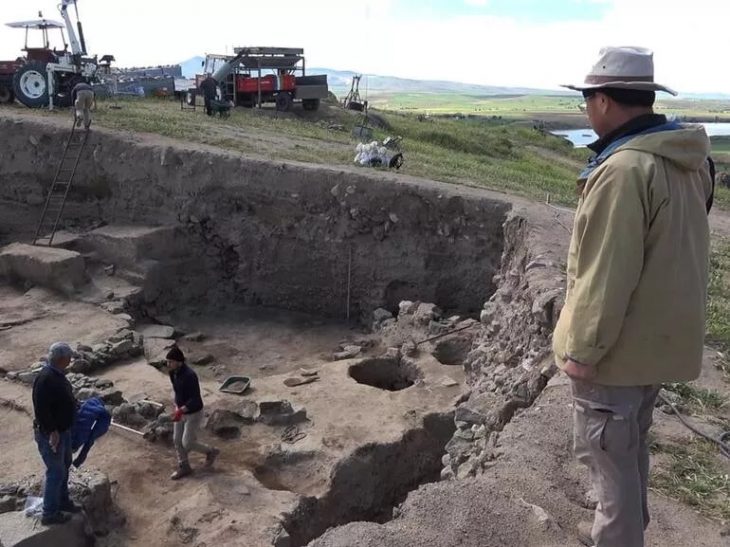
A study published in the journal Nature has genetically identified the origins of the Indo-European language family, which includes over 400 languages spoken by more than 40 percent of the world’s population today.
Ron Pinhasi and his team from the Department of Evolutionary Anthropology at the University of Vienna, in collaboration with David Reich’s ancient DNA laboratory at Harvard University, have made significant strides in uncovering the origins of the Indo-European language family. Their study analyzed ancient DNA from 435 individuals excavated from archaeological sites across Eurasia, dating from 6400 to 2000 BCE. The findings reveal a newly recognized Caucasus-Lower Volga (CLV) population that is connected to all Indo-European-speaking populations.
Indo-European languages (IE), which number over 400 and include major branches such as Germanic, Romance, Slavic, Indo-Iranian, and Celtic, are spoken by nearly half of the world’s population today. Originating from the Proto-Indo-European (PIE) language, historians and linguists have been investigating its origins and spread since the 19th century, as gaps in knowledge still remain.
The new study, which also involved Tom Higham and Olivia Cheronet from the University of Vienna, builds on earlier genetic research that identified the Yamnaya culture (3300-2600 BCE) of the Pontic-Caspian steppes as a significant migratory force into both Europe and Central Asia starting around 3100 BCE. This migration is believed to have had the largest impact on European genomes in the last 5,000 years and is widely regarded as a key factor in the spread of Indo-European languages.
Previously, the only branch of Indo-European languages that did not show any steppe ancestry was Anatolian, including Hittite, which is thought to be the oldest branch to diverge, preserving linguistic features lost in other branches.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“We know people like the Hittites spoke Anatolian from cuneiform tablets,” said senior author David Reich, a professor of genetics at Harvard Medical School and human evolutionary biology in the Faculty of Arts and Sciences. “But these people didn’t have Yamnaya ancestry. We looked hard, with lots of data. We didn’t find anything. So we hypothesized some deeper population was the ultimate source in Indo-European languages.”
