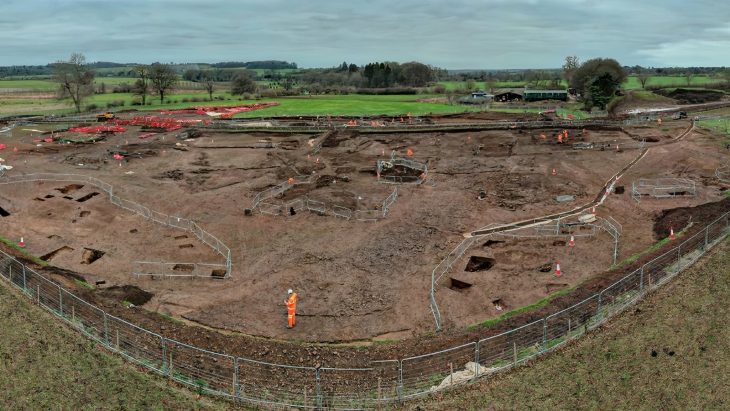
During excavations in Scremby, Lincolnshire in 2018, archaeologists uncovered an enameled copper alloy chalice in a 6th-century AD female grave.
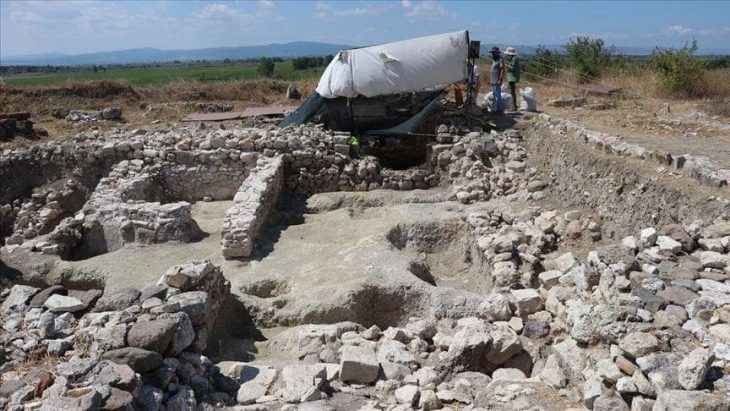
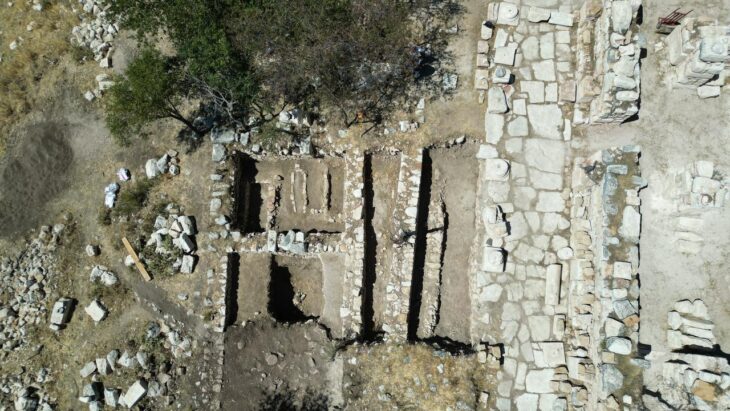
The chalice was discovered during excavations carried out by the University of Sheffield as part of a study of the Migration Period cemetery at Scremby, which contains 49 burials dating between 480 and 540 AD.
