Czech scientists, together with a small experimental brewer, have recreated the country’s first ‘Celtic Beer’ using laboratory analysis of pollen from an early Celtic burial site in Moravia.
The oldest known beer residue and brewing facilities date to 5,500 years ago in the Middle East, but archaeological clues to beer’s history are rare.
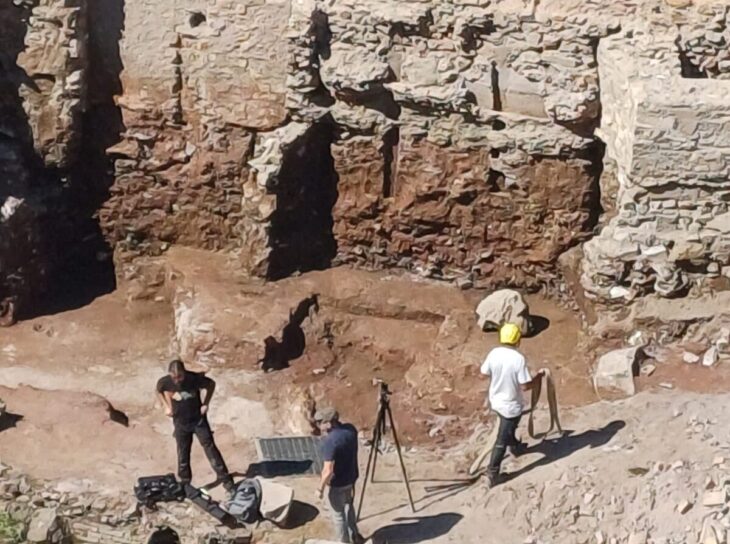
