Exceptional discovery in the necropolis of Tarquinia, located near the western coast in central Italy, north of Rome (a UNESCO site): a new chamber tomb painted with dance and workshop scenes brings the extraordinary funerary art of the Etruscans back into the limelight after centuries of oblivion.
The first discovery dates back to the last days of 2022, when the Soprintendenza staff inspected some cavities that had opened up in farmland near Tarquinia, in the heart of the Etruscan necropolis of Monterozzi. With the help of archaeo-speleologists, the exploration confirmed that these were Etruscan chamber tombs that had already been visited in the past by clandestine excavators.
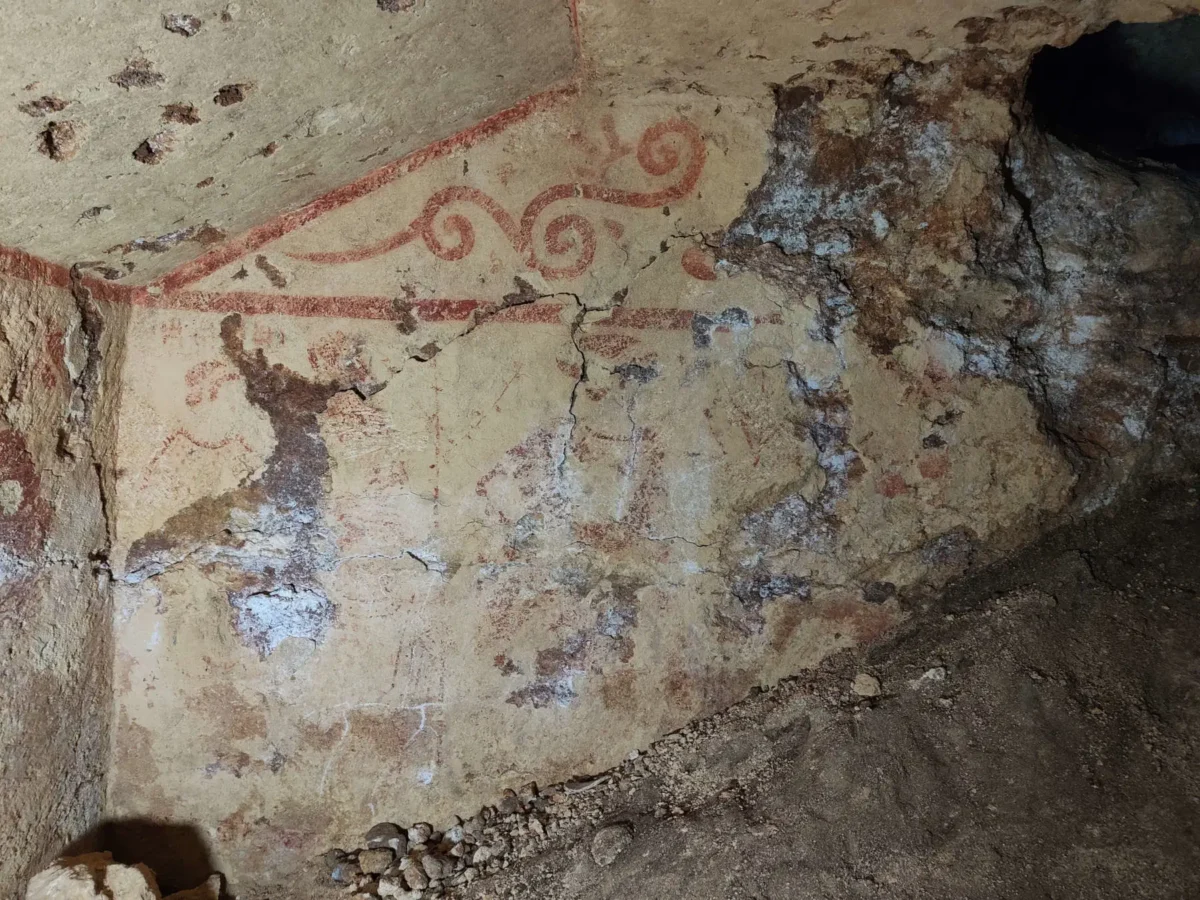
One of the tombs, however, had a surprise in store: part of the left wall had collapsed, revealing access to a deeper chamber tomb, partially filled with earth and debris. Beautifully colored painted scenes decorated the walls, as a sign of the memory of ancient Etruscan civilization.
To protect the site from potential threats posed by grave robbers and careless visitors, the Superintendency conducted the excavation operations under strict confidentiality. Thanks to a significant grant from the Ministry of Culture, archaeologists were able to carry out a thorough intervention to secure the tomb and maintain its delicate balance. Consequently, the announcement of the discovery was delayed for two years to allow for further study of the findings.
