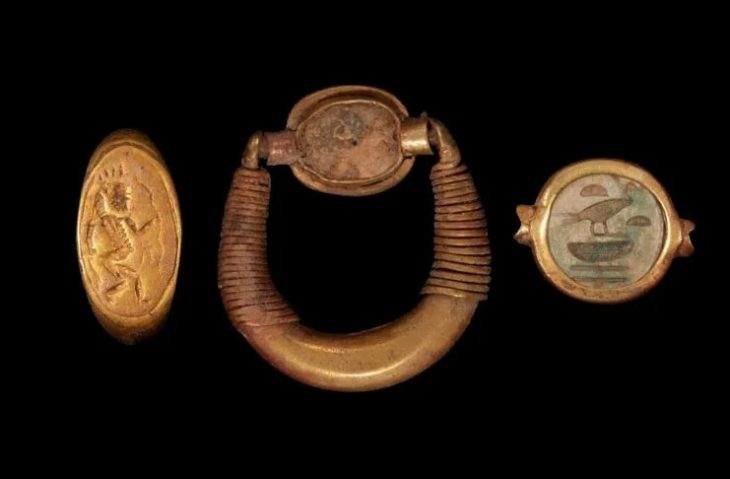
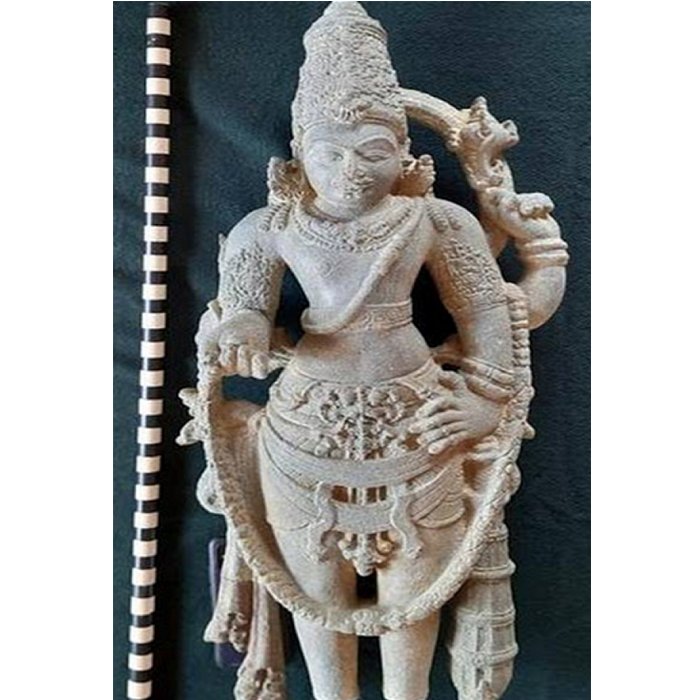
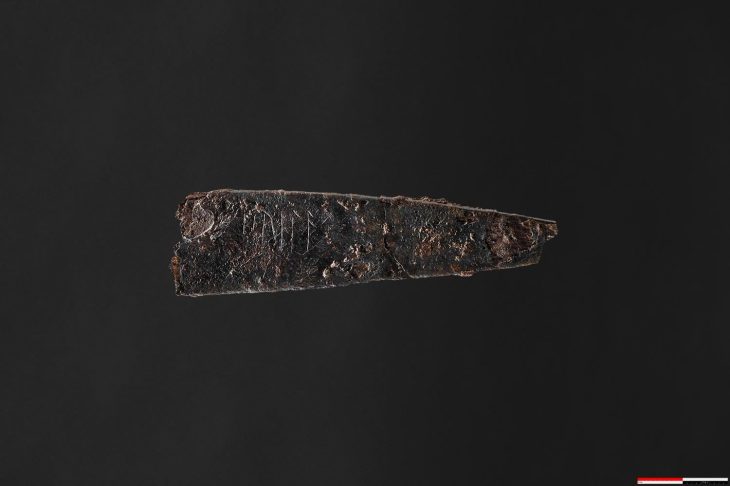
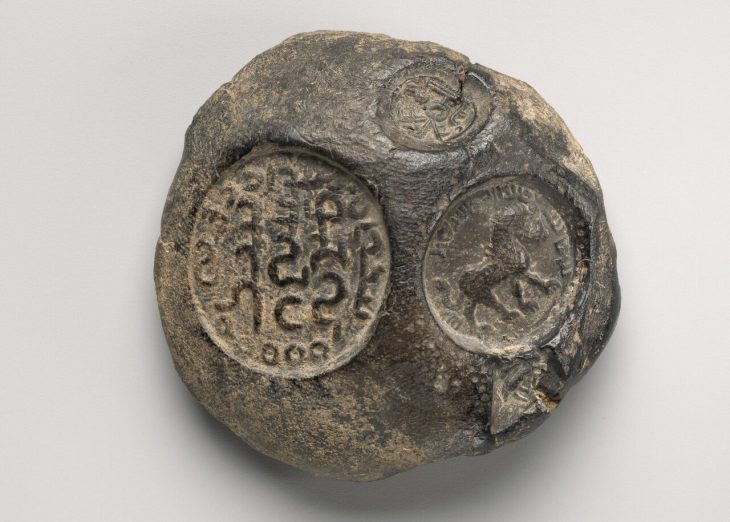
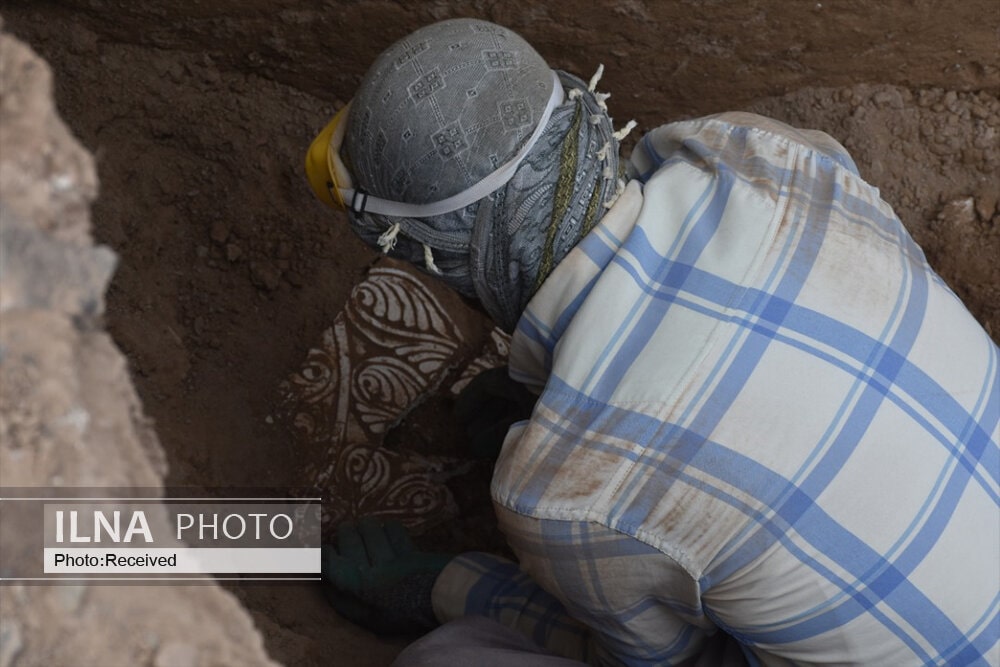
Archaeologists have unearthed ruins of what they believe to be the third-greatest fire temple in ancient Iran during the Sassanid era.
The Sassanid era (224-651 CE) was the longest-lived Persian royal dynasty, ruling for as long as 400 years.
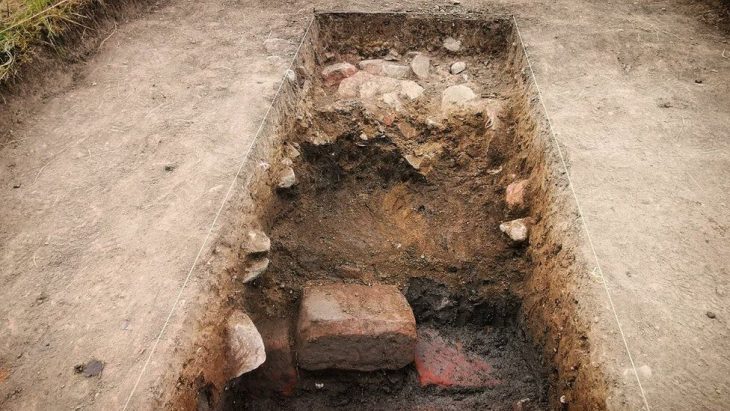
The fifth season of excavation of an ongoing archaeological survey in a valley near the village of Robat-e Sefid/Bazeh Hur in northeastern Iran continues under the headed of archaeologist Meysam Labbaf-Khaniki.
“We have probably discovered the third greatest fire temple that existed in ancient Iran,” archaeologist Meysam Labbaf-Khaniki said on Wednesday, according to ILNA.
“During this archaeological season, we have gathered considerable evidence such as engraved plasterwork and inscriptions that suggest the ruins are related to an important fire temple,” said the archaeologist, as cited by Tehran Times.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Inscriptions and fragments with Pahlavi characters should first be sorted and categorized so that linguists and cultural heritage professionals may read (and understand) them, he stated.
These fresh discoveries are expected to open a new chapter in the history of Iranian arts during the Sassanid epoch, the archaeologist said.
Exquisite stuccoworks embellish capital columns that support the main hall of the fire temple, he said.