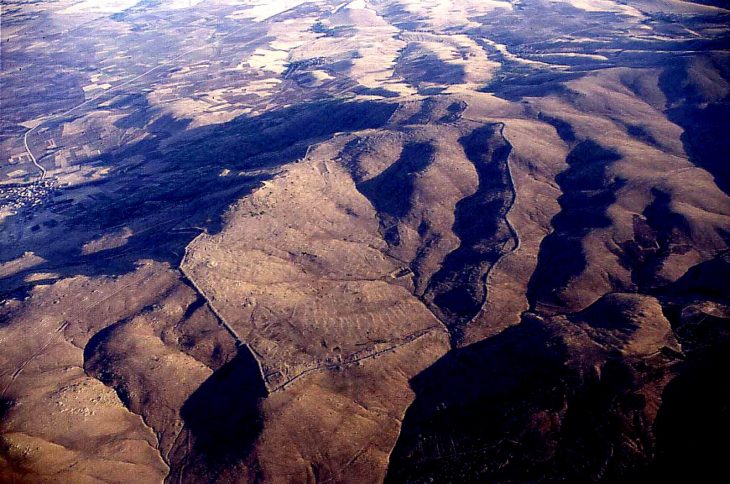
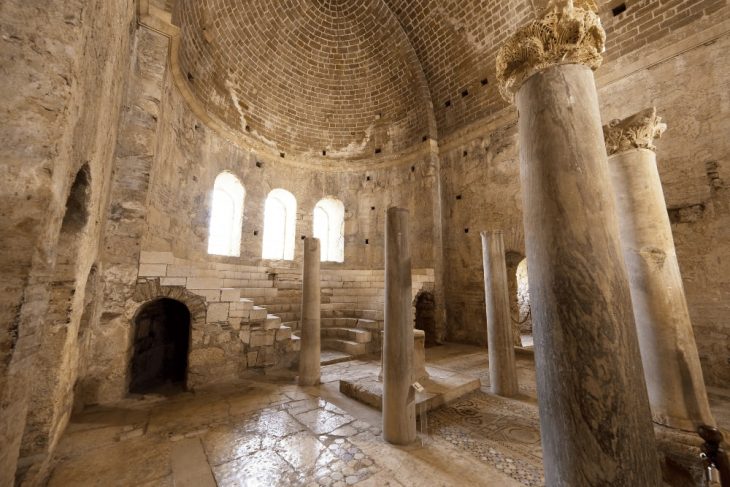
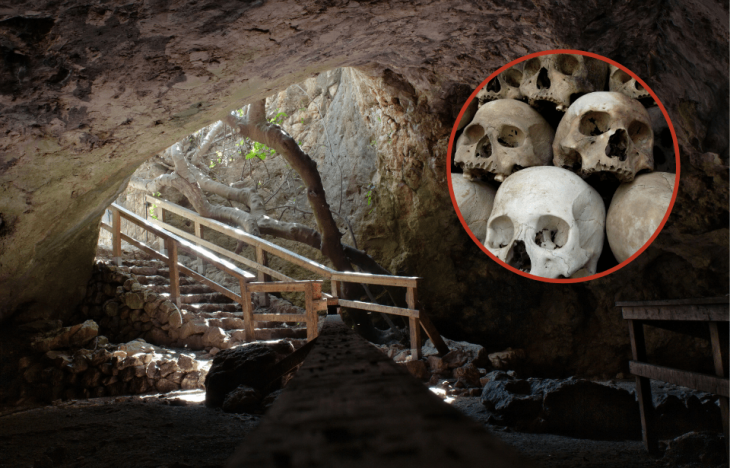
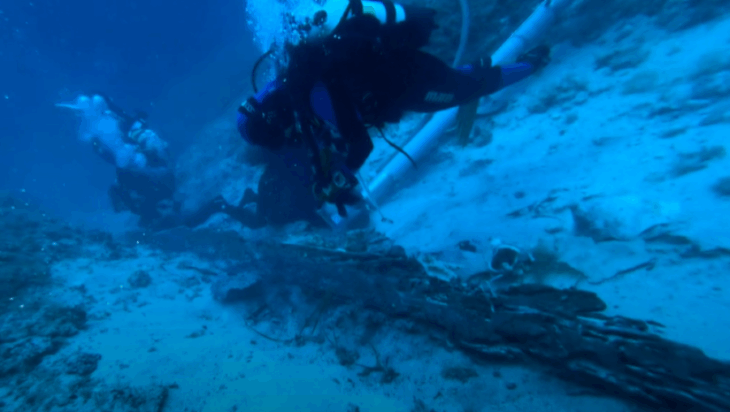
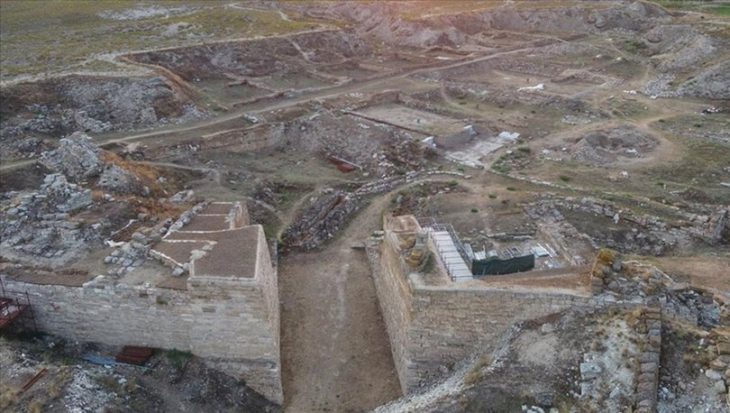
Scientists from Palack University in Olomouc and Charles University in Prague conducted excavations at the well-known Early Iron Age site of Býčí Skála (The Bull Rock Cave)in the Moravian Karst in 2020 and 2021.
