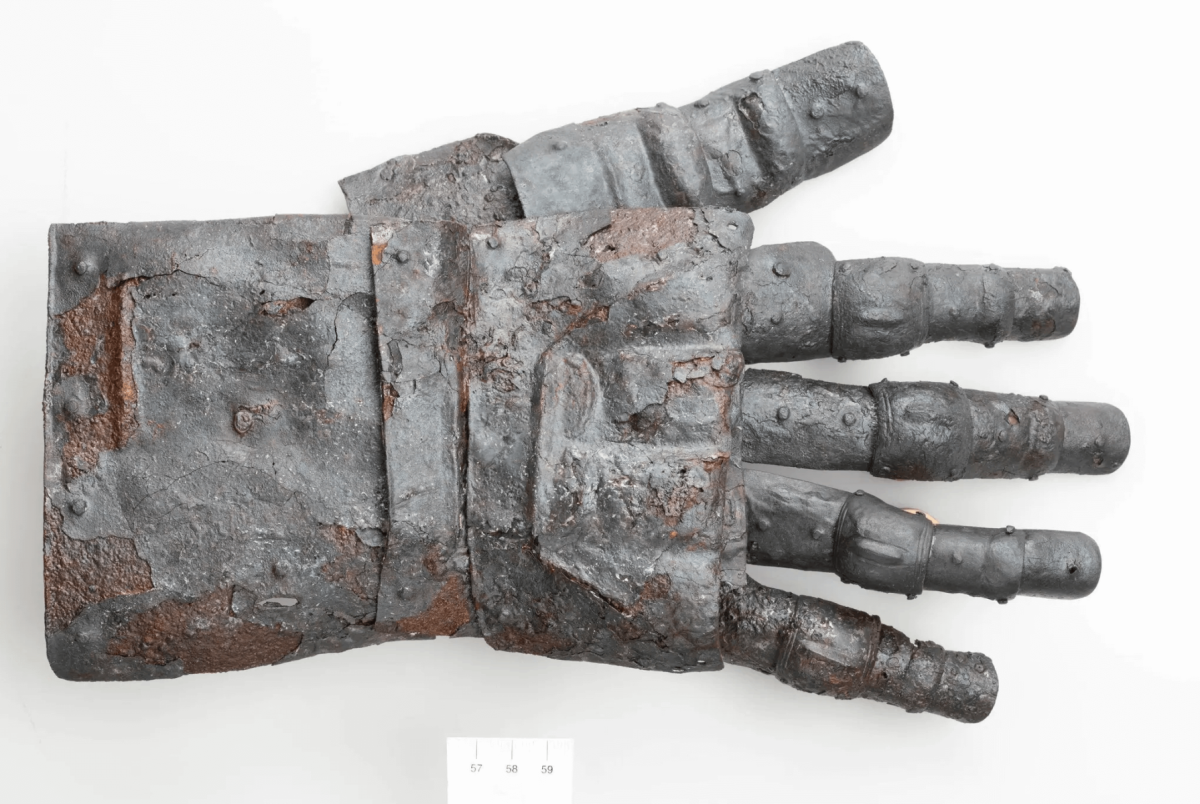
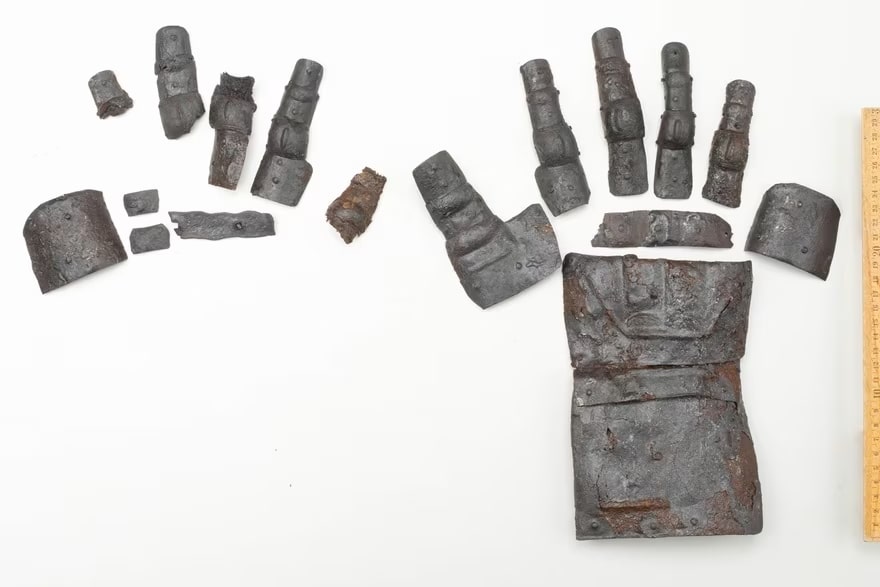
Excavations in Kyburg in the canton of Zürich, northeastern Switzerland have discovered a 14th-century fully preserved gauntlet of armor in exceptional condition.
