Beneath the sun-drenched plains of Cappadocia, where otherworldly “fairy chimney” rock formations pierce the sky, lies a secret world carved into the very heart of the earth.Forget the grand pyramids or towering ziggurats; we’re about to descend into Derinkuyu, an ancient metropolis swallowed by the ground, a testament to human resilience and a whisper from a forgotten past.
Imagine a civilization, facing threats we can only dimly perceive, choosing not to build up, but to delve down, creating a labyrinthine sanctuary that could shelter thousands. This isn’t just an archaeological site; it’s a subterranean saga etched in stone, waiting to unfold its mysteries. Its origins are somewhat debated, but the prevailing archaeological consensus points to construction likely beginning in the Phrygian period (around the 8th-7th centuries BCE). The Phrygians, an Indo-European people who established a significant kingdom in Anatolia, were known for their rock-cut architecture, and Derinkuyu bears hallmarks of their early techniques.
However, the city’s expansion and more complex features likely developed over centuries, with significant contributions from later periods, particularly the Byzantine era (roughly 4th to 15th centuries CE). During this time, Cappadocia was a crucial region for early Christianity, and the need for refuge from various invasions and raids, first from Arab forces and later from the Seljuk Turks, would have spurred the further development and extensive use of these underground complexes.
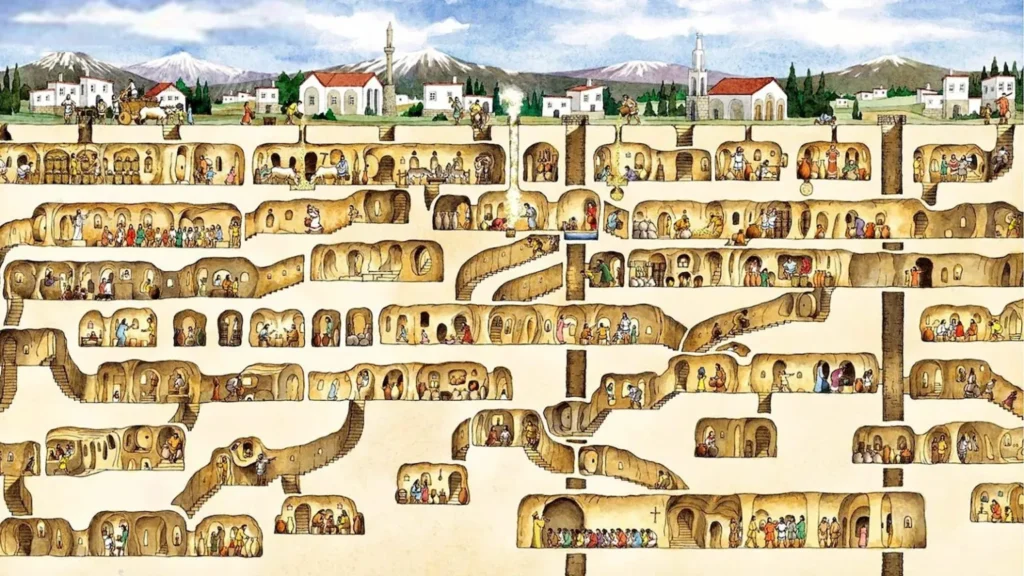
The city served as a refuge during times of conflict, allowing people to escape from invaders. The underground city could accommodate up to 20,000 people, along with their livestock and supplies, making it a significant shelter during turbulent times. The city extends approximately 60 meters deep and consists of multiple levels—around 18 floors! Each level was designed for specific purposes, such as living quarters, storage rooms, and even places of worship.