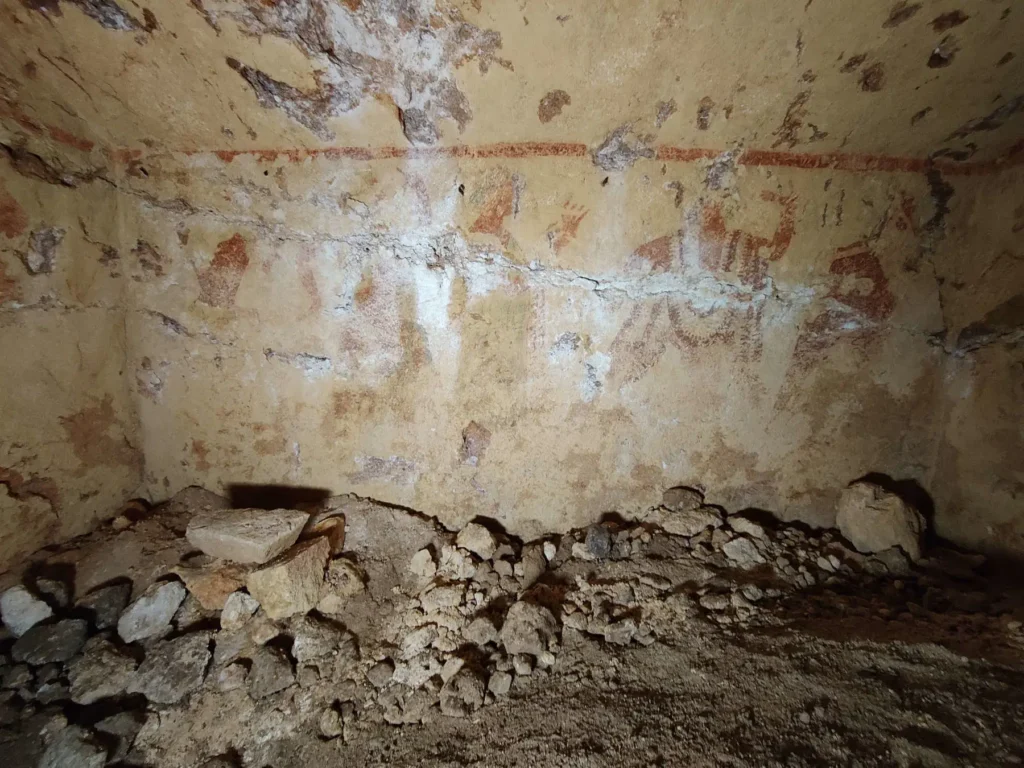

Daniele F. Maras, the archaeological officer in charge of the discovery and now the director of the National Archaeological Museum in Florence, explained that after they restored access to the burial chamber and installed a metal door, the archaeological excavation revealed some interesting findings. He noted that the materials they collected did not belong to the trousseau of the painted tomb, which dates back to the mid-5th century B.C. Instead, these materials had collapsed from an older tomb, which is more than a century older and dates from the end of the Orientalizing period.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The archaeological investigation has uncovered a unique and complex situation at the site, revealing that the painted tomb was excavated deep beneath a pre-existing burial. In ancient times, grave robbers had breached the tomb by piercing the closing slab, looting the original grave goods. Subsequently, the collapse of the upper chamber brought debris and objects that mixed with the remains of the lower tomb. Today, only a few fragments of Attic red-figure pottery remain from what once constituted the grave goods of the painted tomb, highlighting the value of the objects originally laid with the deceased. However, the true treasure of this discovery lies in the stunning frescoes that adorn the walls of the burial chamber.
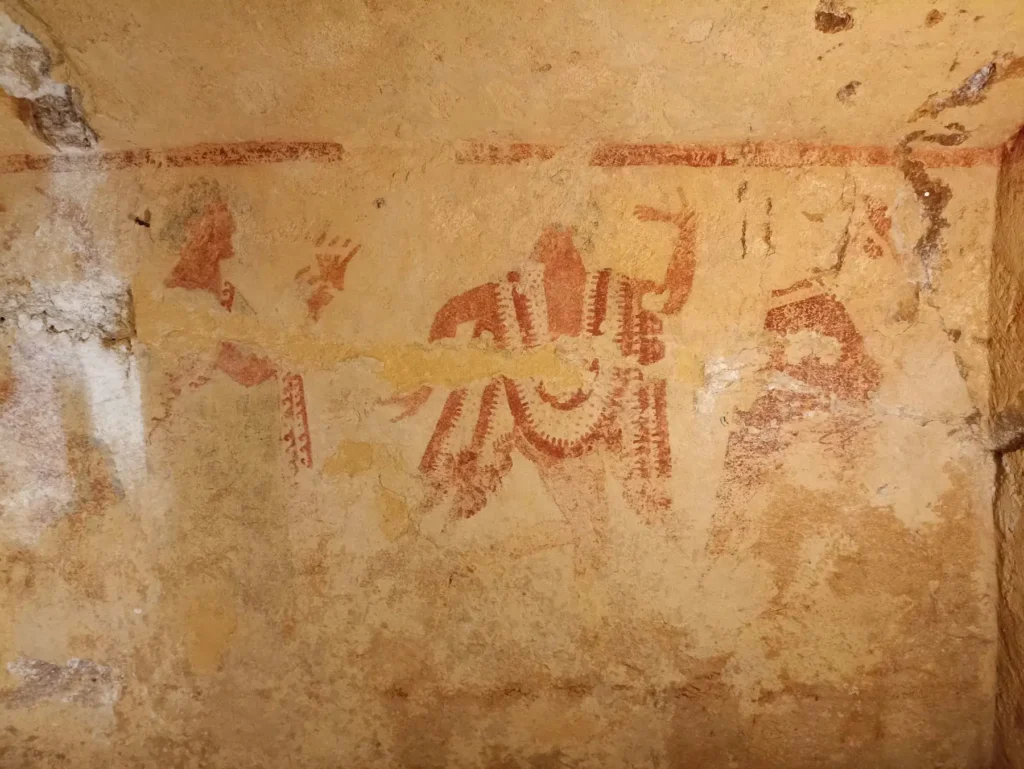
The wall paintings, currently undergoing restoration, provide a unique insight into Etruscan culture. The left wall features a dynamic scene of a frenetic dance, where men and women are depicted moving in a circle around an elegant flute player, reflecting the vitality and celebratory spirit characteristic of the Etruscan people.
