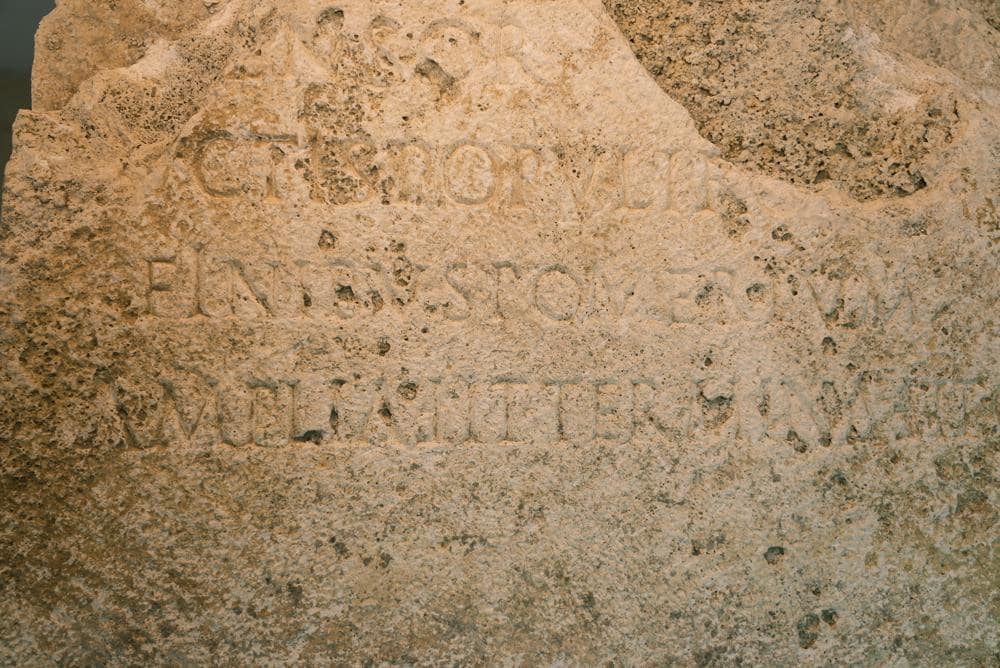Archaeologists unearthed a rare stone outlining ancient Rome’s city borders during excavations for a new sewage system. The stone comes from the reign of Emperor Claudius in 49 A.D. and was discovered during excavations for a new sewage system.
It was discovered on June 17 during excavations for diverted sewage beneath Emperor Augustus’ freshly renovated tomb, just off Rome’s famed Via del Corso.
The pomerial stone, a massive slab of travertine utilized as a religious, military, and political boundary defining the limit of the city proper with Rome’s outlying territories, was unveiled Friday by Rome Mayor Virginia Raggi.
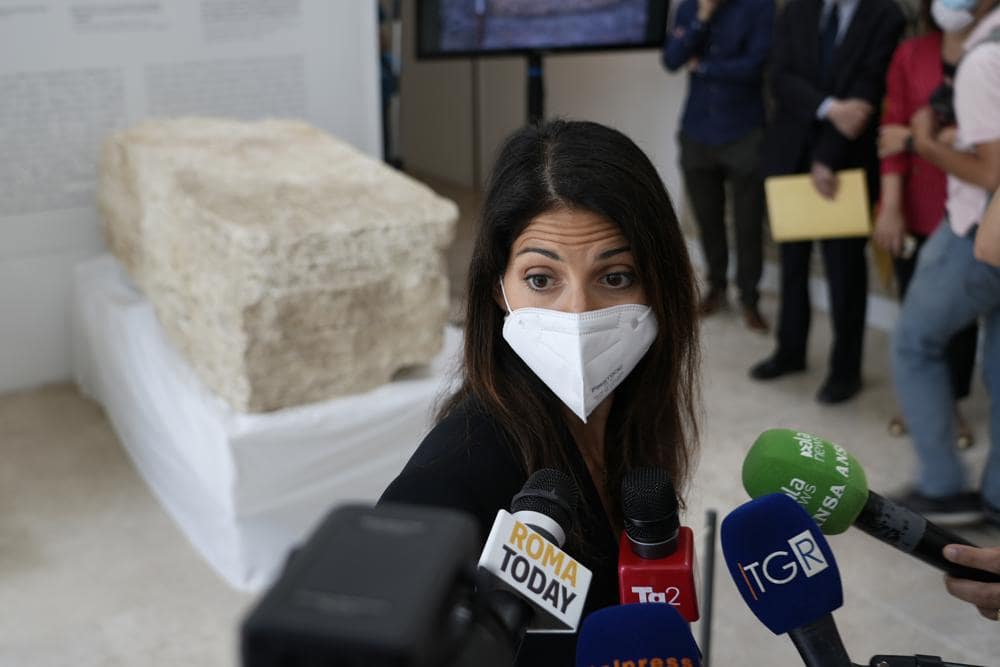

In ancient Rome, the area of the pomerium was a consecrated piece of land along the city walls, where it was forbidden to farm, live or build and through which it was forbidden to enter with weapons.