The geological context is crucial here. Cappadocia’s unique landscape is characterized by soft volcanic tuff, formed by ancient eruptions. This malleable rock was relatively easy to carve, yet strong enough to support the extensive network of tunnels and chambers without collapsing – a testament to the engineering acumen of its builders.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Now, let’s talk about the ingenuity of the design. Derinkuyu wasn’t just a series of haphazard tunnels; it was a carefully planned multi-level settlement designed for extended habitation. Key features include:
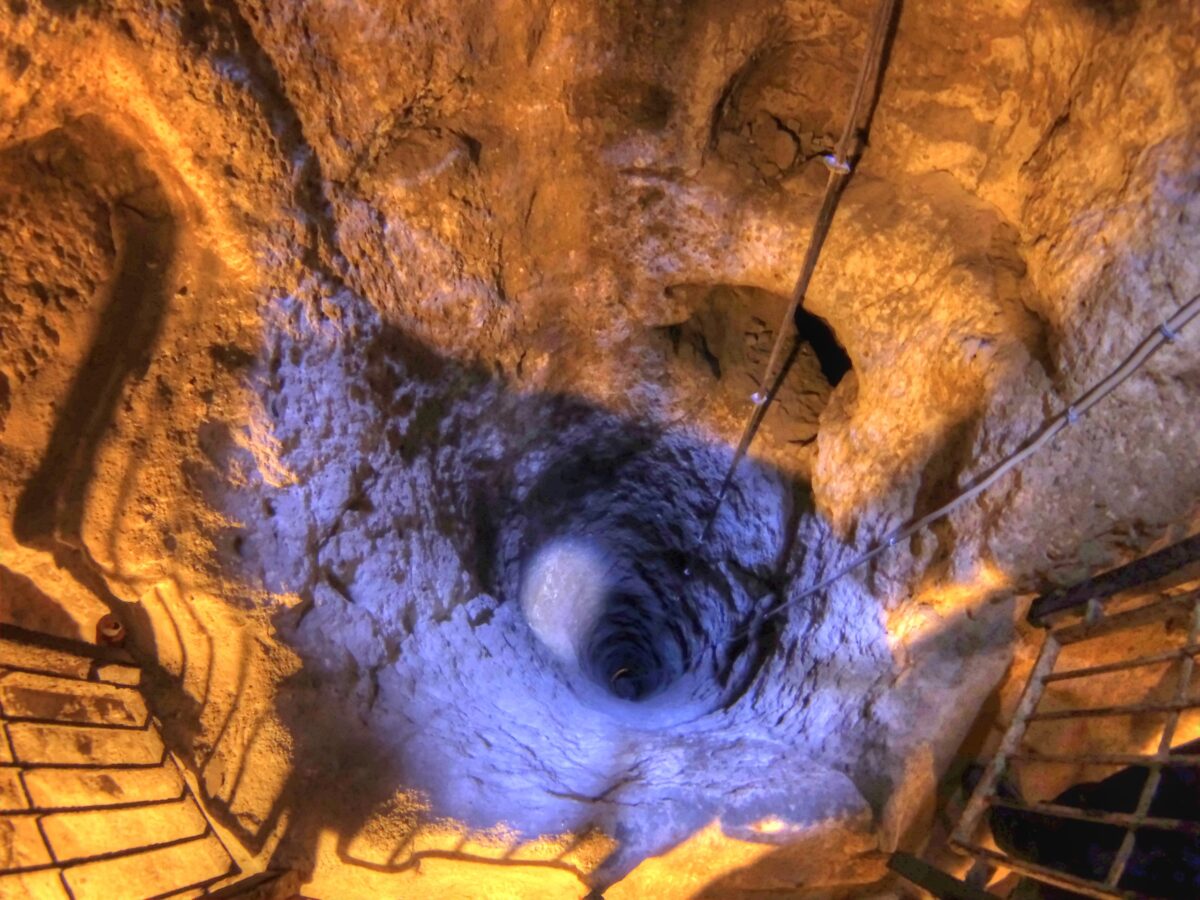
Ventilation Systems: Remarkably, the city possessed sophisticated ventilation shafts that extended down through multiple levels, ensuring a constant supply of fresh air. Some of these shafts are believed to have also served as wells.
Water Management: Evidence of wells and water storage areas highlights the critical need for a sustainable water supply during times of siege.
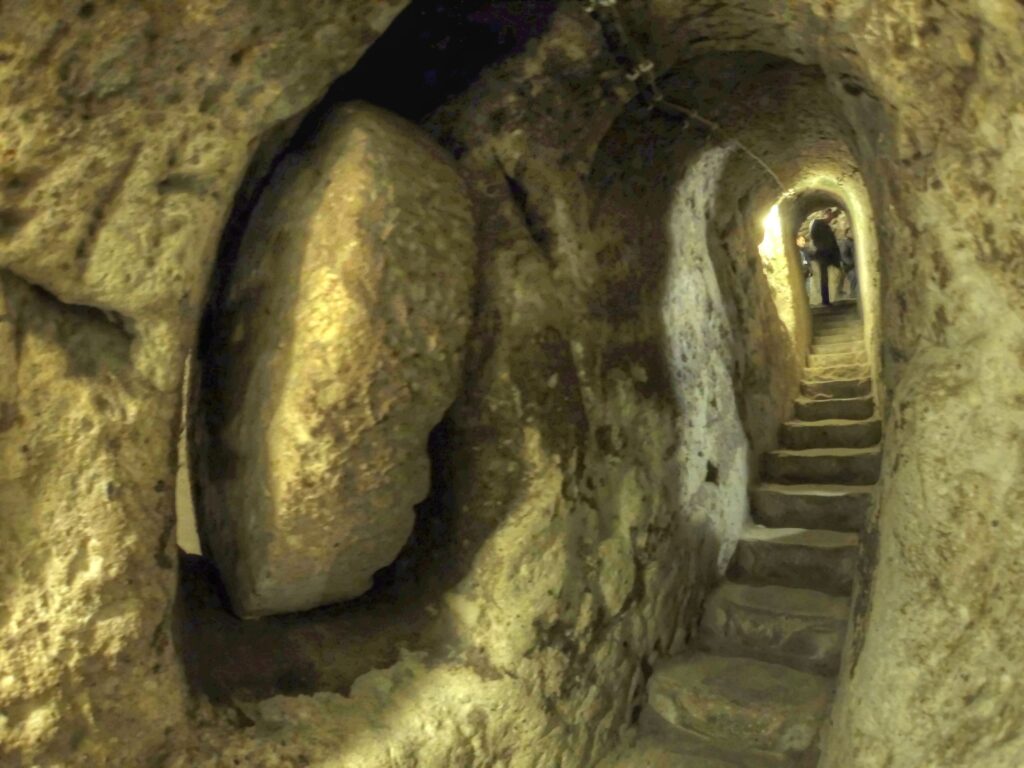

Defensive Measures: The massive circular stone doors, capable of sealing off corridors from the inside, are a clear indication of the city’s primary function as a refuge. These “rolling stones” could weigh several tons and were designed to be moved by a small number of people from within.
