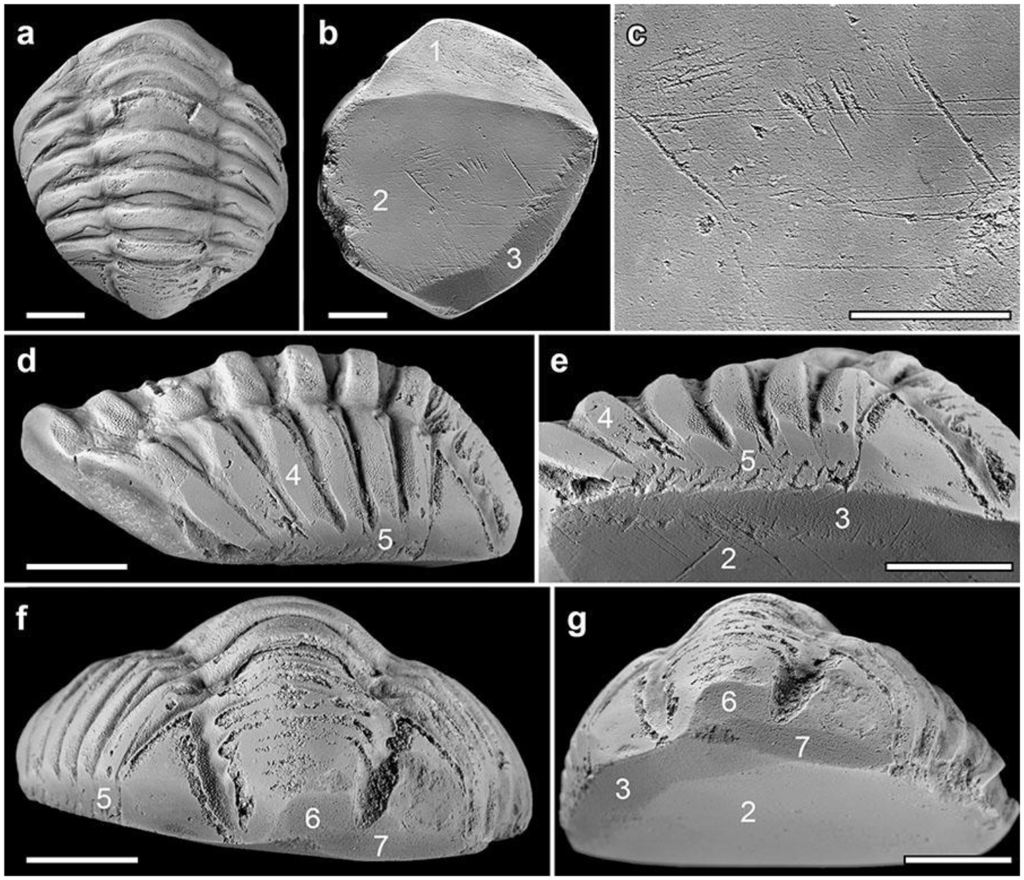

A 430-Kilometer Journey Across Iberia
Geochemical analysis suggests the trilobite originated in the Toledan or Ibor Group formations of central Spain—located over 430 km from the excavation site in Galicia. This implies that the fossil was deliberately transported across the Roman province of Hispania, either through trade networks or as a personal possession.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Its value likely went far beyond aesthetics. Researchers propose the trilobite was seen as a symbolically or spiritually charged object, possibly connected to healing, protection, or magical rites.
“This is not merely a curiosity—it’s a powerful example of how ancient people attributed meaning to the remnants of Earth’s deep past,” said Dr. Adolfo Fernández-Fernández, lead author of the study.
Fossils in Antiquity: More Than Just Stones
While there are documented cases of large fossil bones—like mammoth tusks—being displayed in Roman temples and villas, this is the first confirmed case of an invertebrate fossil being shaped and worn in antiquity. It reveals a new dimension of Roman spirituality and highlights the symbolic use of natural materials in personal or ritual life.
In Roman thought, unusual natural objects often carried symbolic or magical meaning. Fossils, with their strange shapes and mysterious origins, may have been interpreted as divine signs or protective talismans—an interpretation echoed in many other ancient and indigenous cultures.