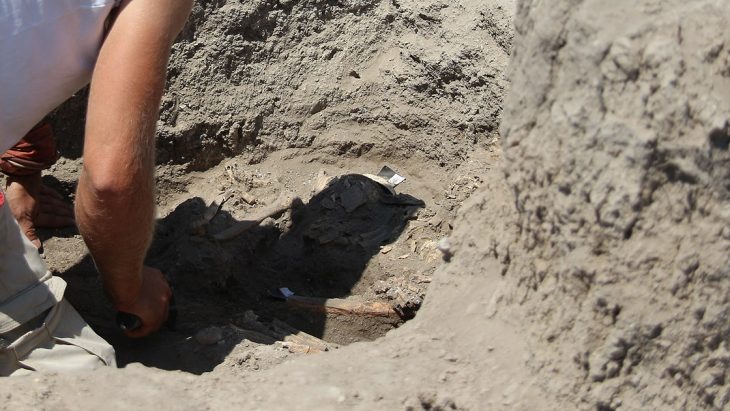
Archaeologists unearthed the 1,800-year-old multicolored goblet upon finding the girl’s sixth-century grave, designated Sk18. They also found only two circular brooches and a pair of bracelets. The placement of the chalice, intact and beside her head, indicated its special significance.
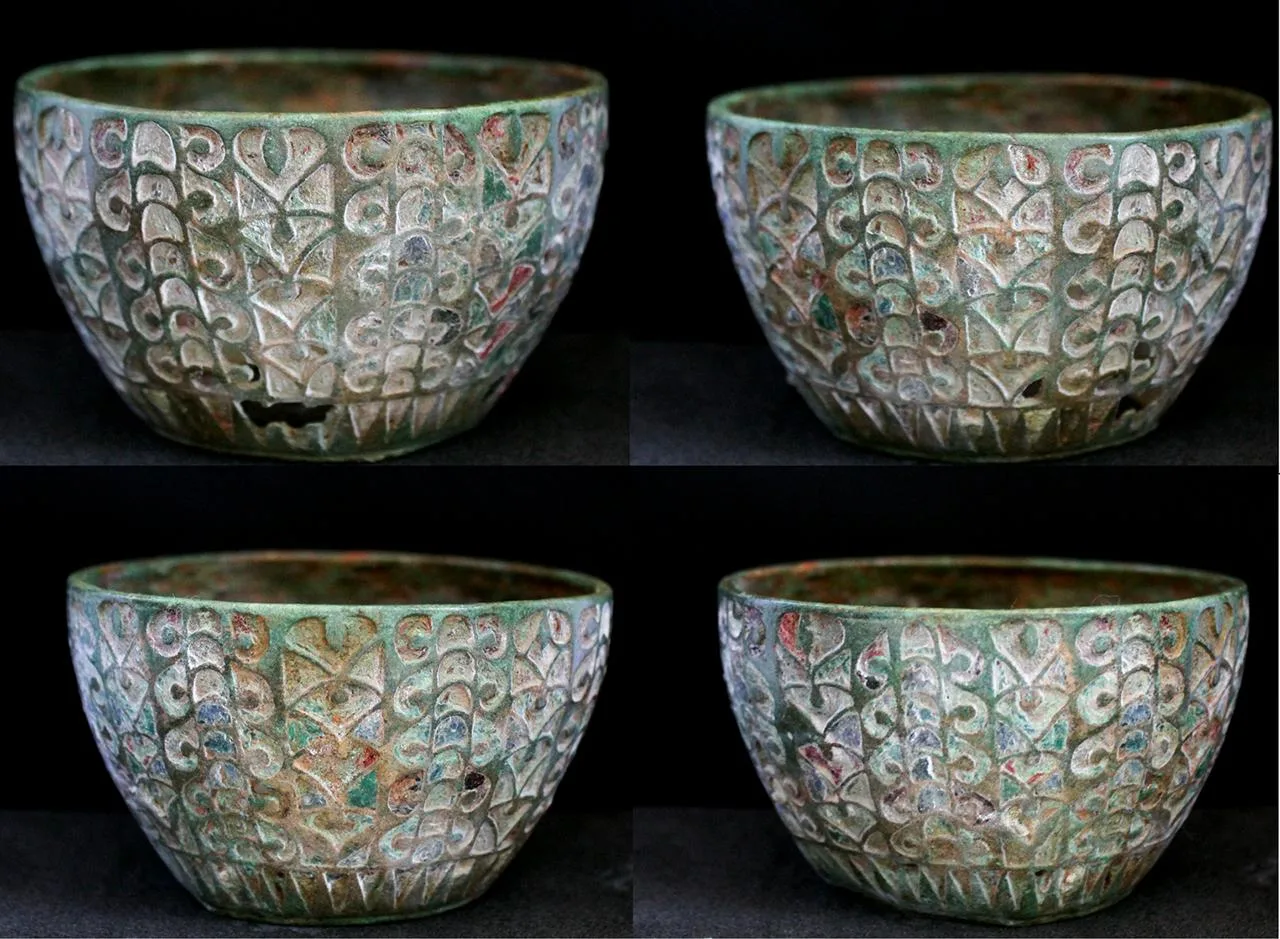
This rare artifact dubbed the ‘Scremby Chalice’, stands out as a unique piece due to its antiquity, Roman origin, and its inclusion in an Anglo-Saxon funerary context.
