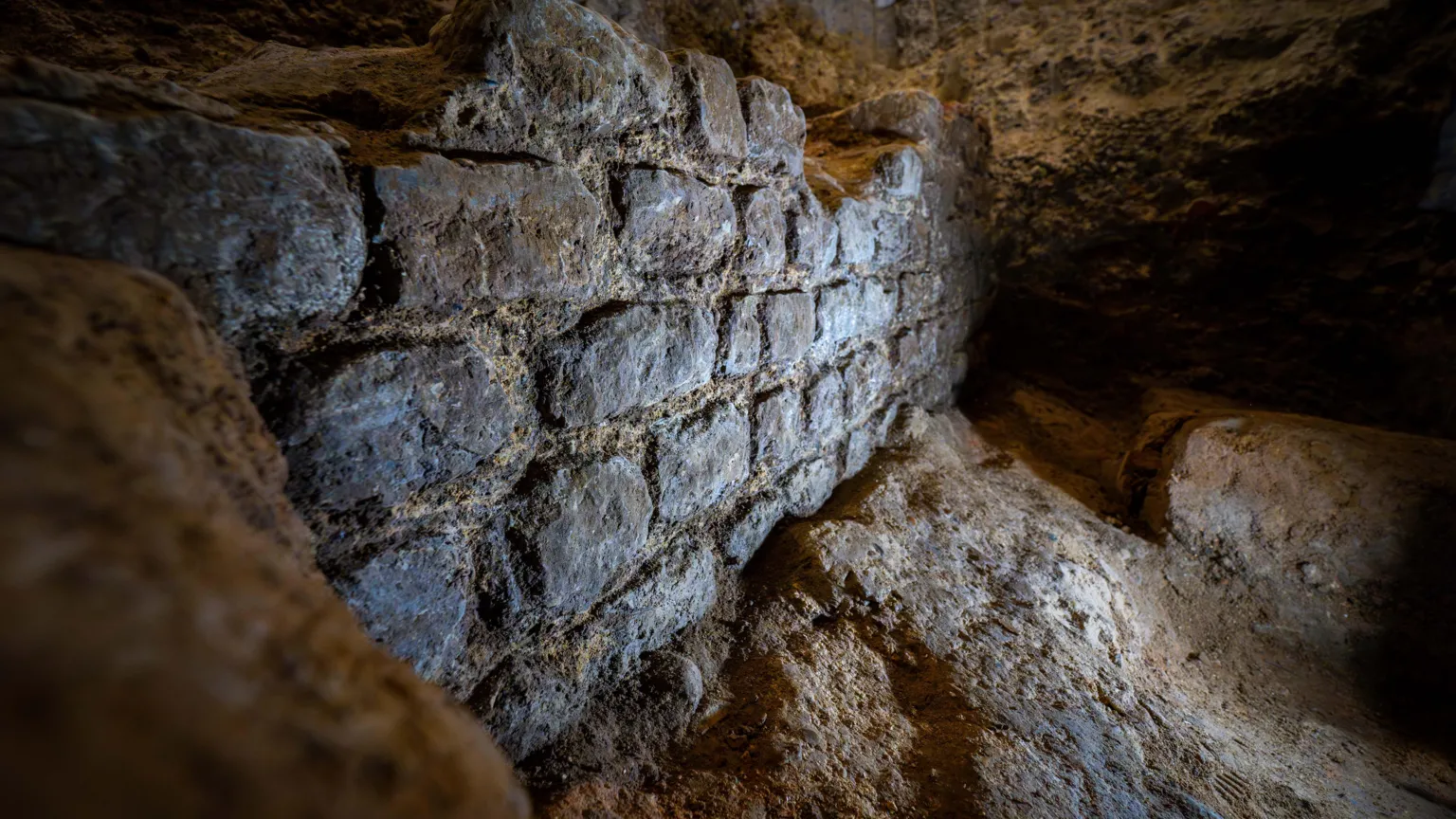
Archaeologists have made a groundbreaking discovery beneath an office building in London, unearthing a substantial section of the ancient city’s first basilica, a public building dating back 2,000 years. This site, where major political, economic, and administrative decisions were made, is being hailed as one of the most important pieces of Roman history found in the city.
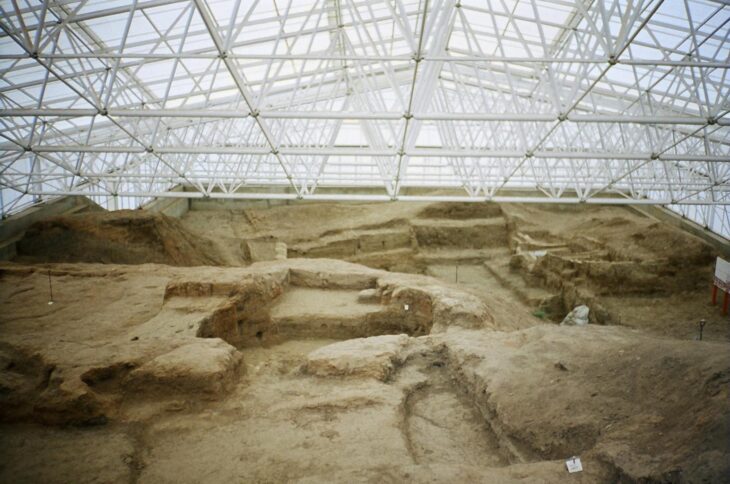
The excavation at 85 Gracechurch Street has revealed sections of stone walls that formed the base of the basilica, which is believed to have stood two-and-a-half storeys high. Sophie Jackson from the Museum of London Archaeology (Mola) described the find as “the heart of Roman London,” emphasizing its significance in understanding the origins of the city and its development as the capital of Britain.
