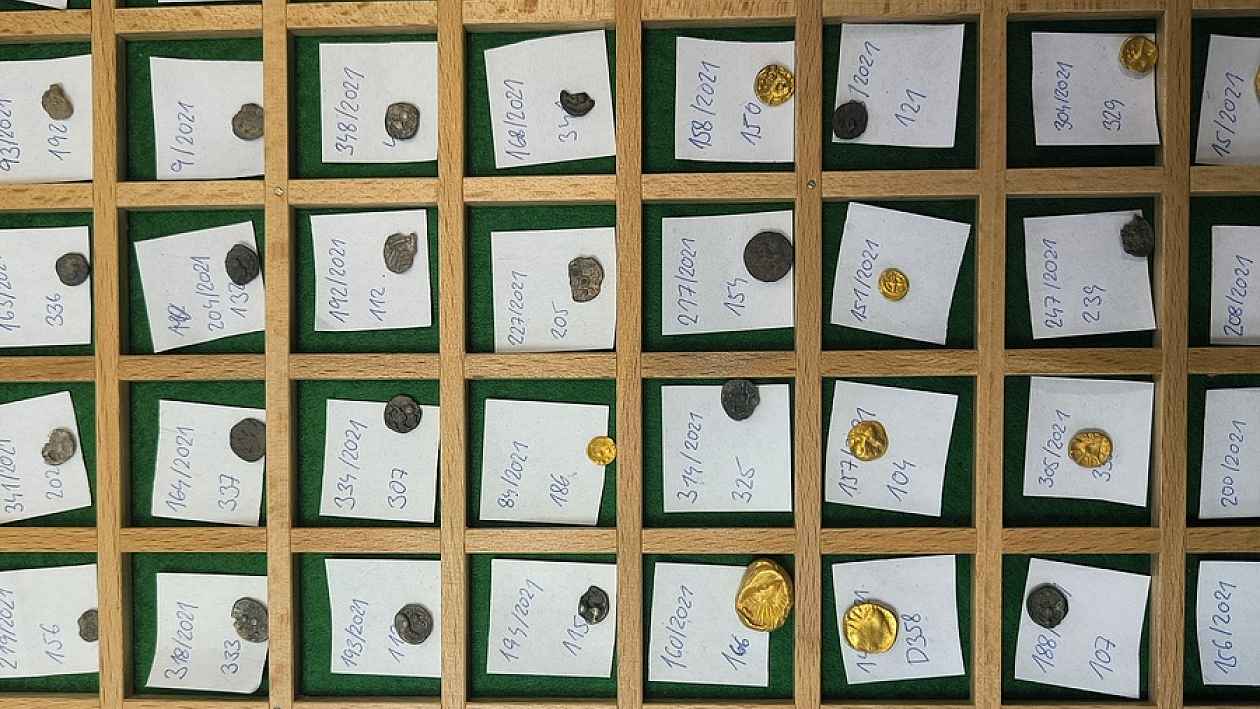
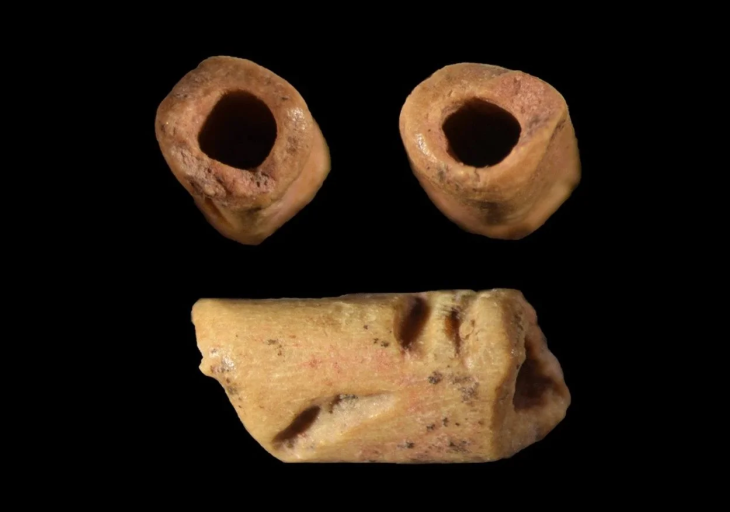
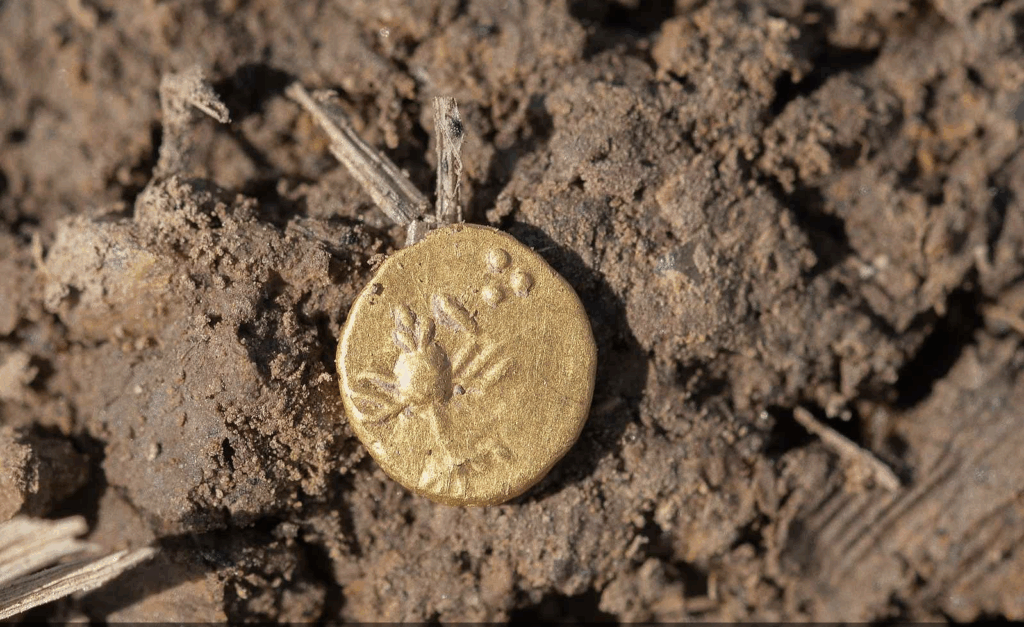
A remarkable archaeological discovery in northern Plzeň has unveiled hundreds of gold and silver Celtic coins, bronze ornaments, and even a small horse figurine — all from a previously unknown Celtic site. The Museum and Gallery of Northern Pilsen in Mariánská Týnice is now presenting these finds in a new exhibition titled “An Unclear Message About the Celts in Northern Plzeň”, open until November 30.
A Secret Site with Extraordinary Finds
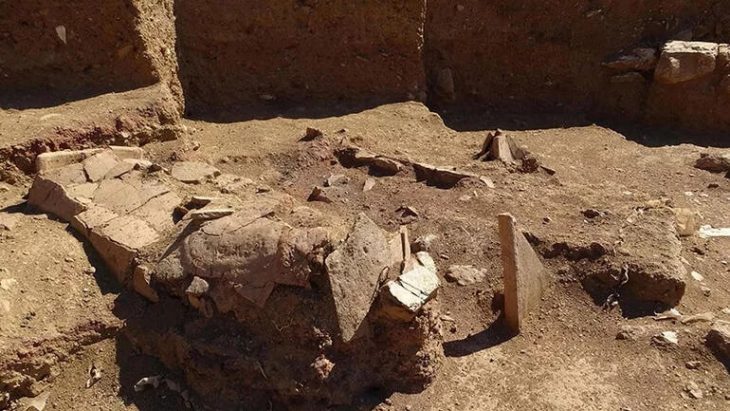
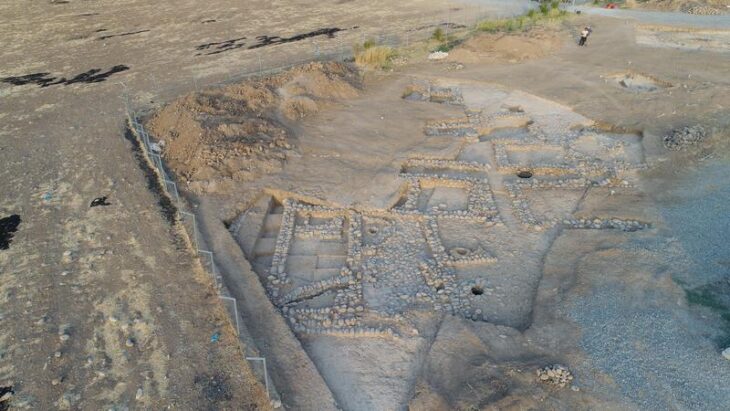
