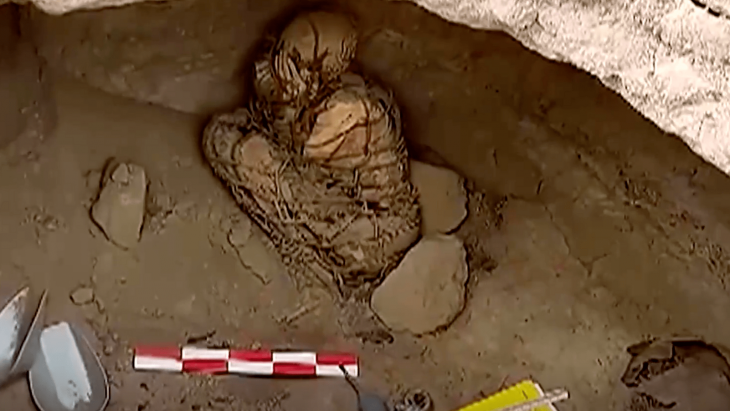
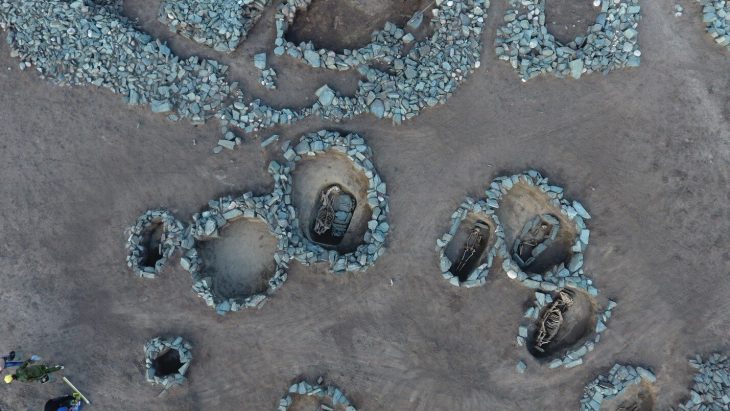
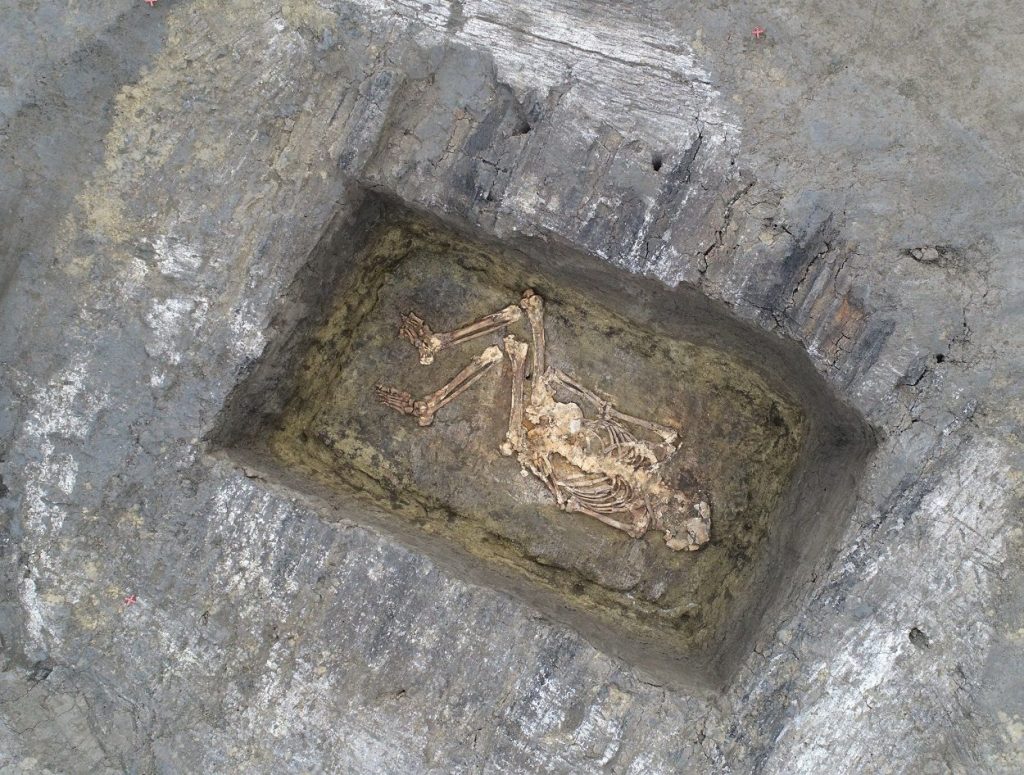
Polish archaeologists excavating two barrow mounds in Vojvodina, in the northern part of the Republic of Serbia, have uncovered the burials of two big men covered with red ochre dye.