The Scremby Chalice is 2.2 inches (5.7 centimeters) tall and could hold roughly 1.2 cups (280 milliliters) of liquid. Inset motifs of half moons and heart shapes were cast into the vessel’s copper-alloy surface and then filled with red, aquamarine and deep bluish-purple enameling. Researchers determined it was crafted using the lost-wax casting technique, showcasing Roman artisanship. The cup’s style and materials suggest it may have been imported to England from France in the middle of the third century A.D., during Britain’s Roman period.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
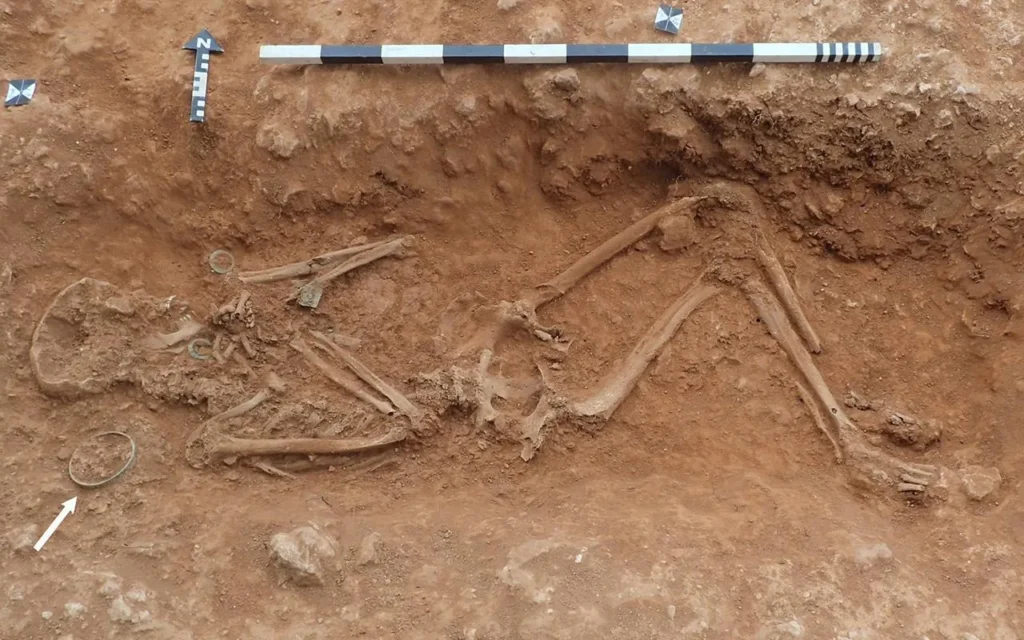

The chalice, placed next to the deceased’s head, was intact and fully functional at the time of burial. This sets it apart from other Roman artifacts that are frequently repurposed as scrap or fragments and discovered in Anglo-Saxon contexts. Researchers believe this points to a potential ceremonial or ritual role for the burial.