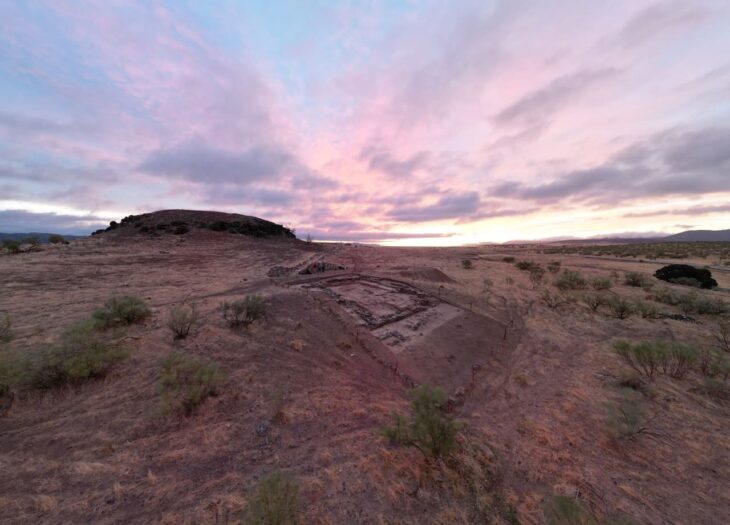
For the past five years, experts from the Archaeological Institute of the Czech Academy of Sciences (AV ČR) and the Museum of Northern Pilsen have been studying and documenting artifacts dated between the 6th and 1st centuries BCE. These discoveries are unique not only for their quantity — hundreds of precious metal coins and objects — but also because they were found in an area where no major Celtic settlement was previously known.
According to Jan Mařík, director of the Archaeological Institute, the project’s primary goal was to protect movable archaeological finds that are at risk from illegal