Researchers from the University of Bologna have discovered an association between proto-cuneiform and even older stone images engraved on ancient cylinder seals in Uruk, in about 3000 BC. The study found that the origins of writing in Mesopotamia lie in images imprinted on ancient stone cylinder seals.
The world’s earliest writing system is believed to have emerged in the region, now modern-day Iraq, about 3200 BC. Known as cuneiform, the script represented both a sound and a meaning. It was preceded by a simpler system called proto-cuneiform, which was in use from 3350 to 3000 BC.
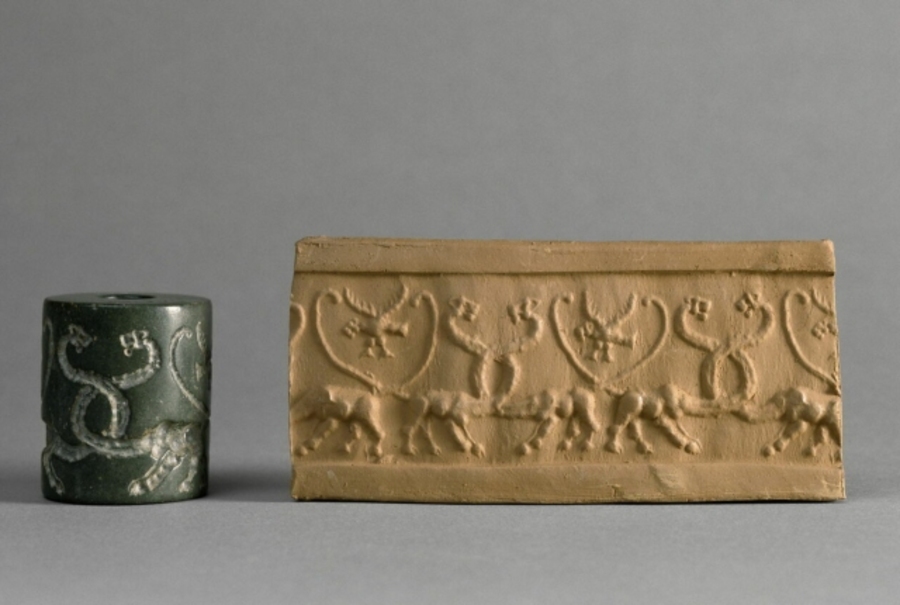
These cylindrical seals were small stone objects with intricate carvings, rolled over clay tablets to leave an impression. Beginning in the middle of the fourth millennium BC, cylinder seals were employed in Uruk, as a component of an accounting system to monitor the manufacturing, storage, and transportation of a variety of consumer goods, especially textile and agricultural items.
Research published in the journal Antiquity shows links between the proto-cuneiform signs that first appeared in Uruk, one of Mesopotamia’s oldest and most significant cities, around 3000 BCE, and the images engraved on these seals, some of which date back approximately 6,000 years.

‘The conceptual leap that allowed the transition from symbolism to actual writing is a fundamental development for human technologies,’ explains Silvia Ferrara, professor in the Department of Classical Philology and Italian Studies at the University of Bologna and lead researcher, who coordinated the research group. ‘The results of this study are a bridging point in the transition from prehistory to history: they show how some images from the still prehistoric era were incorporated into one of the first writing systems devised by man’.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Silvia Ferrara said images on the seals were used in close association with the first writing. But there is a lot they did not know about the relationship between the two.
“When they began researching this, the researchers expected to find some shared shapes. But they discovered direct parallels between late prehistoric seals and proto-cuneiform signs,” Prof Ferrara said.
Ferrara and her team have discovered a number of recurrent themes on these seals, such as patterns associated with the transportation of textiles and ceramics. The fact that early proto-cuneiform signs share these same themes suggests that the seals’ symbols may have directly influenced or served as inspiration for the proto-cuneiform system.
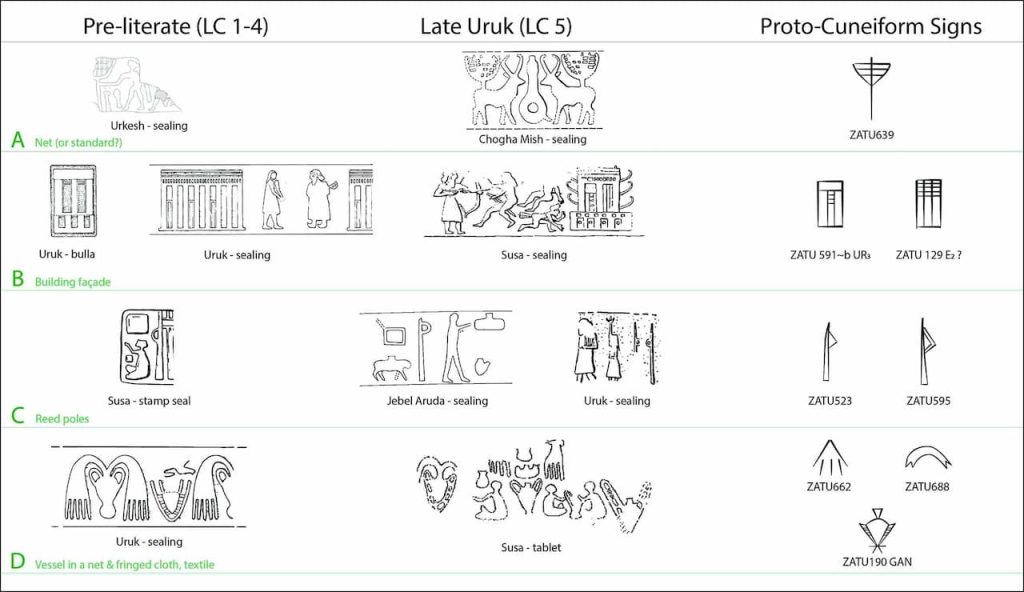
The researchers observed that earlier prehistoric seal motifs do not resemble proto-cuneiform icons as much as later prehistoric ones, and gained valuable insights into the time frame of the evolution of symbol traditions that influenced the invention of writing.
Additionally supporting the notion that seal motifs developed from particular administrative functions to a structured writing system is the research team’s methodical comparison of seal motifs with proto-cuneiform signs. A lineage of symbolic representation that developed alongside Mesopotamia’s early urban and economic growth can be seen by following the evolution of these images into proto-cuneiform signs, as co-researchers Kathryn Kelley and Mattia Cartolano point out.
The study was published in Antiquity.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.15184/aqy.2024.165
Cover Image Credit: Franck Raux / GrandPalaisRmn – Musée du Louvre
















