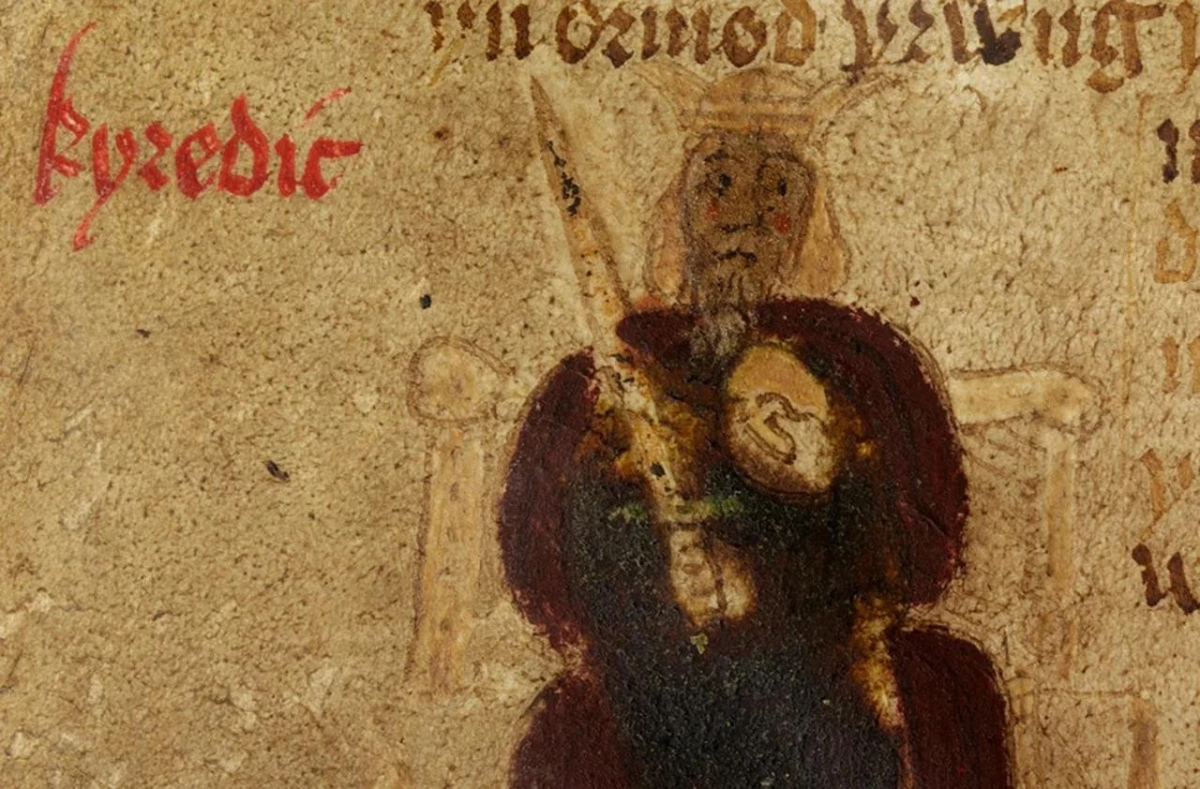
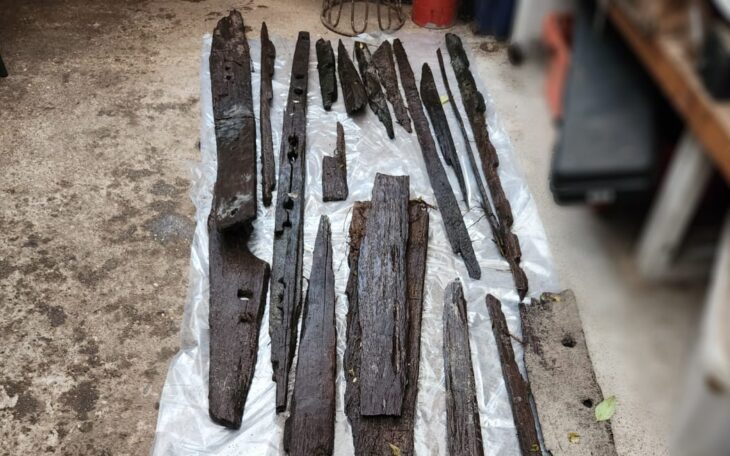
The possible final resting place of Cerdic, the enigmatic founder of the Kingdom of Wessex and a key figure in the history of post-Roman Britain, has come to light more than a thousand years after he was named in an ancient royal charter.
An enigmatic figure from the same era as the legendary King Arthur in post-Roman British history, Cerdic rose to prominence as a warlord in a series of bloody battles in Hampshire during the sixth century. It is thought Cerdic reigned from around 519 to 534 AD.
Cerdic is believed to be the first king of Wessex, however, his existence has been widely disputed. Historical writer Paul Harper, who carried out research on a Dark Age king for his book, believes the outskirts of Andover could be the potential burial site of the mysterious ruler.