treasure hunters, ploughing, and natural erosion. “Illegal metal detectorists pose a significant threat to our cultural heritage. To prevent further damage, the exact location of the site remains confidential,” Mařík explained.
Rare Coins and Unprecedented Artifacts
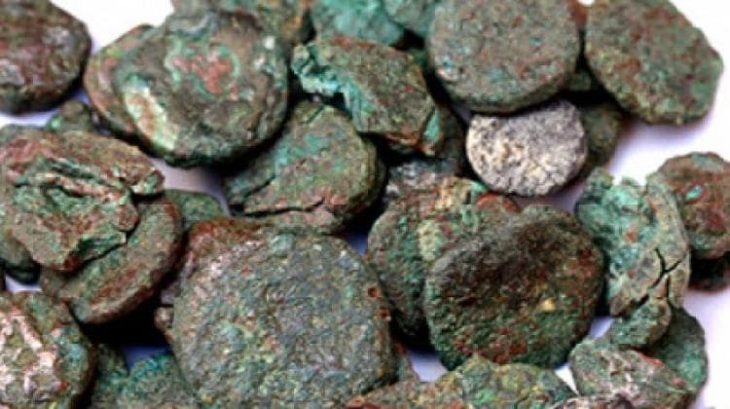
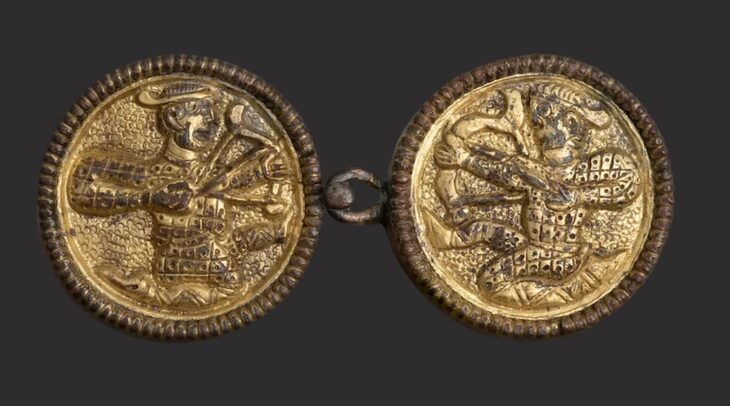
Archaeologist Daniel Stráník from the Mariánská Týnice museum emphasized that this site is exceptional at least on a Central European scale. “Among the gold and silver coins, we have identified previously unknown types that could reshape our understanding of Celtic coinage in Bohemia,” Stráník said.
