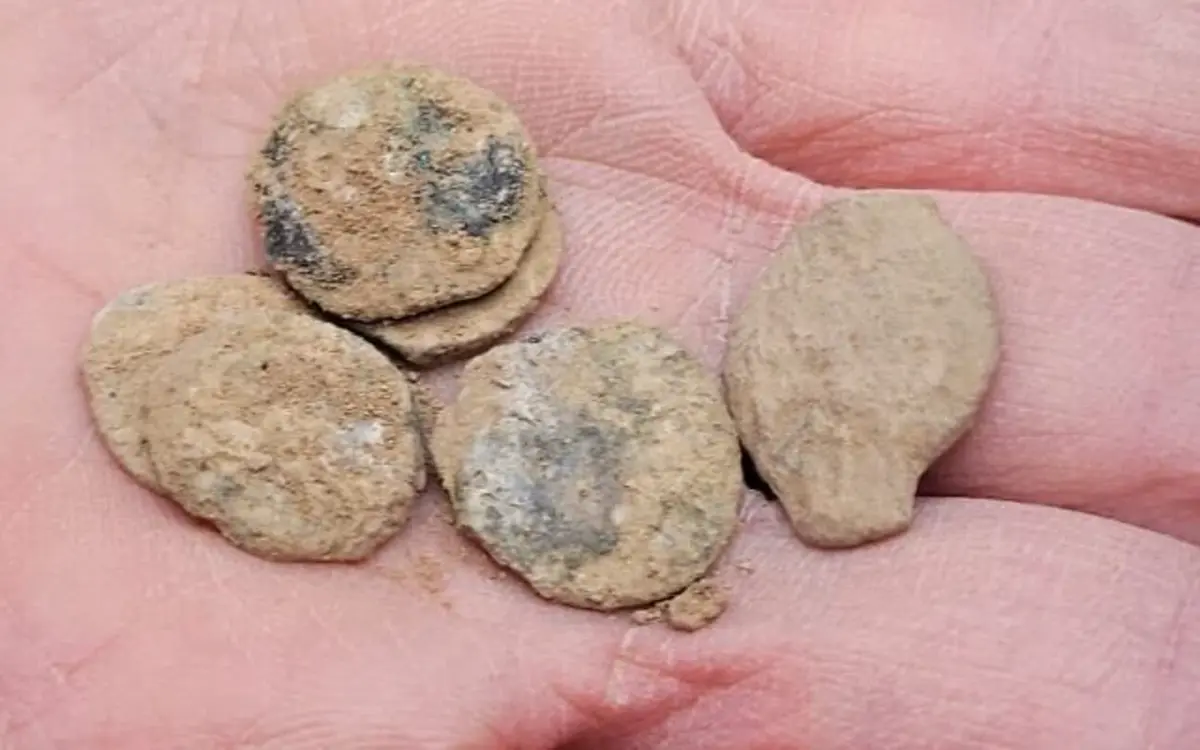
A team of archaeologists from the University of Haifa discovered a rare hoard of approximately 160 coins during an excavation in the Jordan Valley, dating back to the Hasmonean period (the reign of Alexander Yannai (104-76 BCE)).
The discovery was made by a University of Haifa team led by Dr. Shay Bar and Dr. Yoav Farhi from the Zinman Institute of Archaeology.
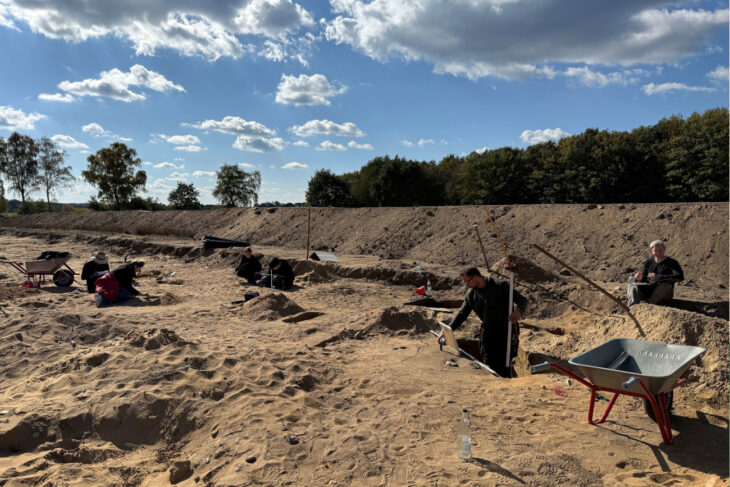
The rare coins from the Hasmonean period were uncovered in an archaeological dig in the Jordan Valley in what is thought to have been a roadside station, on what was then a main road along Nahal Tirzah that ascended to the Alexandrion Fortress, also known as Sarbata, north of Jericho in what is now the West Bank.