In contrast, the back wall reveals the figures of a woman—possibly the deceased—and two young men; however, a portion of the decoration has been irretrievably lost due to structural collapse. The right wall presents an even more enigmatic depiction of a working metal workshop. Scholars speculate that this may represent the mythical workshop of the god Sethlans, the Etruscan equivalent of Hephaestus, or a royal workshop associated with the family of the interred individual.
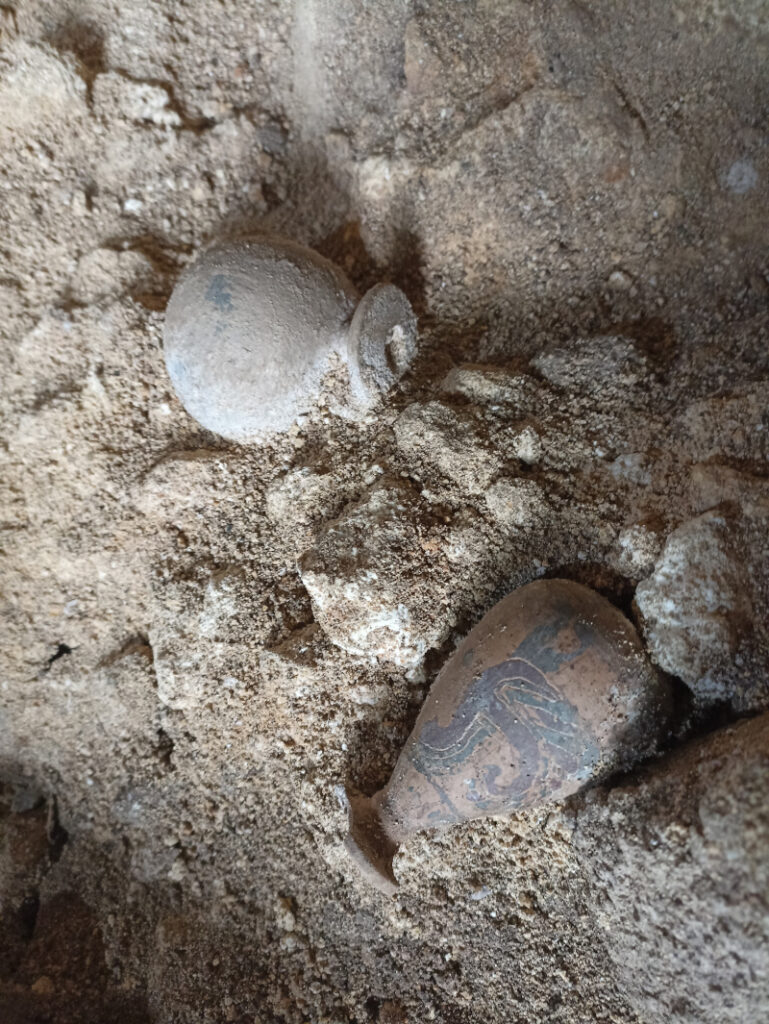

Restoration work on the site is ongoing and demands extreme precision. Superintendent Margita Eichberg expressed satisfaction with the progress, noting that “the extraordinary level of the paintings” is already evident in the initial restoration efforts conducted by Adele Cecchini and Mariangela Santella, which have highlighted the refinement of the details in the figures of the flutist and one of the dancers. Daniele Maras added that this discovery marks the first new painted tomb with a figured frieze to be found in Tarquinia in decades, emphasizing its intriguing potential due to its historical significance, artistic quality, and the uniqueness of some of the depicted scenes.
Soprintendenza Archeologia Belle Arti e Paesaggio
Cover Image Credit: Soprintendenza Archeologia Belle Arti e Paesaggio