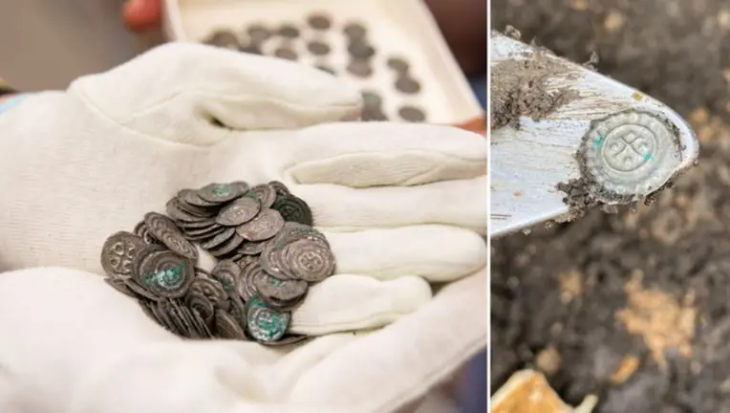
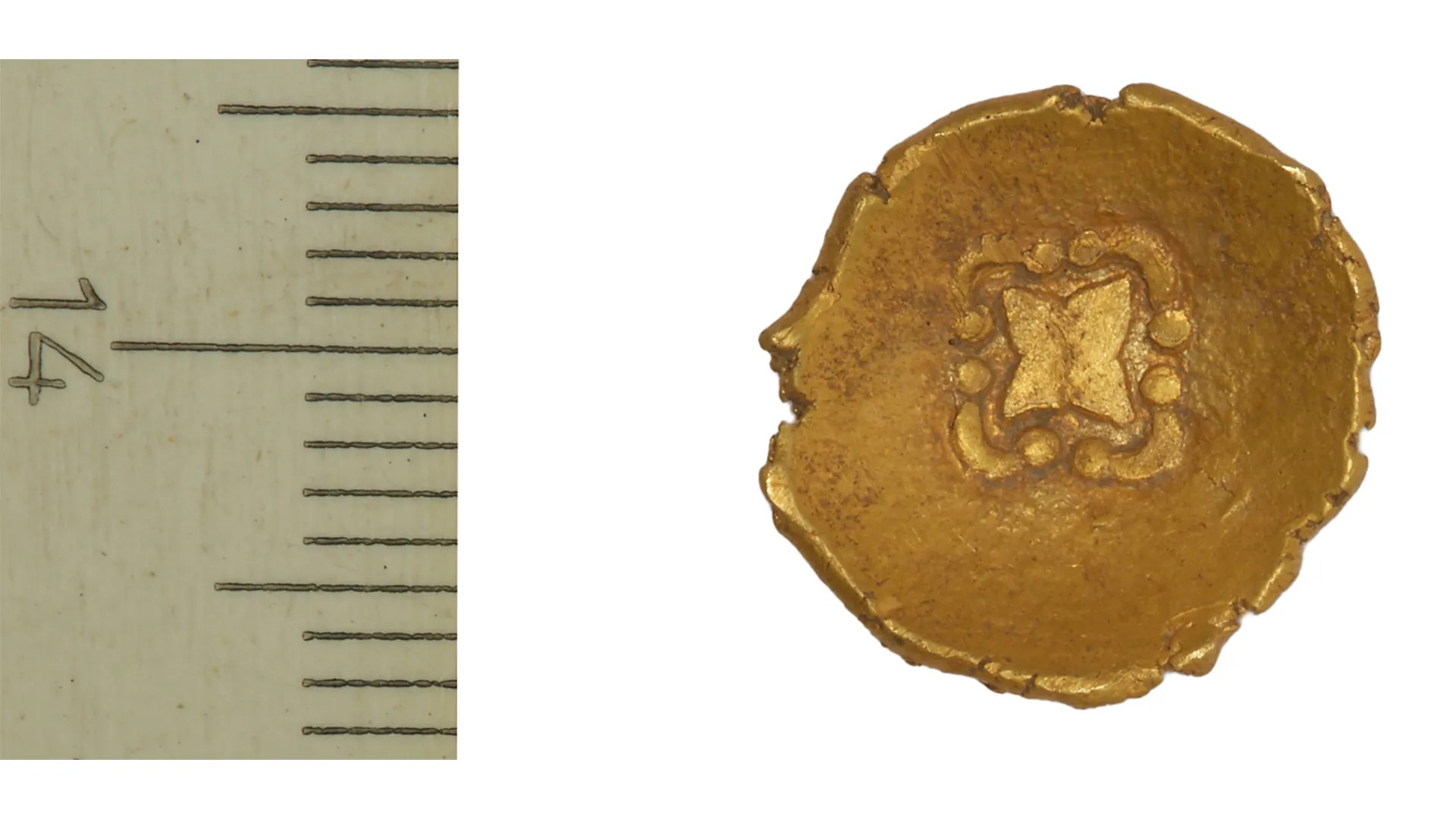
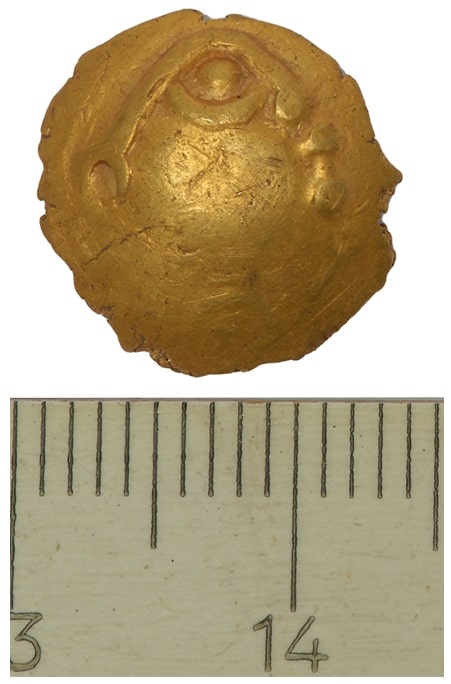
An extremely rare “rainbow cup” Celtic coin dated to the second or first century B.C. has been discovered next to the Lech River in southeastern Germany. According to legend, “rainbow cups” are gold drops that appear to fall to Earth at the end of rainbows.
The coin features a rare design of a four-pointed star surrounded by arches on one side. There are only four known examples of rainbow cups with these markings (including this one), and this example is the only one with a verified find location.
The finder, a collaborator with state archaeological officials, discovered the coin this spring about 45 miles (70 kilometers) west of Munich on the Lech River in the southern state of Bavaria.
Bernward Ziegaustold Live Science in an email, a senior curator in the State Archaeological Collection’s numismatic department: It’s unknown how the 0.07-ounce (1.9 grams) coin ended up there, but the spot isn’t far from an ancient road.
This road went from what is now Trento in northern Italy and later became known as the Roman road Via Claudia Augusta that went across the Alps, Ziegaus said.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

“Perhaps the coin was accidentally lost along the way,” he said.