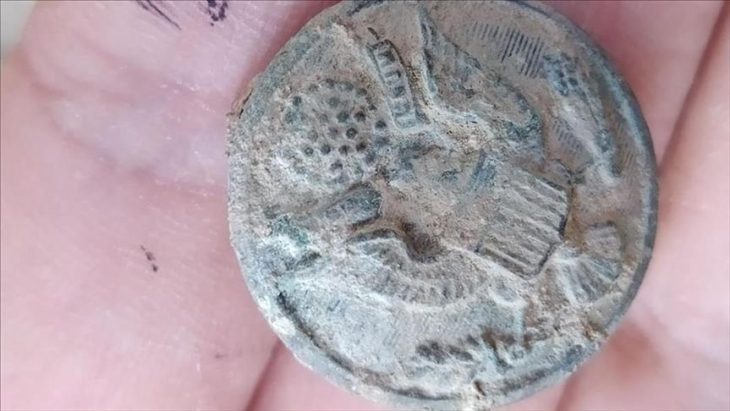
The treasure that was discovered included about 160 coins, all of them belonging to King Alexander Yanai, whose Hebrew name was Jonathan. Alexander Yanai. He reigned in the years 104-76 BCE. He was the son of Yochanan Hyrcanus, the grandson of Shimon the Hasmonean (brother of Judah the Maccabee), and the great-grandson of Mattathias Miriam Ness—the rebellion against the forces of Antiochus IV Epiphanes. The famous revolt, which broke out in 167 BCE, Among other things, it led to the purification of the Temple and the establishment of the Hanukkah holiday in the Jewish tradition.
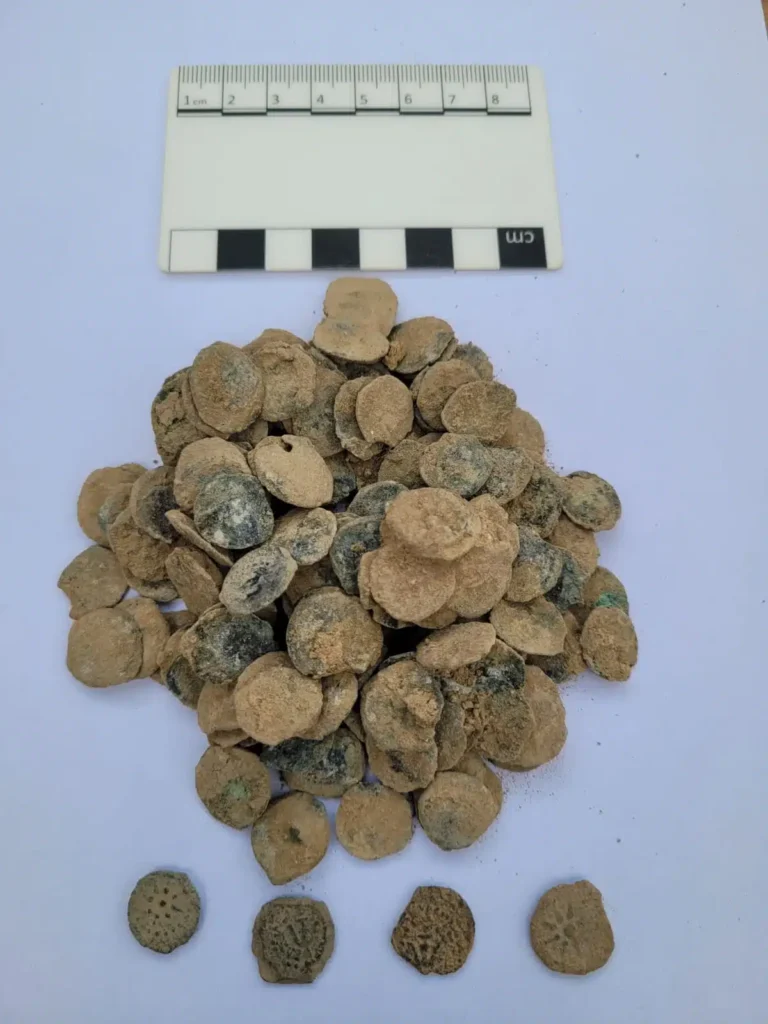

The coins, all minted in 80/79 BCE during the 25th year of Yannai’s reign, bear distinctive markings. Each features an eight-pointed star with Aramaic text reading “King Alexander Year 25” on one side, while the reverse displays an anchor surrounded by Greek text identifying it as “[coin] of King Alexander.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
In archaeological research, such extensive coin collections are uncommon. According to Dr. Bar, the coins were probably concealed behind or inside a wall and wrapped in a leather sack or other organic material that eventually decomposed.
The discovery site revealed more than just the coin cache. Archaeologists found a previously unknown road station along the route to Herodium fortress (Alexandrium), complete with a ritual bath (mikveh), water reservoir, and several other structures along the Tirzah Valley banks.
“It is really a rare moment to discover so many coins,” Dr. Bar stated. He added that these findings indicate the important role of this place. The fortress, which overlooks the Jordan Valley, was razed at some point during the Jewish Revolt against Rome (66–74 CE).
As part of Israel’s archaeological heritage sites, the University of Haifa team intends to develop the site for public access, offering a concrete link to this important era in Jewish history.
Cover Image Credit: Some of a cache of newly discovered Maccabi-era coins. Credit: Dr. Shai Bar/Zinman Institute of Archaeology at the University of Haifa