The discovery occurred during preparations for the demolition and redevelopment of the office building. Previous archaeological investigations had indicated the approximate location of the basilica, prompting the team to dig several test pits beneath the concrete floor. On their third attempt, they uncovered a substantial piece of Roman masonry.
The basilica, constructed around 80 AD shortly after the Roman invasion of Britain, was part of London’s forum, a social and commercial hub featuring a large open market square surrounded by shops and offices. It served as the town hall, a place for conducting business, resolving legal matters, and making important decisions for London and beyond.
Although the first basilica and forum were only in use for about 20 years before being replaced by a larger second forum, the discovery has prompted a change in plans for the building’s owners, Hertshten Properties. The Roman remains will be fully excavated and incorporated into the new office design, pending planning approval, and will be opened to the public.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Architect James Taylor from Woods Bagot noted the technical challenges of redesigning the building around the archaeological site, including repositioning columns and reducing the building’s height to preserve the discovered stones. He expressed enthusiasm for the potential of the space, stating that seeing people engage with the historical remains will be “absolutely incredible.”
Historic England’s Chief Executive, Duncan Wilson, stated, To find the dais of the Basilica, the heart of London’s Roman Forum, surviving beneath today’s bustling square mile is really something special. To capitalise on this extraordinary discovery we have helped shape a new public display of the archaeological remains, offering a brand new visitor experience in the City. This underscores our belief that well-displayed and interpreted archaeology brings real value and character to a development, celebrating the heritage of places whilst delivering something new.'”
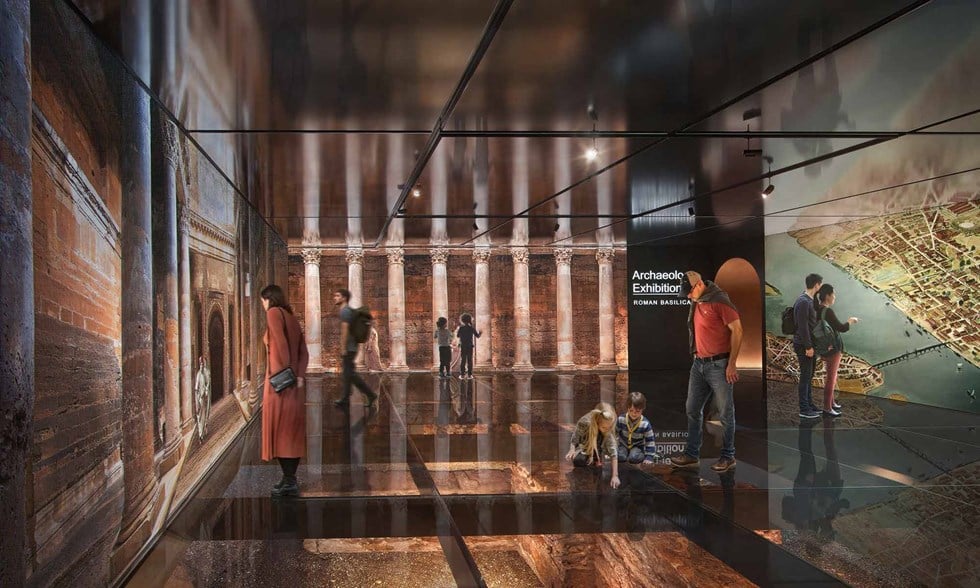

Hertshten Properties, the site owners, have unveiled updated proposals for the location, which include plans to integrate the surviving archaeological remains into a new public exhibition. The project aims to create an event space and immersive experience in collaboration with the London Museum, formerly known as the Museum of London.
This discovery adds to the growing collection of Roman history found beneath London’s Square Mile. Efforts are underway to creatively showcase these sites to the public, with parts of an amphitheatre displayed under glass at the Guildhall Art Gallery and the Temple of Mithras at Bloomberg’s offices featuring an immersive sound and light installation.
Chris Hayward from the City of London Corporation highlighted the emotional connection people can experience with Roman London, noting the contrast between the ancient city and the modern skyline. He emphasized the importance of combining progress with preservation, allowing the public to appreciate the rich history that lies beneath their feet.
Cover Image Credit: Tony Jolliffe/ BBC News
















