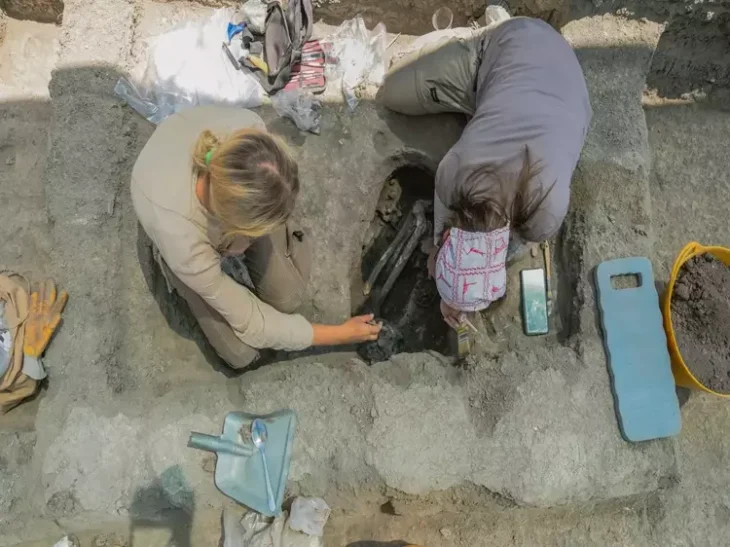
Archaeologists from the National Institute of Anthropology and History (INAH) in Guerrero discovered a prehistoric settlement spread across 29 hectares in the El Cerrito neighborhood of Tecpan de Galeana. This site may be the old Apancalecana settlement location, which was previously only mentioned in pre-Hispanic codices.
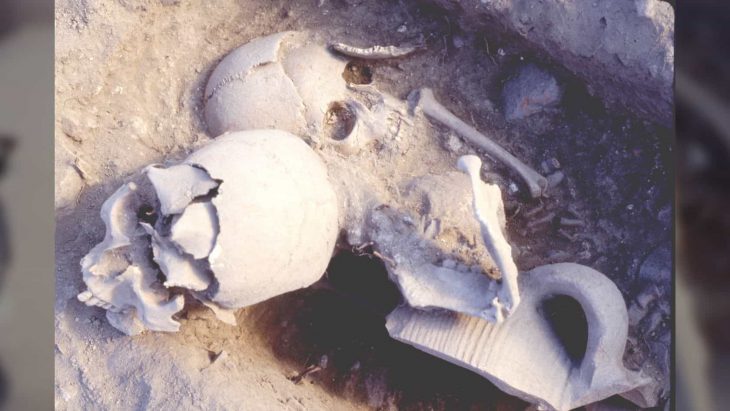
According to the INAH, after citizens were alerted about the presence of prehispanic vestiges archaeologists from its Center in Guerrero went to the site and registered 26 mounds, as altars and long structures in good condition, as well as residential areas and courts of ball game.
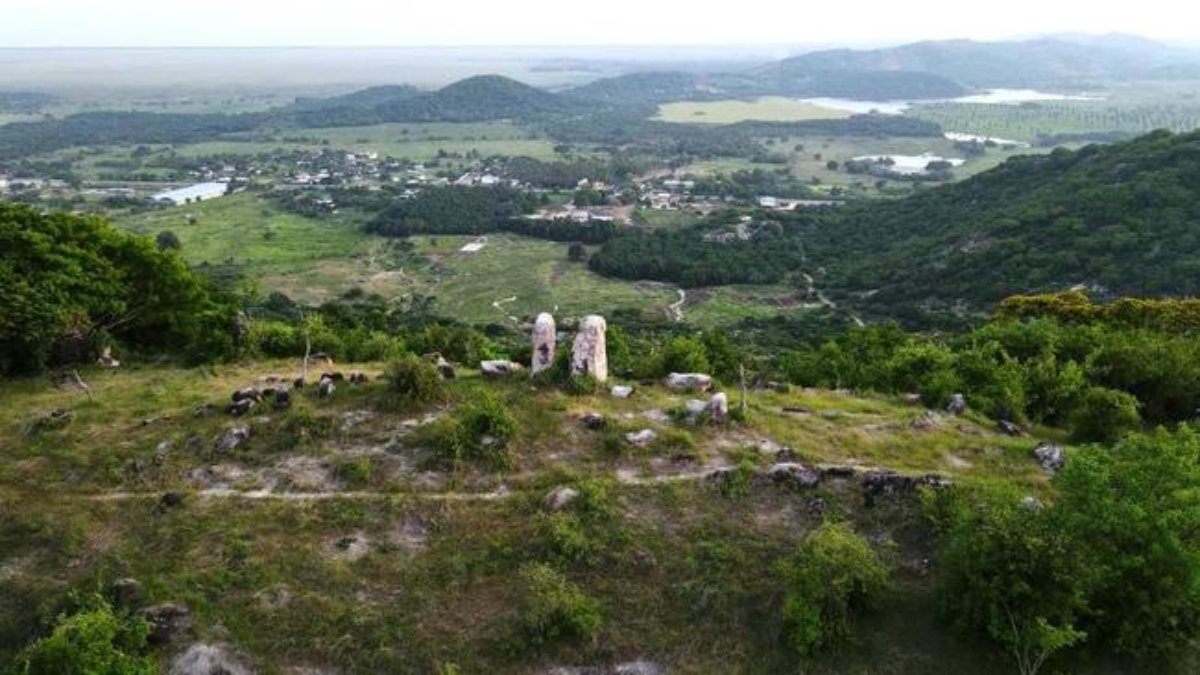
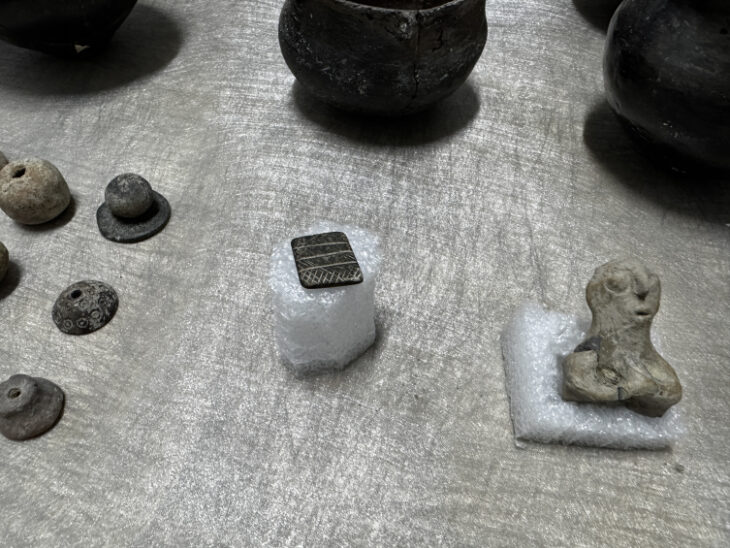
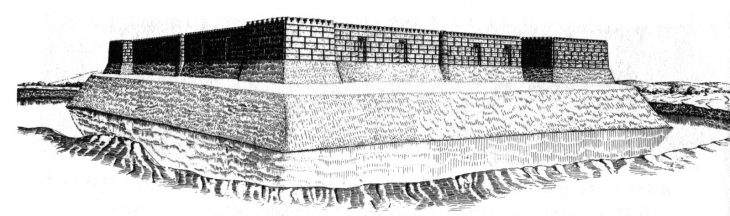
These sets are distributed peripherally to a large mound, whose base is 73.5 meters by 60 meters, and 25 meters high, with adjacent spaces, such as squares, where two smooth stelae, two rock outcrops with wells, and little.
Because the site is strategically located 850 meters from the eastern bank of the Tecpan River and one kilometer from the Laguna de Tetitlán, hollows were identified within this complex that is combined with the elongated structures, possibly associated with water storage and dams.
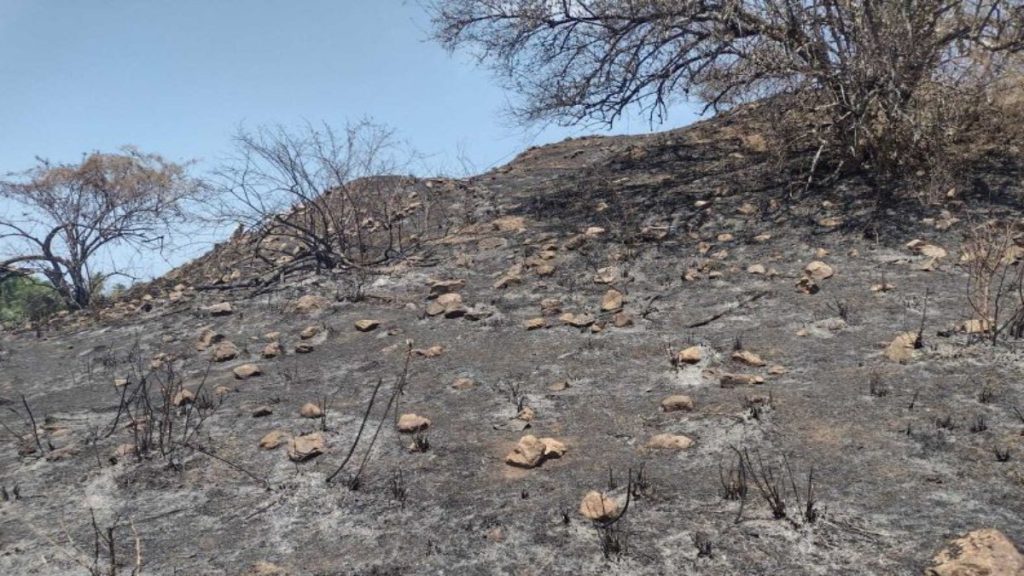

A study of the ceramic material recovered on the surface suggests that the site was first inhabited during the Classic period around AD 200 to 650.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Aerial photography taken by the speleologist Frédéric Henri Jean-Marc Bochet during the mapping process allowed the location of an altar with two twin stelae on top of the nearby Cerro del Mono, which is where the main mound of the recently discovered settlement is located.
When comparing the dimensions and proximity of the site with the town of Tecpan de Galeana and the toponymic glyph that appears in a petroglyph, with sources from the 16th century, Lobato Rodríguez suggests that it could correspond to the old main town of Apancalecan, referred to on Plate 18 of the Codex Matrícula de Tributos, which after the Spanish invasion became Tequepa, as recorded on a map by the cartographer Abraham Ortelius, from 1570. However, the location of the settlement was lost until now.
Regarding the Nahua meaning of Apancalecan, the word is made up of apan (apantli, ditch water channel), calli (house), and can (locative), which is why it has been translated as “Place of the house with water channels”. The place name of this town is illustrated by a temple over which water runs with chalchihuites and snails, which coincides with the proposed translation according to the Nahua words taken from Remy Simeon’s dictionary.
Cover Photo: Photo: Ministry of Culture / Government of Mexico