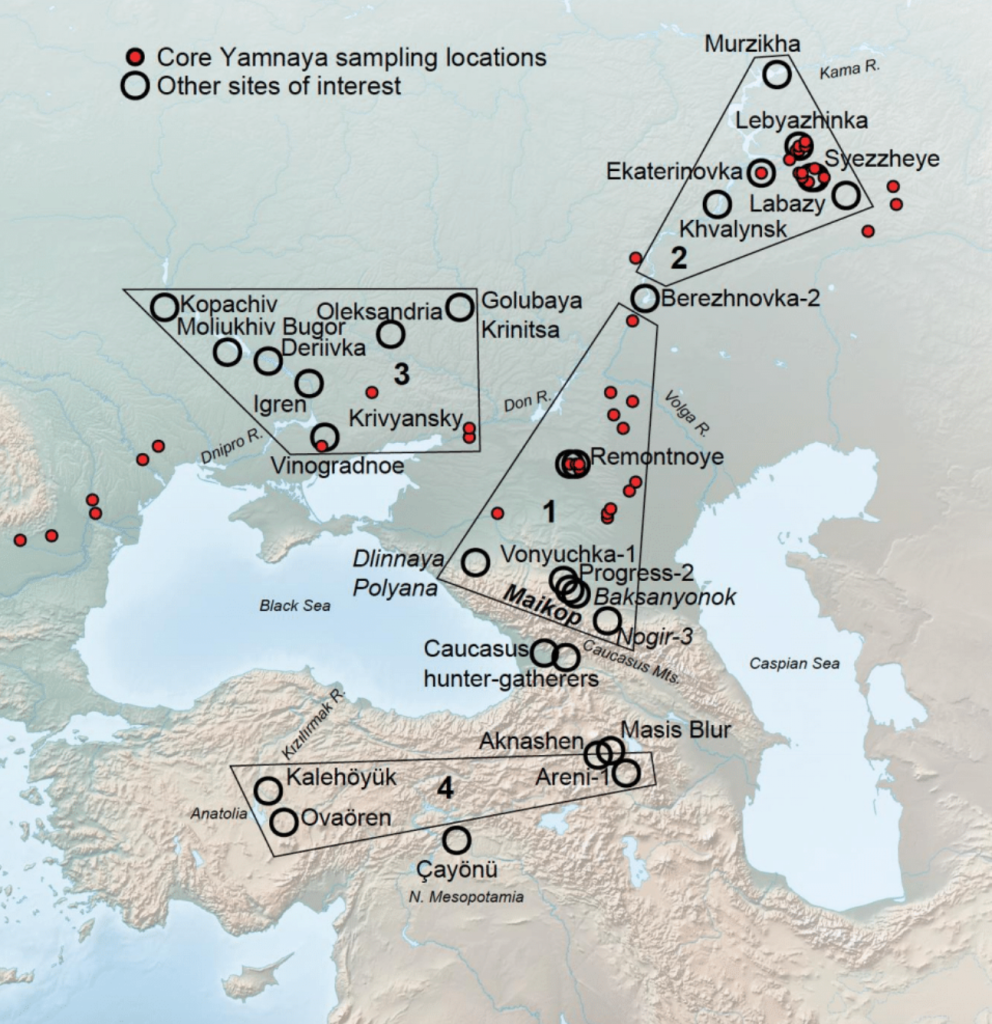
Earlier studies had not detected steppe ancestry among the Hittites, but the new paper argues that Anatolian languages descended from a group that had not been adequately described before—a Eneolithic population dating from 4500 to 3500 BCE in the steppes between the North Caucasus Mountains and the lower Volga. The genetics of this newly recognized CLV population indicate that at least five individuals in Anatolia, dating to before or during the Hittite era, exhibit CLV ancestry.
The study reveals that the Yamnaya population derived approximately 80% of its ancestry from the Caucasus Lower Volga (CLV) group, which also contributed at least one-tenth of the ancestry of Bronze Age central Anatolians, the speakers of Hittite. This suggests that the CLV people may be the original source of these lineages, establishing newly uncovered connections to both the Yamnaya and the ancient Indo-Anatolian speakers who once inhabited parts of present-day Turkey.
“The CLV group can therefore be connected to all IE-speaking populations and is the best candidate for the population that spoke Indo-Anatolian, the ancestor of both Hittite and all later IE languages,” explains Ron Pinhasi. The results further suggest that the integration of the proto-Indo-Anatolian language, shared by both Anatolian and Indo-European peoples, reached its peak among CLV communities between 4400 and 4000 BCE.
“The discovery of the CLV population as the missing link in the Indo-European story marks a turning point in the 200-year quest to reconstruct the origins of the Indo-Europeans and the routes by which these people spread across Europe and parts of Asia,” concludes Ron Pinhasi.
“It’s the first time we have a genetic picture unifying all Indo-European languages,” said co-lead author Losif Lazaridis, a research associate in HEB.
In conclusion, this groundbreaking research not only illuminates the genetic foundations of the Indo-European language family but also reshapes our understanding of its historical narrative. By identifying the Caucasus Lower Volga population as a crucial link to the origins of these languages, the study provides a comprehensive genetic framework that unifies diverse linguistic branches.