The “heads” side of the 0.5-inch-wide (13 millimeters) coin “shows a stylized human head with a large eye,” with the nose and lips depicted as dots, Ziegaus said. A metal analysis revealed that the coin is 77% gold, 18% silver and 5% copper.
There are only three known rainbow cups with the star-and-arch motif. “The interpretation of the motive is difficult,” Ziegaus said. “The star is perhaps a symbol for the four cardinal points, the arches are to be understood as signs for the horizon and the rising and setting of the moon.
Bavaria’s oldest Celtic coins date to the third century B.C., but the Roman conquest of the region in 15 B.C. led to the end of Celtic minting. After that, Roman coins became the main currency in the region.
The finder, Michael Schwaiger, was offered 6,000 for both coins, but he refused, as well he should. The landowner signed his rights over to the finder and Schwaiger donated both coins to the State Archaeological Collection.
The other three known rainbow bowls are in private hands, and state officials plan to exhibit the Denklingen coins in a new permanent exhibition at the State Archaeological Collection in Munich after the renovation of the facility is complete in March 2024.
Due to concerns about their ability to be adequately secured following the theft of the Celtic gold coin hoard from the museum in Manching, rainbow bowls are unlikely to be put on display at a local museum in Denklingen.
Image credit: © Photo Stefanie Friedrich, Archaeological State Collection (Munich)