Only five 14th-century gauntlets have been discovered in Switzerland thus far, according to the Zurich cantonal infrastructure department on Tuesday. However, their state of preservation is nowhere near that of the glove discovered in Kyburg. All the iron parts of this one have been found, and some of the fingers are even completely free of corrosion and look as good as new.
The metal parts of the glove were originally riveted to a leather glove. The 25 pieces were also firmly attached to each other, giving the glove great flexibility.
The entire gauntlet measures more than 14 inches long. Individual iron plates overlap like scales and are connected by side rivets. Originally, they would have been riveted to a leather or fabric material before being sewn onto a leather or textile glove. The small plates and flexible underlayers allowed the wearer to comfortably grip a sword and make a fist.
The castle is first mentioned in 1027 under the name of Chuigeburg (“cows-fort”), which name points to an original use as a refuge castle for livestock.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The first fortification at this site was likely built in the second half of the 10th century by the counts of Winterthur. The early castle was destroyed in 1028 or 1030 by Emperor Conrad II. It was rebuilt and soon became the center of the county of Kyburg which was formed in 1053 as a possession of the counts of Dillingen.

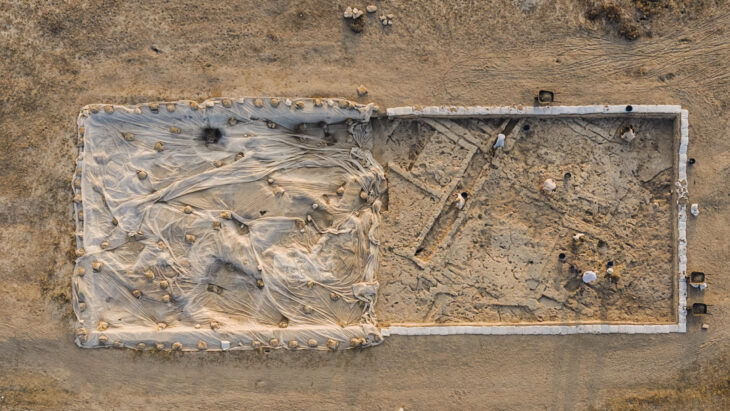
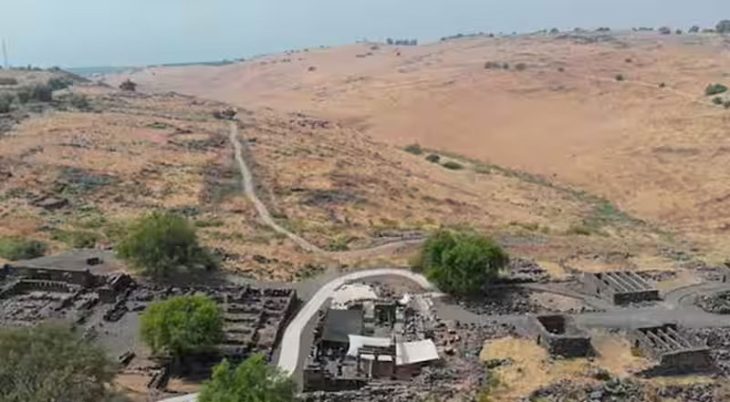
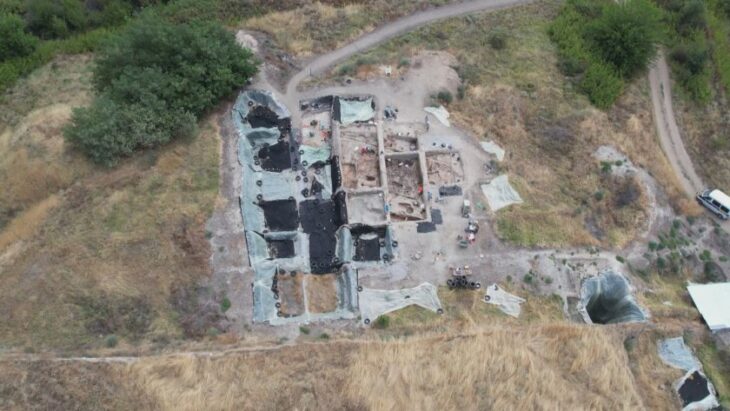
Cantonal archaeologists excavated a site southeast of the castle in the winter of 2021/22 in a rescue operation before constructing a home with a basement.
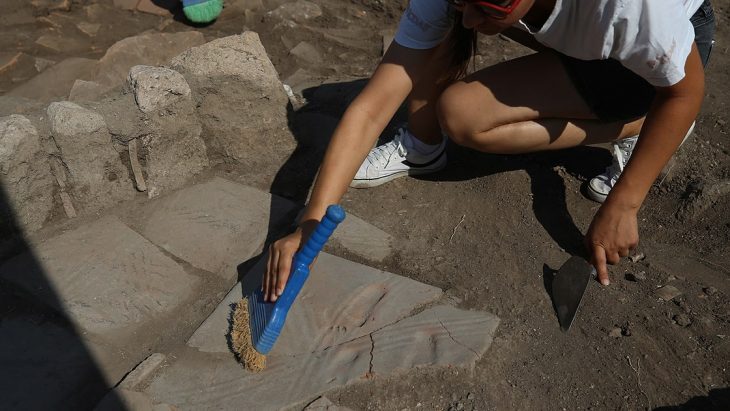
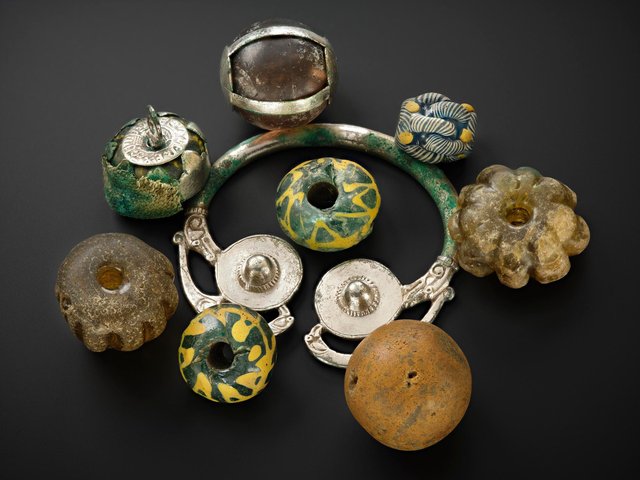
Archaeologists discovered a medieval weaving cellar that had burned down in the 14th century. Forging may also have taken place in its immediate vicinity; in addition to a casting mold, the archaeologists also discovered over 50 well-preserved metal objects such as hammers, keys, and projectile points – as well as the glove.
Archaeologists also found a completely preserved 14th-century gauntlet, in addition to fragments of its counterpart worn on the other hand.
It is not yet known who the glove belonged to, or why this type of object is so rarely found. Scientific work must now establish whether armour gloves were so rare at the time or whether they were melted down.
A copy of this armour glove will be on display at Kyburg Castle from the end of March as part of its permanent exhibition, complemented by a reconstruction of the rest of the armour. The original will be on display for three weeks in September.
Photo: Canton of Zurich