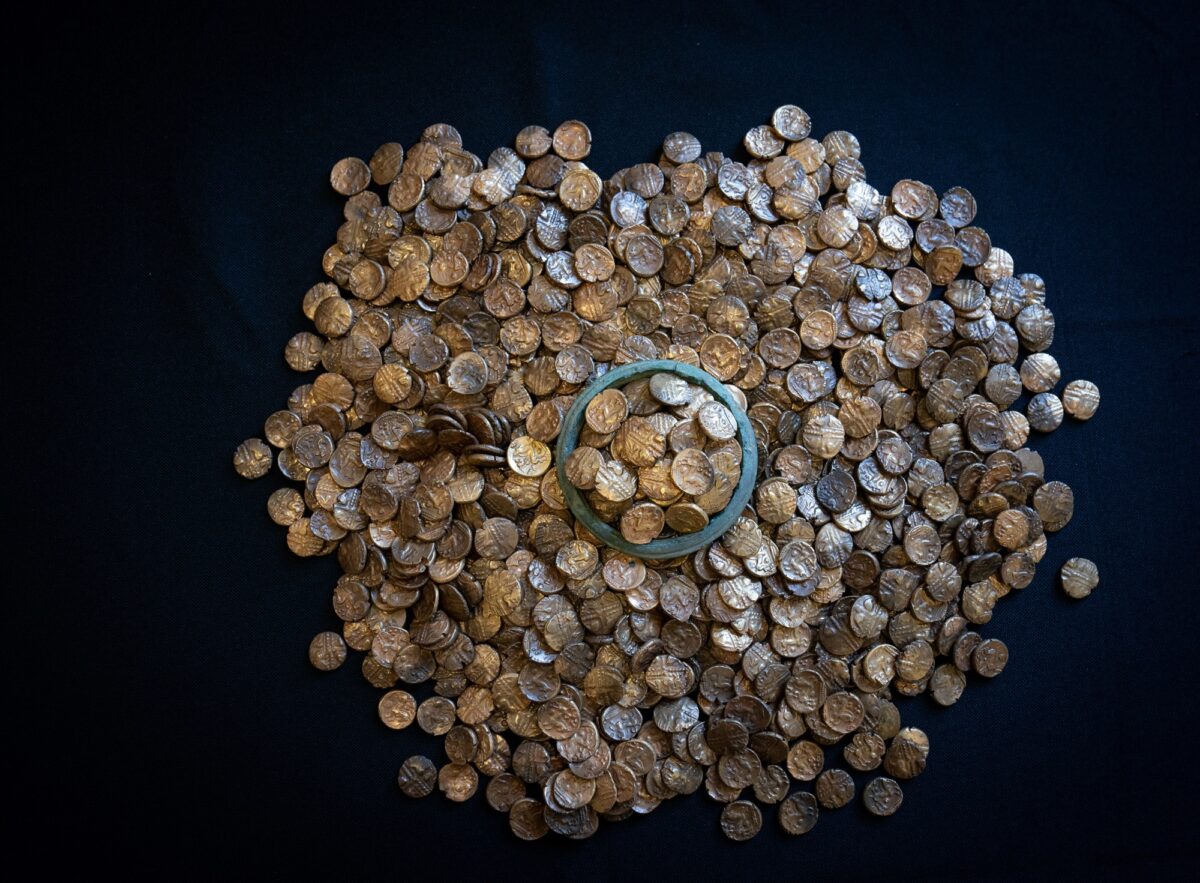
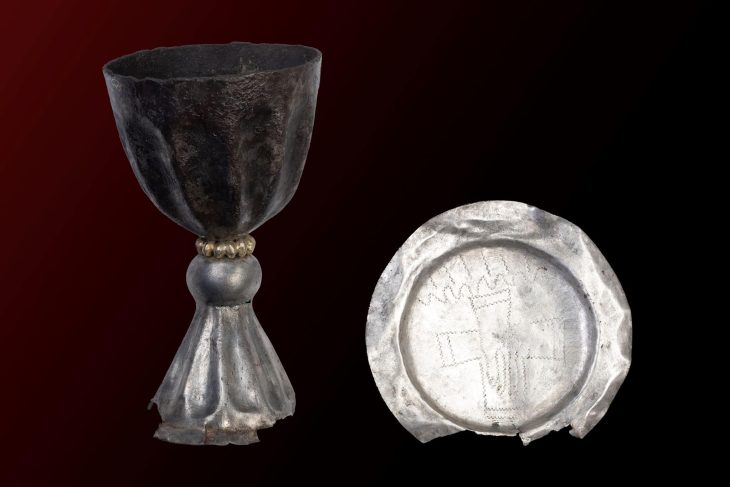
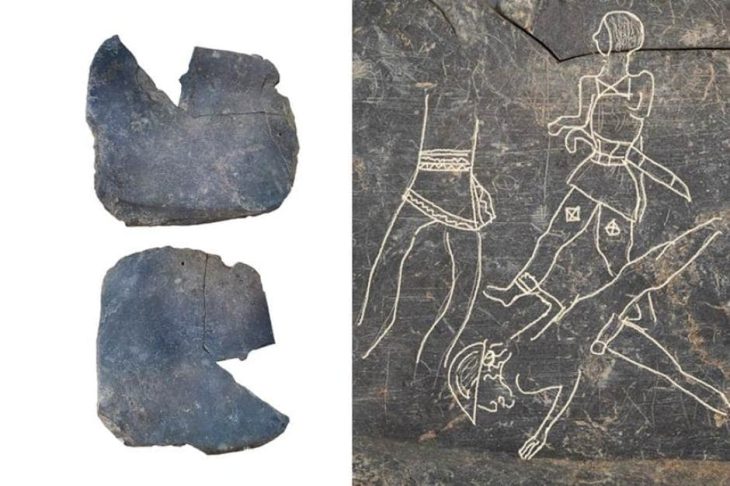
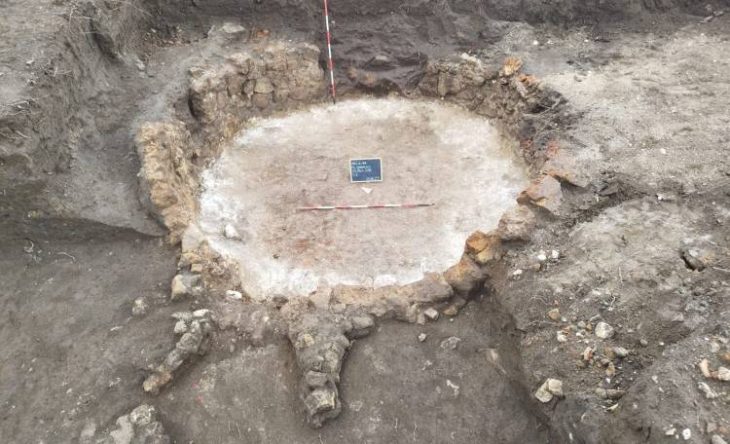
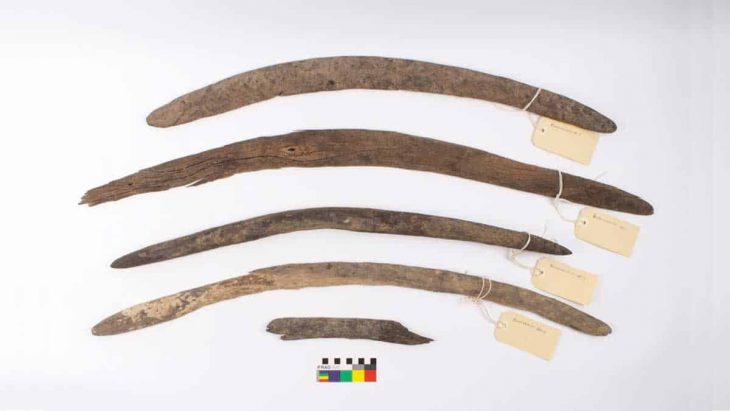
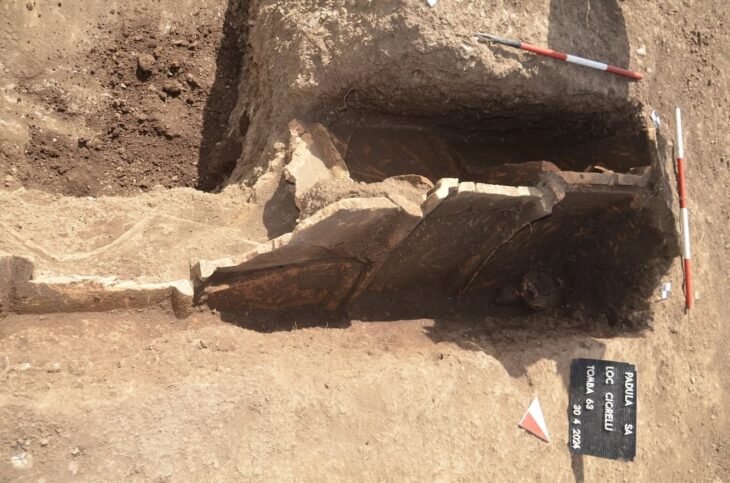
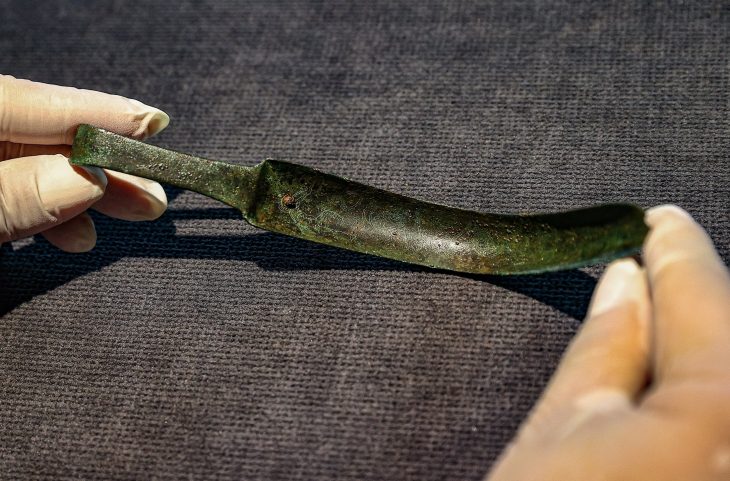
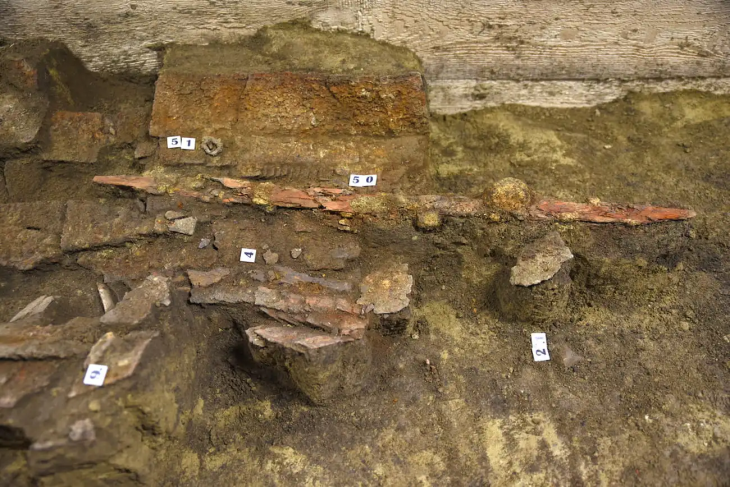
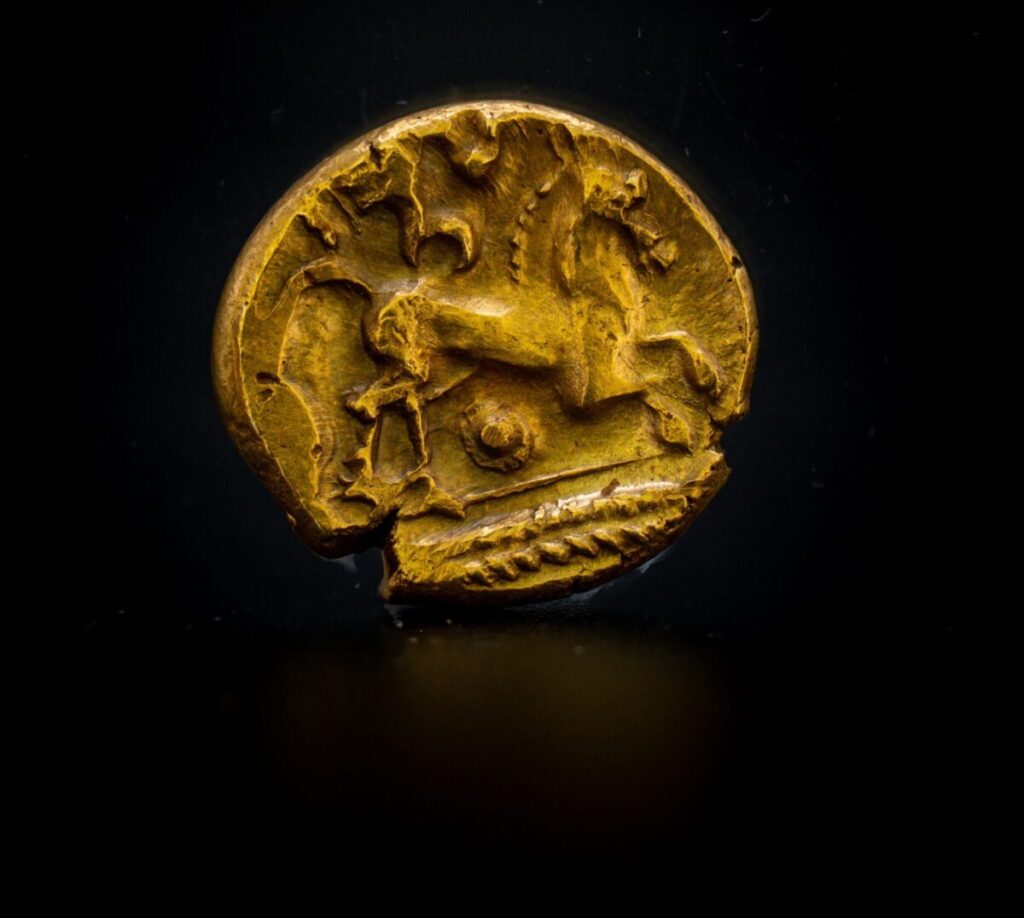
In a stunning revelation, British authorities have recently announced the discovery of an unparalleled Iron Age coin hoard, a singular find detailed in a statement from Chelmsford City Life. This extraordinary collection, known as the Great Baddow Hoard, represents a momentous unearthing in the annals of British archaeology.
This “one-of-a-kind” treasure trove offers unprecedented insights into a pivotal era in British history, a time when indigenous tribes transitioned from importing Celtic coinage to minting their own regional currencies. The period also coincided with significant upheaval, notably Julius Caesar‘s second invasion of Britain in 54 BC.