Claudio Parisi Presicce, director of the Archaeological Museums of Rome, said the stone has civic and symbolic significance at a news conference beside the tomb in the Ara Pacis museum.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
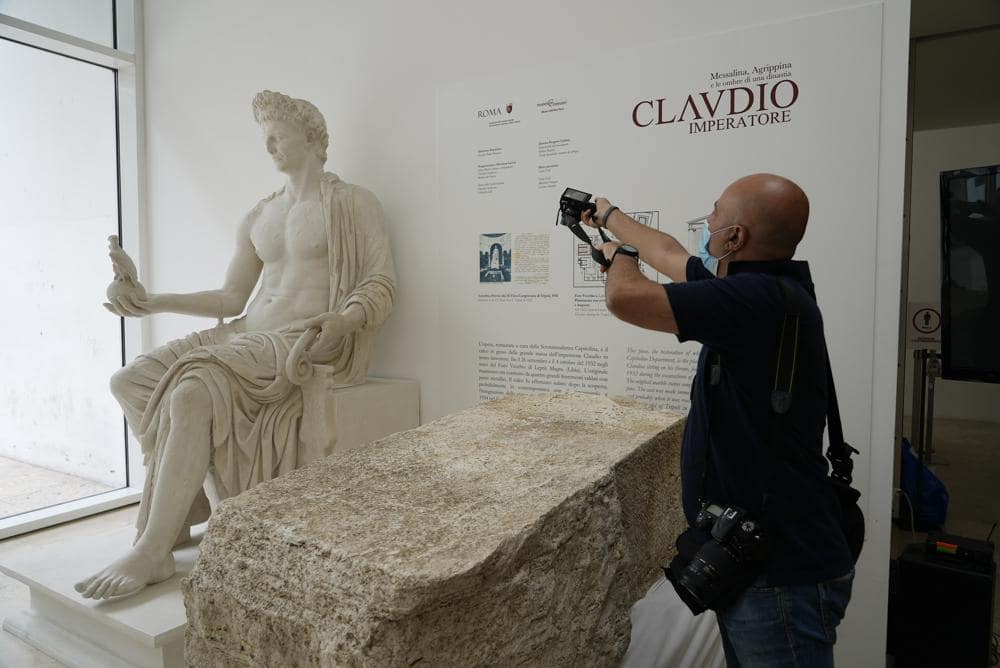

“The founding act of the city of Rome starts from the realization of this ’pomerium,‴ he said of the consecrated area. The stone features an inscription that allowed archaeologists to date it to Claudius and the expansion of the pomerium in 49 A.D., which established Rome’s new city limits.
Raggi noted that only 10 other stones of this kind had been discovered in Rome, the last one 100 years ago.
“Rome never ceases to amaze and always shows off its new treasures,” she said.
The stone will be on display at the Ara Pacis museum, the Richard Meier-designed home of a 1st-century altar until the Augustus museum opens.