The most intriguing finding came from the residue analysis of the chalice’s interior. Unheated and raw traces of pig fat were found in lipid residues, suggesting non-culinary uses. The fat may have had a medicinal or ceremonial function, according to researchers, which is consistent with Byzantine texts from the sixth century that mention using pig fat to treat infections.
The chalice’s inclusion in Sk18’s funeral highlights its possible use as a status symbol or spiritual symbol. The chalice might have represented strength or continuity with the Roman past because Anglo-Saxon contexts frequently associated Roman materials with mysticism.
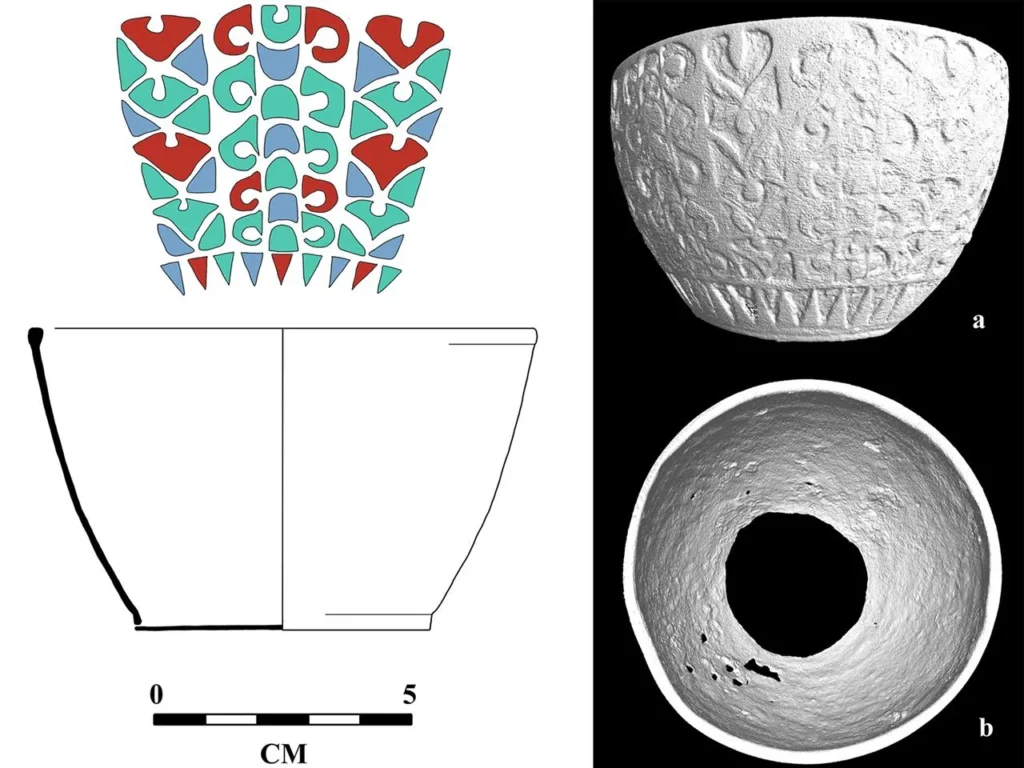
Researchers investigate two primary theories regarding the chalice’s arrival in this context. It might have been recovered from an earlier Roman burial, according to the first theory, which is supported by other archaeological discoveries. As a sort of relic or family heirloom, the second, though less popular, theory suggests that the chalice may have been meticulously preserved for generations.
The research was published in the November issue of the European Journal of Archaeology.
Willmott H, Thompson L, Lundy J, Crichton-Turley C-E., “From Roman Table to Anglo-Saxon Grave: An Archaeological Biography of the Scremby Cup.” European Journal of Archaeology. 2024;27(4):507-525. doi.org/10.1017/eaa.2024.12
Cover Image Credit: H: Willmott et al., European Journal of Archaeology