Archaeologists believe the sheer volume of the gold coins hints at potential conflict between the neighboring Trinovantes and Catuvellauni tribes, suggesting the hoard may have even been intended as a tribute payment to Julius Caesar himself. Museum of Chelmsford Curator Claire Willetts emphasizes the hoard’s significance, stating it provides the first archaeological evidence corroborating Roman accounts of aggression between these Iron Age groups. The discovery within traditionally Trinovantian territory could indicate westward tribal movements, aligning with the turmoil documented during Caesar’s campaigns.

Chelmsford City Councillor Jennie Lardge highlights the hoard’s local importance: “Not a lot is known about Chelmsford’s Iron Age history, and the Great Baddow Hoard helps us fill some of the gaps in the archaeological record of this period.” The acquisition of the hoard by the Museum of Chelmsford was made possible through a substantial £250,000 grant from The National Lottery Heritage Fund, along with contributions from local organizations. This funding will not only support the display but also facilitate further research and community engagement projects.
While the discovery itself is a momentous occasion, it’s also underscored by a cautionary tale regarding responsible metal detecting. The detectorist who found the hoard on private land had not obtained prior permission and subsequently failed to declare the find according to the Treasure Act 1996. This led to a conviction for attempted theft and failure to notify the coroner, resulting in the finder receiving no reward, which was instead granted solely to the landowner.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Despite the circumstances of its discovery, the Great Baddow Hoard remains a find of national significance. Lori Rogerson, the Essex Finds Liaison Officer, anticipates the public’s reaction: “In the coming years, visitors seeing the hoard at the Museum of Chelmsford will be in awe at its size and gold content, and they’ll be led to ask questions such as, ‘Who owned such a large stash of precious coins?’ and, ‘Why was it put in the ground, never to be returned to?'”
The hoard is scheduled to go on temporary display in the summer of 2026, followed by a permanent exhibition from spring 2027, offering a unique opportunity for locals and visitors alike to connect with a fascinating chapter of Britain’s ancient past. This extraordinary collection promises to shed new light on the complexities of Iron Age Britain and the impact of Roman influence.
Cover Image Credit: The Great Baddow Hoard. Image credit: Fountains Media/Museum of Chelmsford