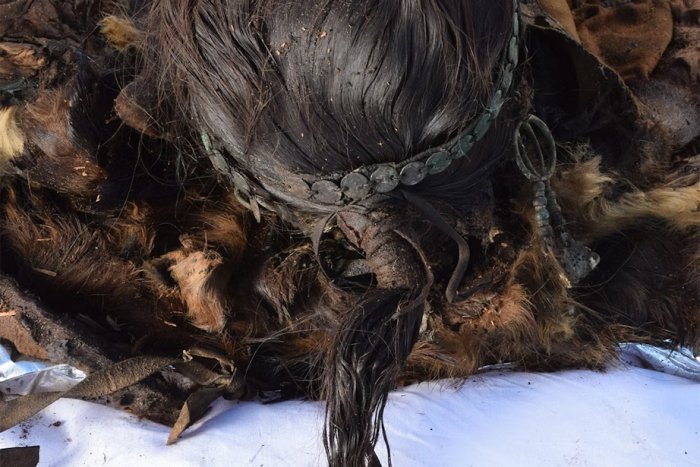
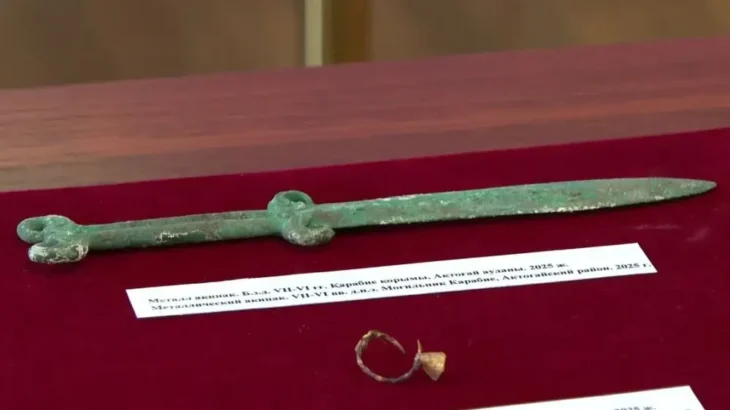
A 4,000-year-old tablet found in Kültepe shows that the first company in Anatolia was established by 12 people with 15 kilograms of gold.
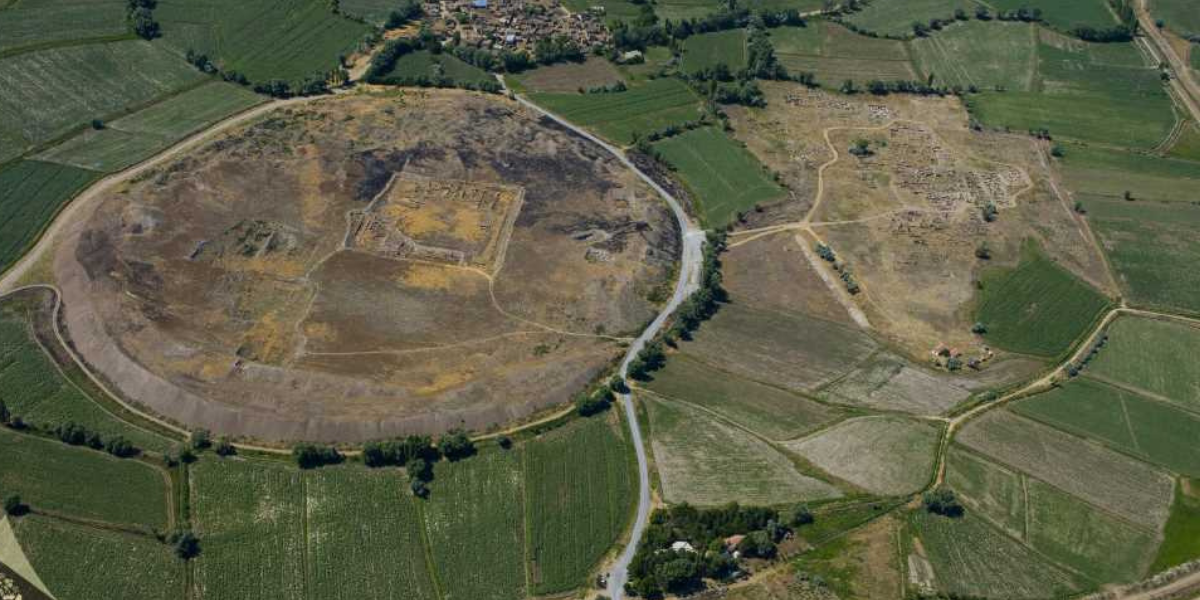
The excavations carried out in Kültepe Kaniş-Karum Ruins on the Kayseri-Sivas highway shed light on the commercial past of Anatolia.
