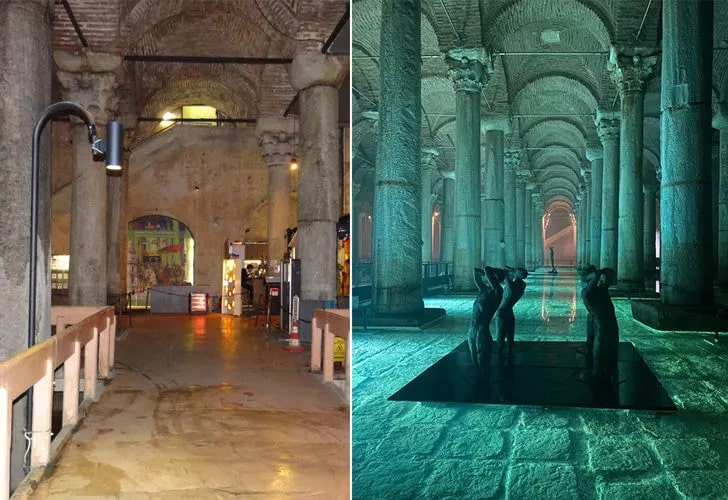
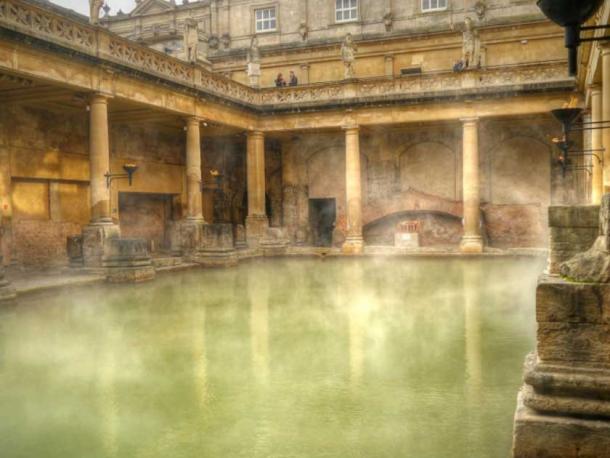
Archeologists in Carlisle, England, discovered a treasure trove at the bottom of the drain system of an ancient Roman bathhouse near Hadrian’s Wall.
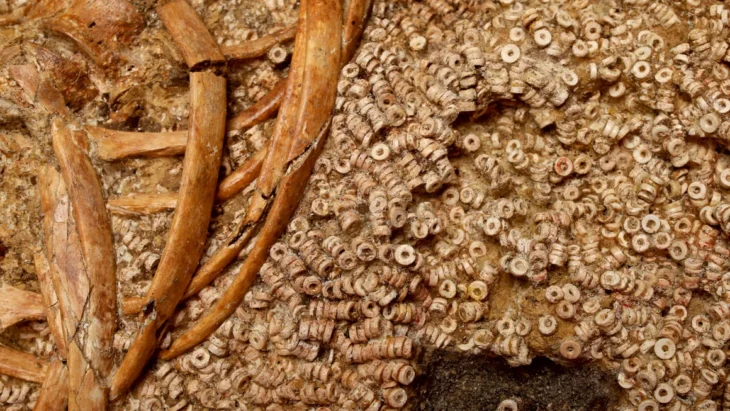
Approximately 30 intricately carved semiprecious stones were discovered. The stones, known as intaglios, had slipped down the drains of the pools and saunas two millennia ago.
Around 5,000 years ago, the tradition of carving intaglios began in Mesopotamia. They were frequently used to “sign” documents by pressing them into soft clay. Intaglios spread throughout the ancient world over millennia, eventually becoming fashionable items for the wealthy. According to Cicero, a Roman statesman, and author, some Romans wore portraits of their favorite philosophers on their rings.
The stones had fallen out of their ring setting, their glue probably weakened in the steam baths. Losing them would have been painful as they were engraved gems known as intaglios. Although only a few millimeters in diameter, they bear images whose exceptional craftsmanship suggests they would have been expensive items in their time – the late 2nd or 3rd century.

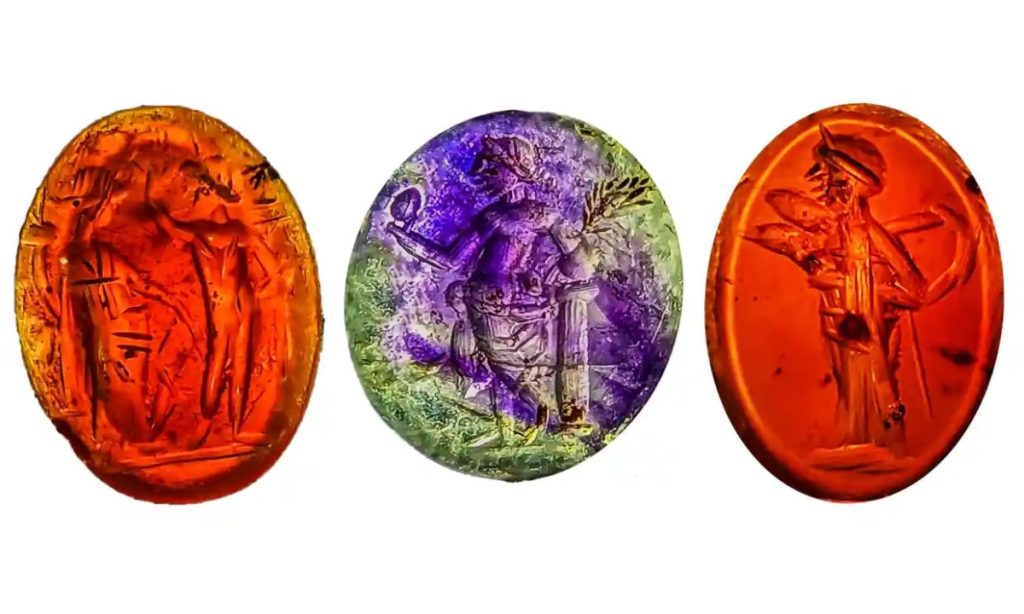
A bather lost an amethyst depicting Venus holding either a flower or a mirror. Another lost a reddish-brown jasper with a satyr seated on rocks by a sacred pillar.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Frank Giecco, an expert on Roman Britain who is leading the excavations at the bathhouse, was amazed by the collection: “It’s incredible,” he said. “It captured everyone’s imagination. They just fell out of the rings of the people using the baths. They were set with plant glue and fell out of the ring settings in the hot and sweaty bathhouse.”
“Some of the intaglios are minuscule, around 5mm; 16mm is the largest intaglio. The craftsmanship to engrave such tiny things is incredible,” Giecco said.

The drain discoveries also include more than 40 women’s hairpins and 35 glass beads, probably from a necklace.
The bathhouse adjoined the main Roman fort on Hadrian’s Wall, the empire’s northern border, which housed an elite cavalry unit and had ties to the imperial court. Excavations will continue next year.
Cover Photo: A selection of the intaglios is found at the Carlisle Cricket Club site. Photo: Anna Giecco/ Wardell Armstrong