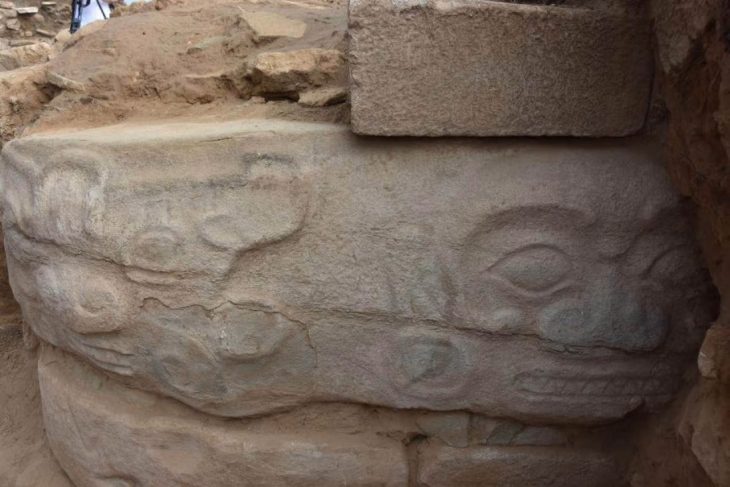
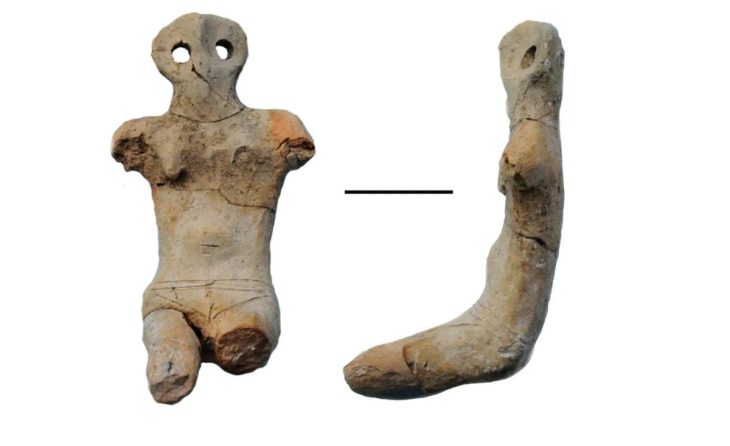
Here one of the most famous archeological discoveries in central Europe was made by Dr. J. Wankel. He discovered one of the most important cult and burial sites of the Hallstatt people (pre-Celtic inhabitants of Europe’s central and Alpine regions). On the floor of this hall were over 40 skeletons, hundreds of jewels made of amber, glass, bronze, gold, and other materials, weapons, metallurgical and smith tools, pottery, and offerings. The majority of them are now on display at Vienna’s Museum of Natural History.
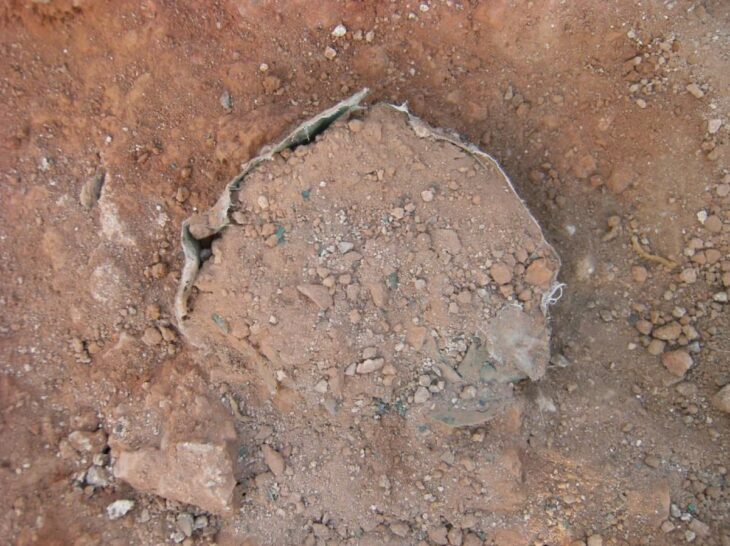
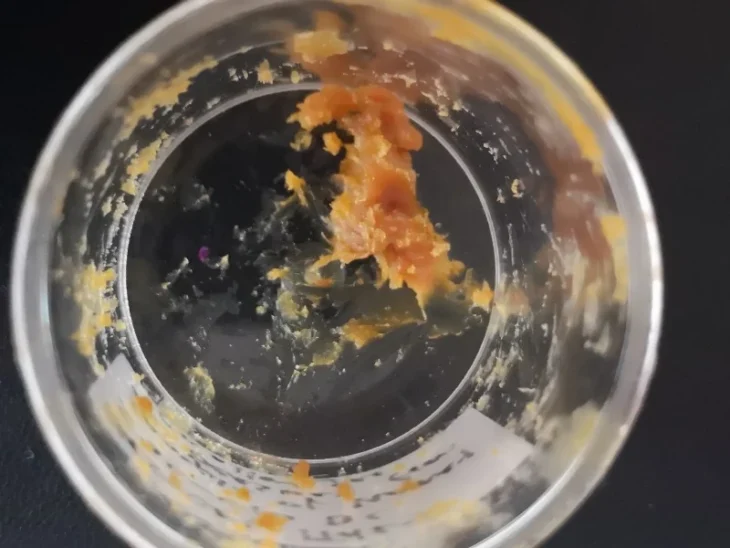