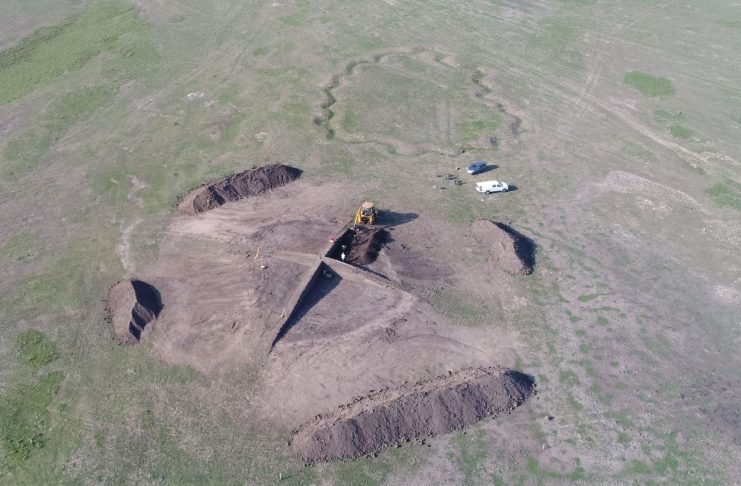
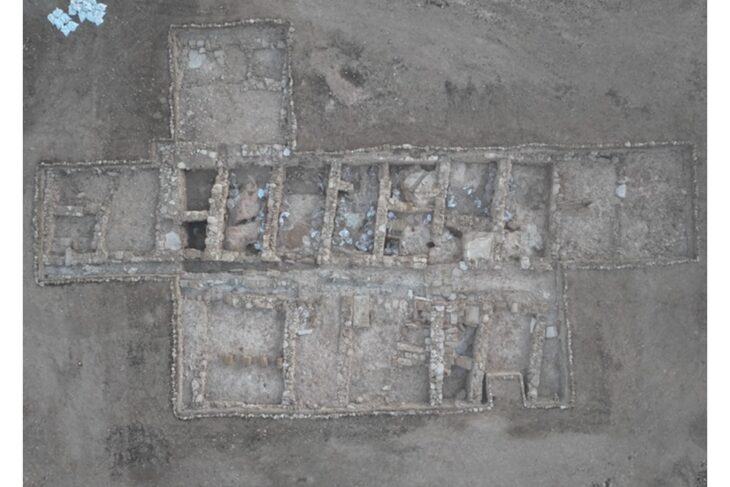
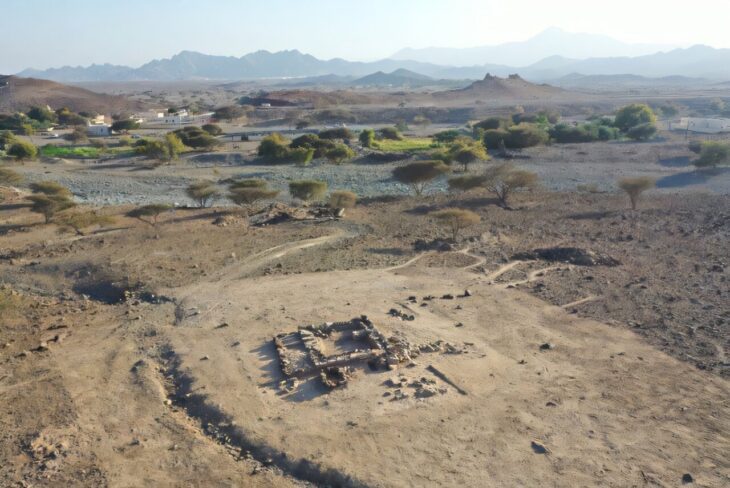
The research was carried out in two large mounds 40 m in diameter and 3-4 m high in the Šajkaška region (Vojvodina autonomous region) at the westernmost tip of the Eurasian steppe. In each had two large, wooden burial chambers.
Both burial mounds were built in two phases. In the beginning – when the first deceased were deposited, it was much smaller, about 3-2.9 thousand BC. When the second grave was excavated about 100-200 years later, their diameter and height increased significantly.
The unusual height of those buried, suggests that the deceased originally came from the steppes of southern Russia or Ukraine, who found their way to Vojvodina around 5,000 years ago as part of a nomadic community.

The burials were discovered by the Institute of Archaeology and Ethnology of the Polish Academy of Sciences (IAEPAN) in two large barrow mounds first excavated between 2016-2018, of which the results of the study have only now been published.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
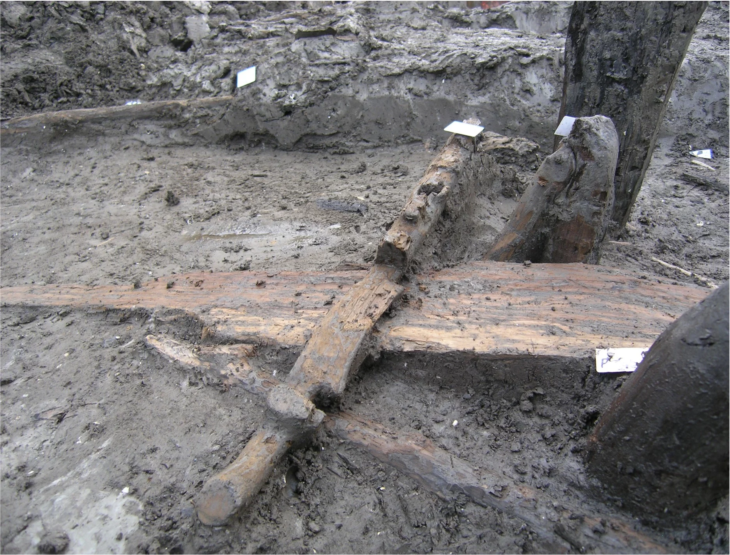
Dr. Piotr Włodarczak from IAEPAN who led the excavations noted the lack of grave goods, but suggests that the ochre dye was seen as a ‘sacred colour’ for important funeral rituals.
Ochre is a natural clay earth pigment, a mixture of ferric oxide and varying amounts of clay and sand. When mixed with a large amount of hematite, or dehydrated iron oxide it creates a pigment with a reddish tint.
“The ritual use of ochre and the placement of individual burials in large mounds suggests that they are associated with communities inhabiting the Eastern European steppe areas ” said Włodarczak.
Similarities can be found with the Yamnaya culture, a late Copper Age to early Bronze Age archaeological culture, who would bury their dead covered in Ochre in tumuli (kurgans) containing simple pit chambers.
The project was funded by the National Science Center. It was conducted in cooperation with the Vojvodina Museum in Novi Sad.
Cover Photo: Dr. Piotr Włodarczak