The cult of sacred fire forms the basis of Zoroastrianism. In the Zoroastrian fire temples, the fire was not worshiped at all. Still, because of its dynamism, warmth, protection role, and the nature of transformation, it is commonly mentioned as an aspect of divine power.

However, the outside façade of a Zoroastrian fire temple is nearly usually purposefully unassuming and devoid of ornamentation. This may reflect historic tradition (supported by the prosaic nature of fire temple technical terms ) that the primary aim of a fire temple is to house a holy fire, rather than to glorify what is otherwise just a structure.
The basic structure of present-day fire temples is always the same. There are no indigenous sources older than the 19th century that describe an Iranian fire temple (the 9th-century theologian Manushchir observed that they had a standard floor plan, but what this might have been is unknown), and it is possible that the temples there today have features that are original of Indian origin.
At the entrance to a fire temple, one comes into a large space or hall where congregation (also non-religious) or special ceremonies may take place. Off to the side of this (or sometimes a floor level up or down) the devotee enters an anteroom smaller than the hall he/she has just passed through. Connected to this anteroom, or enclosed within it, but not visible from the hall, is the innermost sanctum (in Zoroastrian terminology, the atashgah, literally ‘place of the fire in which the actual fire-altar stands).
The Zoroastrian place of worship is called fire temple because they perform their prayers in the presence of fire. In ancient Iran, the head of the family always kept the fire burning, so keeping the fire lit became a tradition. Keeping the flames lit was a divine symbol for worship in Iranian fire temples.