As Ron Pinhasi aptly notes, this discovery represents a pivotal moment in the long-standing quest to trace the roots and migrations of Indo-European speakers across Europe and Asia. With this new genetic evidence, researchers are now better equipped to explore the intricate tapestry of human history and the profound connections that have shaped our linguistic heritage.
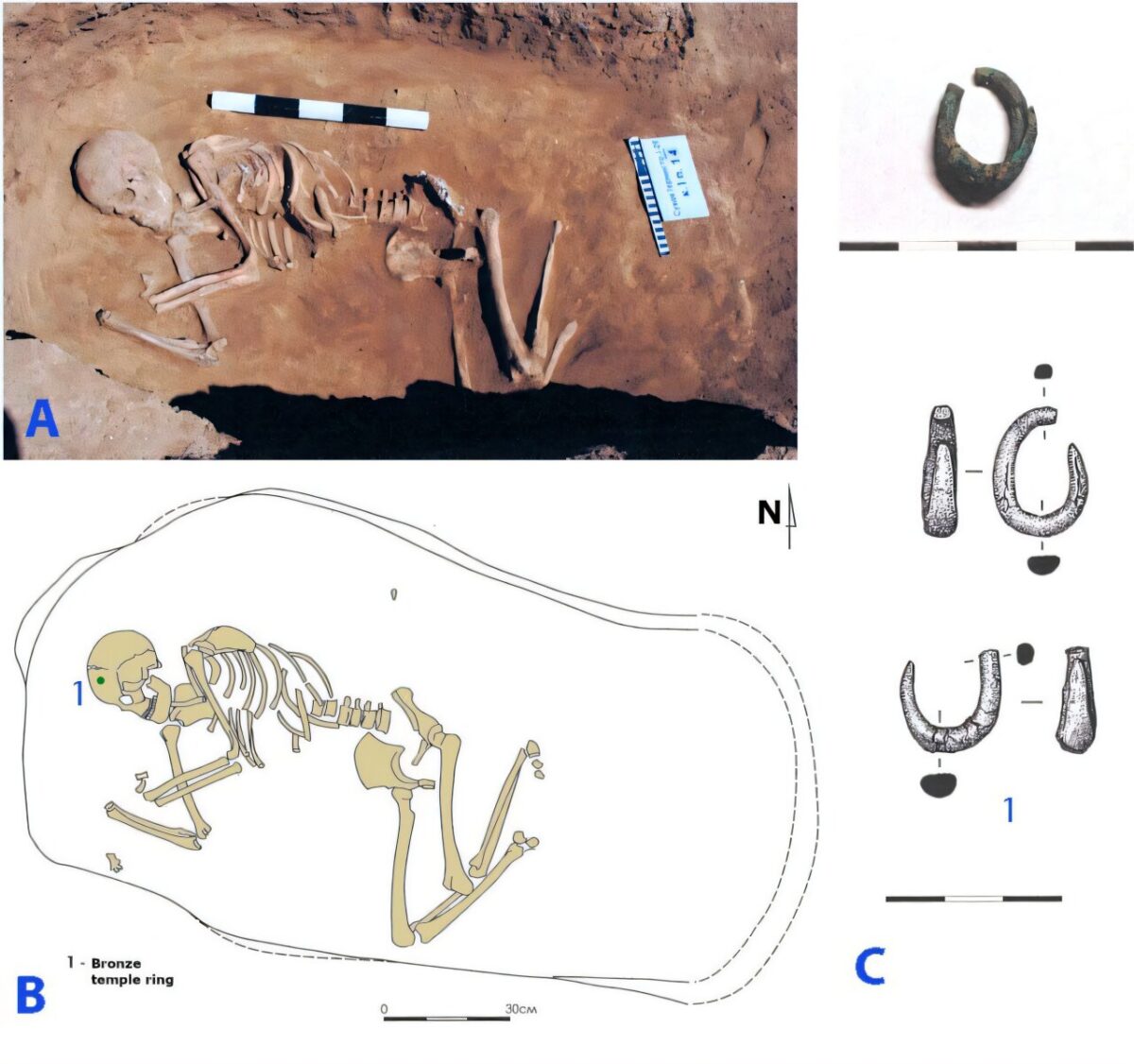
Cover Image Credit: Photo of Remontnoye (3766–3637 calBCE), with a spiral temple ring. Credit: Natalia Shishlina (co-author of “The Genetic Origin of the Indo-Europeans”
