Zuzana Golec Mírová, one of the team members, told Radio Prague that the aim of the excavations was to collect samples of soil for detailed laboratory analysis: “We discovered the remains of burial chambers, which were quite common in the Hallstat period and inside those chambers there was soil, as well as organic and botanical remains. We took samples for chemical analysis, but also for pollen analysis, which turned out to be crucial.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
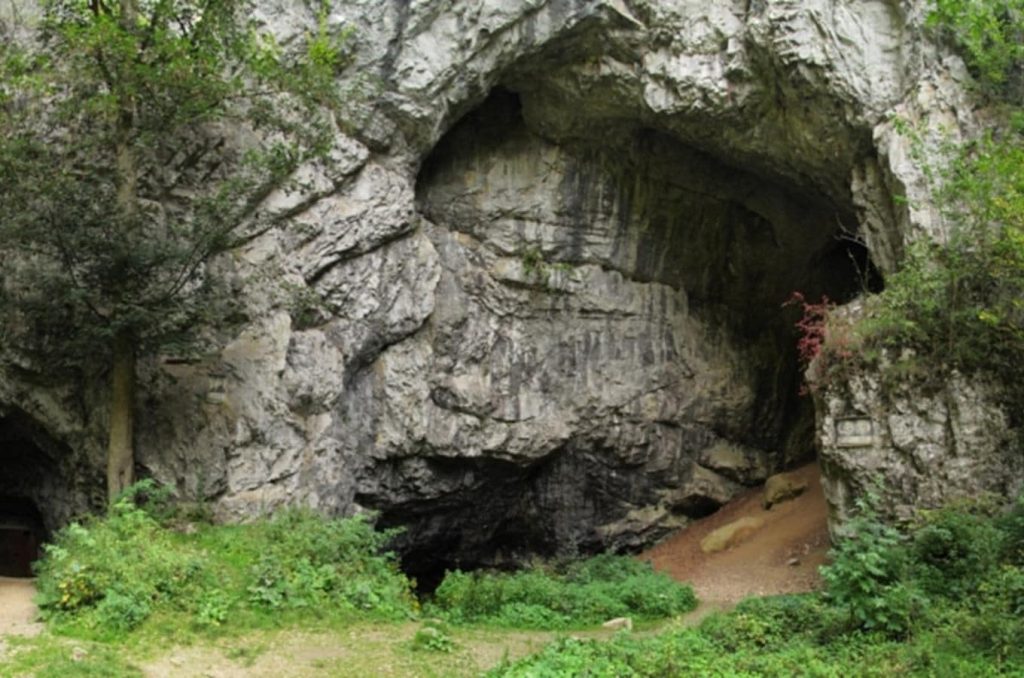

Celts consisted of Iron Age tribes, loosely tied by language and culture, that inhabited much of Western Europe from about the 11th to the first century B.C. We don’t actually know what the Celts called themselves. The name ‘Celts’ is a modern name that is used to describe many tribes of people who lived during the Iron Age.
