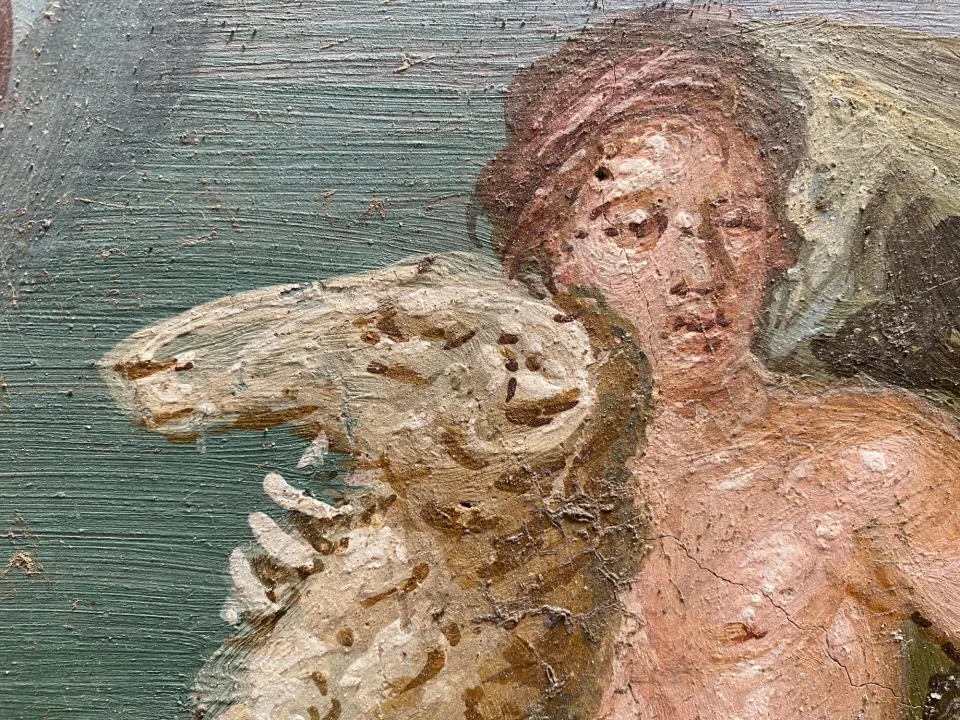
Archaeologists excavating a house adjacent to the House of Leda in Insula 6, Regio V, in the ancient Roman city of Pompeii have unearthed a fresco depicting the Greek mythological siblings Phrixus and Helle (also known as Ellie).
Still astonishingly colorful some 2,000 years after the eruption of Mount Vesuvius wiped out the city, the frescoes were unearthed during restoration work around the mansion of the House of Leda.
The director of Pompeii Archaeological Park, Gabriel Zuchtriegel, described the discovery as a poignant reflection of history unfolding.
The unearthed fresco depicts two refugees at sea from ancient Greece, Phrixus and Elle, brother and sister who flee their home after being driven out by their stepmother, who has bribed Delphi’s oracle to have the children killed in order to end the famine that has befallen their homeland. The two siblings are rescued by Hera, and they escape on the Golden Fleece ram. Elle slips from the ram and drowns in the strait between Europe and Asia (named after her, or the Hellespont). In the fresco, she is seen disappearing into the waves, while her brother Frisso survives.
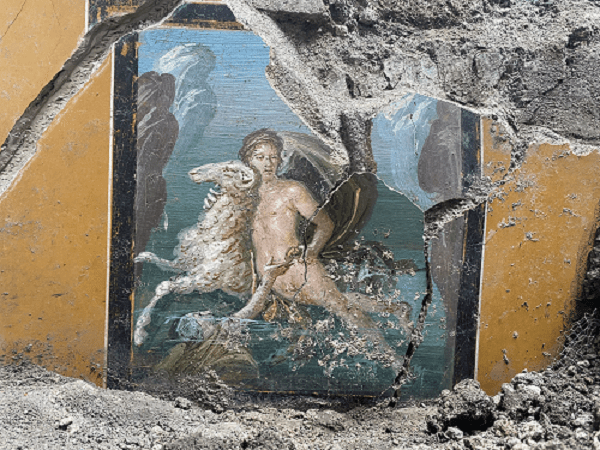

It is “a fresco in an excellent state of preservation,” as Archaeological Park director Gabriel Zuchtriegel put it, depicting “a myth typical of ancient Greece, but also of Pompeii, where Greek myth is very much present in all homes and is also an example of how myth, storytelling through images, wall decoration becomes part of a lived environment like this small house, not very large, but richly decorated, which tries through the paintings to emulate, to imitate the tone of life of the elites.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The fresco is painted as if it were a framed picture, hung on a yellow wall. Others depicting still life images and several portraits of women have also been newly revealed.
Zuchtriegel also expressed hope for making these meticulously preserved homes available to the public shortly, emphasizing the cultural and historical significance of this latest discovery.
Unexpected discoveries in recent months include thirteen Nativity-style statuettes that revealed evidence of pagan ritual customs in the ancient Roman city and, in June of last year, a remarkable still-life fresco that resembled a pizza and contained an object that appeared to be a pineapple.
Cover Photo: Pompeii Archaeological Park