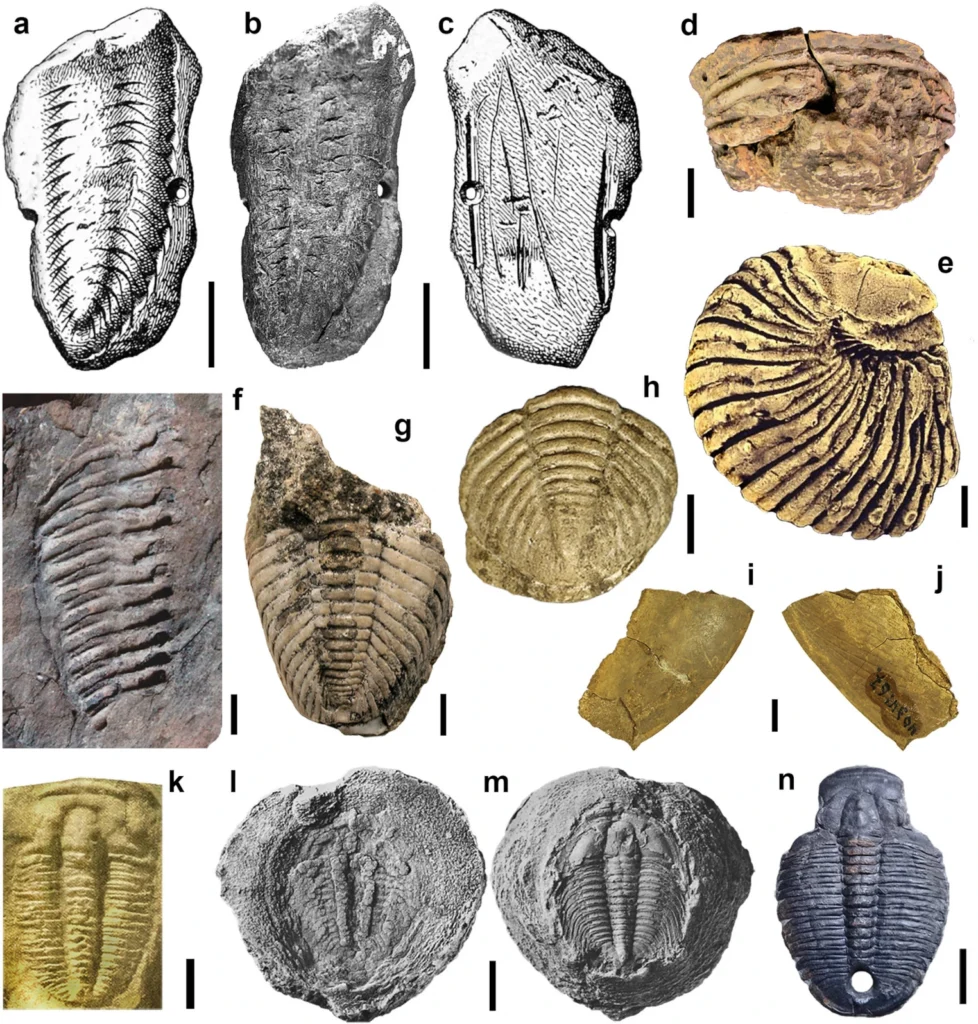

Rare on a Global Scale
Globally, only eleven trilobite fossils have ever been recovered from archaeological contexts, with examples found in:
What makes the Armea trilobite exceptional is the intentional modification and the specific historical context: early Roman Hispania. It demonstrates not only that fossils were known to ancient peoples but that they were manipulated and invested with meaning—far earlier and more widely than previously thought.
Shifting the Timeline of Human-Fossil Interaction
This trilobite is now considered the earliest evidence of trilobite use in classical antiquity and the only example directly linked to the Roman world. It pushes the timeline of human-fossil interaction back further and reaffirms the idea that fossils have long been valued for more than scientific knowledge—as objects of wonder, reverence, and belief.
Fernández-Fernández, A., Valle-Abad, P., Rodríguez -Nóvoa, A.A. et al. Significance of fossils in Roman times: the first trilobite find in an early Empire context. Archaeol Anthropol Sci 17, 166 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12520-025-02266-8
Cover Image Credit: Fernández-Fernández et al., Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12520-025-02266-8
