The Brno Botanical Institute’s pollen analysis revealed traces of millet and various herbs in the samples, which are ingredients commonly used by Celts to make beer.
“Usually in the prehistorical beer there are ingredients used for the taste and ingredients used for preserving the content. There is meadowsweet or filipendula ulmaria, sage or salvia officinalis and mugwort or Artemisia vulgaris, which make the sour bitter taste of the beer of course.
“What was quite unexpected was the discovery of clover, which is quite unusual and isn’t usually used in beer. But then we realised that it’s most common pollen found in the honey. So it is possible that this beer was sweetened with honey.”
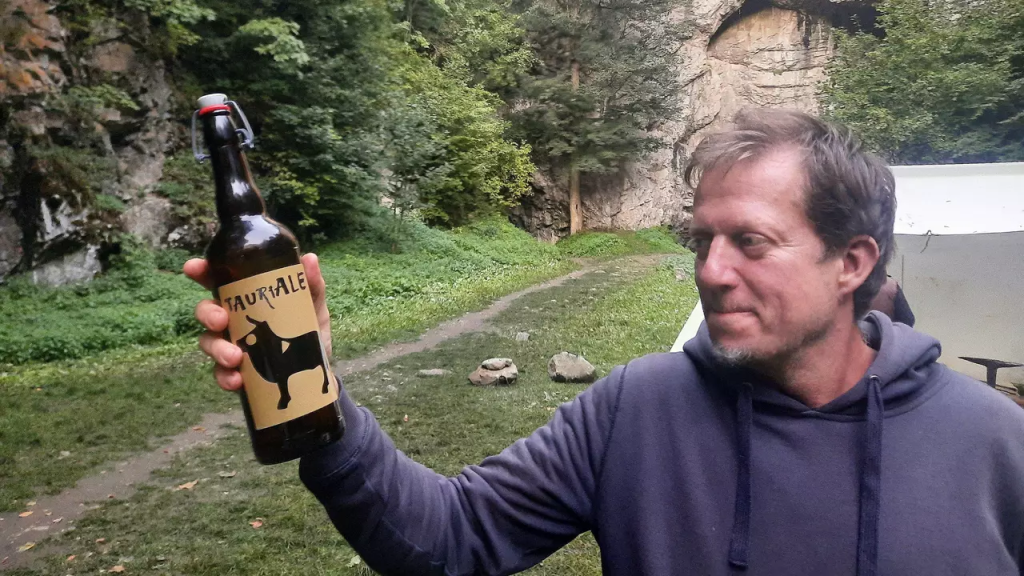

According to Zuzana Golec-Mrová, scientists are convinced that the raw materials for brewing beer were placed in the graves as burial gifts, which was a common practice among the Celts and other ancient peoples.
The first batch of TauriALE – as the scientists have named it – was produced in cooperation with a micro-brewery called Lesia. TauriALE, the name refers to Bull Rock (Taurus is Latin for bull), while the -ale suffix in the name indicates that this is a beer without hops.
And where are the hops? Until the early Middle Ages, it was not used in brewing beer, the bitterness of beer was provided by herbs. These herbal beers are non-hopped ales, not hopped beers.
According to Mrs. Golec Mírová, consumers will probably be surprised by its taste:
“It’s a little bit different from today’s beers because it is not based on hops. The herbs give it a bitter and sour flavour and the taste is similar to gruit, which is a type of hop-free beer.”
Called TauriALE will be produced in the future by Palack University’s Eureka brewery in Olomouc and will be available on special occasions.