Living and Communal Spaces: Excavations have revealed evidence of domestic areas, including kitchens (with soot-stained ceilings indicating fireplaces), sleeping quarters, and communal gathering spaces.
Agricultural Infrastructure: The presence of stables suggests that livestock were also brought underground, a vital consideration for long-term survival. Storage rooms for grains and other foodstuffs further underscore the self-sufficiency of the city during times of crisis.
Religious and Educational Facilities: Some levels appear to have housed areas that may have served as chapels or even rudimentary schools, indicating that life, even in hiding, continued beyond mere survival.
The connection to other underground cities in the region, such as Kaymaklı, via subterranean tunnels adds another layer of complexity to the understanding of these networks. It suggests a potentially interconnected system of refuges, allowing for communication and possibly even the movement of people between them in times of extreme danger.
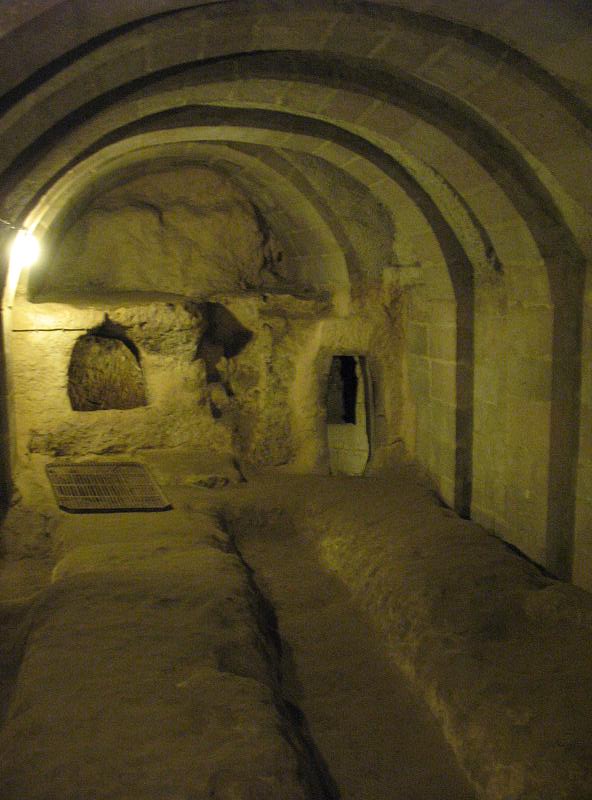

The rediscovery of Derinkuyu in modern times is also an interesting chapter. It was reportedly found in 1969 by a local resident who stumbled upon a hidden entrance while renovating his house. Subsequent archaeological investigations have gradually revealed the extent and significance of this subterranean marvel.
While the precise dating and the identity of the original builders are still subjects of scholarly debate, the evidence strongly suggests a prolonged period of construction and use, adapting to the needs of successive populations facing various threats. Derinkuyu stands as a powerful example of human adaptation, resourcefulness, and the enduring need for shelter and security throughout history. It offers a unique window into the as stood the test of time and continues to captivate the imagination of all who encounter it.
Derinkuyu Underground City is not just an archaeological site; it’s a window into the past, revealing the ingenuity and resilience of ancient civilizations. It invites us to ponder the lives of those who once sought refuge within its walls and the mysteries that still linger in its depths. If you ever have the opportunity to visit, you’ll be walking through history, exploring a place that has stood the test of time and continues to captivate the imagination of all who encounter it.
Cover Image Credit: A deep ventilation well in the city. Credit: Public Domain
