The collection also includes Hallstatt-era gold jewelry, bronze fibulae, pins, bracelets, pendants, and a bronze horse figurine — all of which illustrate the artistry and craftsmanship of the ancient Celts who once roamed this region.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
A Seasonal Celtic Center?
Current research suggests that the site might not have been permanently inhabited. Archaeologist David Daněček from the AV ČR proposes that it could have served as a seasonal gathering or trading location. “It may have been a place where people met for trade, exchanging goods and currency. The scattered nature of small items, such as coins, suggests temporary activities rather than long-term settlement,” he explained.
Several cut gold and silver ingots found on the site reinforce the idea that this location could have played a role in ancient commerce and minting practices, possibly under the supervision of local rulers. This interpretation aligns with known patterns from smaller Celtic centers in Austria and Moravia.
Preserving the Celtic Legacy
Currently, only a selection of the artifacts is on display in the museum’s small gallery. “The most exceptional pieces are stored securely and will be revealed once the full research project is complete,” said Pavel Kodera, director of the Museum of Northern Pilsen.
“In the future, we are considering creating a permanent exhibition dedicated to the Celts, offering an entirely new perspective on their life in our region.”

The Celts in the Czech Lands: A Rich but Elusive History
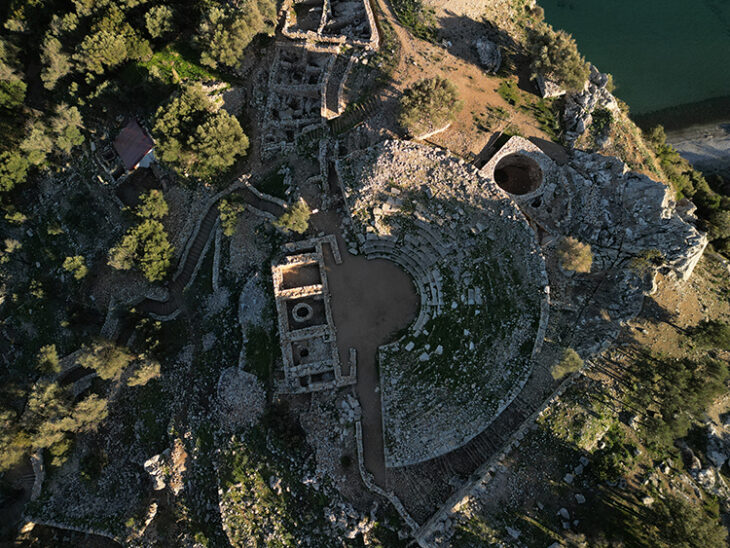
The Celtic presence in what is now the Czech Republic dates back to the La Tène period (approximately 450–50 BCE). The Boii tribe, from which the ancient name Boiohaemum (and later Bohemia) originates, once dominated this area. They founded fortified settlements known as oppida, such as Závist near Prague and Staré Hradisko in Moravia, which served as political and economic centers.
Celtic culture in the region was highly advanced, known for metalworking, coin minting, and trade networks that stretched from the British Isles to the Balkans. The discovery in northern Plzeň adds a new chapter to this story — indicating that Celtic influence extended further than previously thought, even into regions without known oppida.
A Glimpse into a Forgotten World
The Mariánská Týnice exhibition not only celebrates these discoveries but also invites visitors to reconsider the mystery and mobility of Celtic life in Central Europe. Each object, from a simple coin to a delicately crafted bronze ornament, serves as a tangible link to a civilization that once thrived here over two millennia ago.
As new research continues, archaeologists hope that this secretive site will shed light on the economic, cultural, and spiritual life of the Celts in Bohemia. For now, the exhibition offers a rare opportunity for the public to experience the splendor of a people whose legacy still shapes the identity of the Czech lands today.
Cover Image Credit: Museum and Gallery of Northern Pilsen