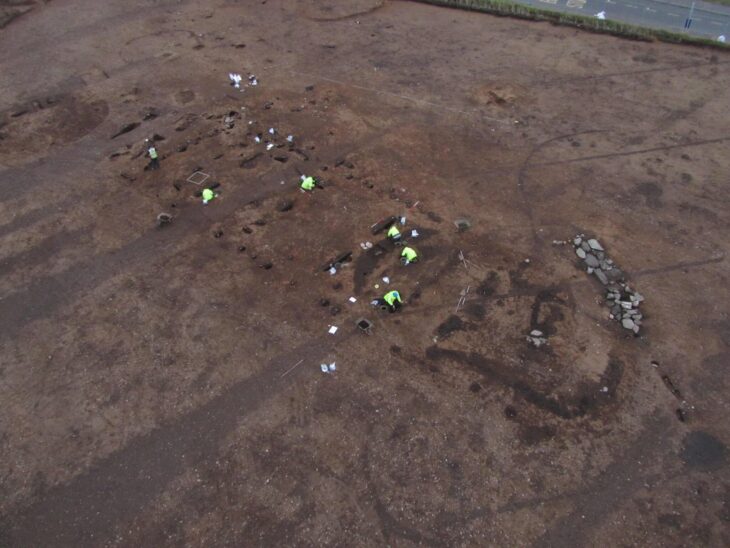
Inspired by the research of academic George Grundy, author Paul Harper led an investigation that uncovered a burial mound believed to correspond to Cerdic’s Barrow, mentioned in a 10th-century charter granted by King Edward the Elder to Winchester Cathedral. The charter delineated the boundary of land, referencing ‘Ceardices Beorg’ or ‘Cerdic’s Barrow,’ within what is now St Mary Bourne parish in Hampshire.
Though the tumulus has since been plowed over, aerial photography from the 1960s and 70s revealed traces of a massive barrow measuring 72 feet (21.9 meters) in diameter and standing up to 12 feet (3.6 meters) tall!
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
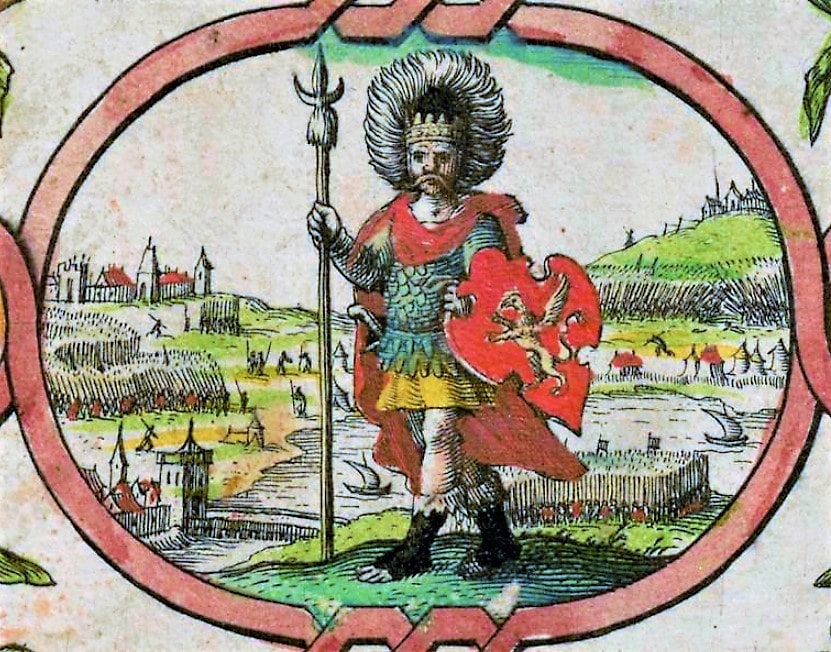

Cerdic is thought to have been an Anglo-Saxon invader, but his Brittonic name and his descendants’ names point to a more nuanced story that may involve interactions between Anglo-Saxon and native British cultures. Many scholars argue that his rule likely began later than stated in the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle.
“The exciting discovery has brought the story of Cerdic from a lost period of British history to life,” Mr Harper said. “This could be overwhelming proof that Cerdic was not just a product of fantasy in the chaotic aftermath of post-Roman Britain but a real warlord who forged a powerful realm which evolved into the nation of England. Barring King Arthur, no other figure from the early medieval period achieved such legendary status.”
Tracing the locations of notable locations mentioned in the ancient charter, such as a Willow Grove, a Barrow of the Ash Tree, and a Roman Road, allowed the investigation to determine the location of the barrow near Andover in Hampshire. Cerdic is thought to have been buried in a freshly built mound or a repurposed Bronze Age barrow, as was customary in the early Anglo-Saxon era.
According to the author, the placement of Cerdic’s Barrow was a deliberate statement of power, strategically located near ancient roads and a massive Offa’s Dyke style ditch, serving as a warning to his rivals. Additionally, references to wooded enclosures associated with deer hunting in the charter suggest sentimental value for Cerdic in this corner of Hampshire.
In his new book, Harper describes his extensive research into Cerdic’s rise from the chaos that followed the fall of the Western Roman Empire. As a result of his protection of civilians and territorial conflicts with Anglo-Saxon and Romano-British kingdoms, he ascended to power with the Gewisse. Cerdic established an area that would influence British history, despite having to contend with hitherto unheard-of difficulties like pandemics and natural disasters.
In the future, Harper hopes to learn more about Cerdic’s legacy through archaeological surveys conducted on the site with landowner permission.
Paul Harper’s new book, CERDIC: Mysterious Dark Age King Who Founded England, is available on Amazon and goes into great detail about Cerdic.
Cover Photo: Image and name of Cerdic, from the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle. Photo: Paul Harper