In the initial years of the 2nd millennium, the Assyrians founded multiple trading settlements in Anatolia. In archaeological terminology, the period of the Assyrian colonies, covering the first two centuries or so of the second millennium, is commonly known as the Middle Bronze Age. During this period, the Assyrians were very active in international trading and commercial ventures. The focal point of the merchant operations was the city of Nesa or Kanesh (Kültepe, also known as Kanesh or Nesha).
Kültepe is considered one of the oldest trade centers of Anatolia and has a history of 6 thousand years. Excavations have been going on continuously for 75 years and more than 20 thousand cuneiform tablets have been found so far. These tablets reveal the commercial activities of the period in detail.
Kültepe Excavation Head Professor Fikri Kulakoğlu said that the first company in Anatolia was founded 4 thousand years ago by 12 people with 15 kilos of gold.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
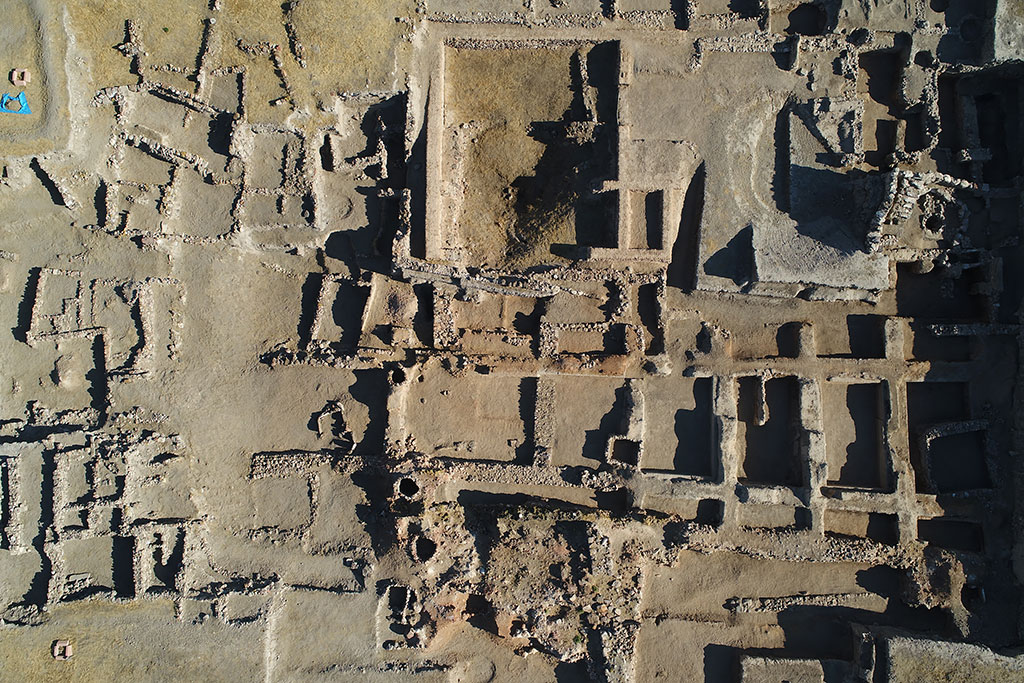

Prof. Dr. Kulakoğlu states that most of the tablets in Kültepe were for commercial purposes and all kinds of financial transactions were recorded. Many details ranging from the expenditures of caravans to credit and debit relations are included in these tablets. This shows that Kültepe was a very active and large trade center at that time.
Prof. Dr. Kulakoğlu stated that the information obtained from the tablets revealed that the first company established in Anatolia was established with a capital of 15 kilograms of gold and that this company had 12 partners. Each partner became a shareholder of the company by giving gold in different proportions. The capital of the company was managed by a merchant named Amur Ishtar for 12 years and one third of the profit was shared. All transactions related to the company were sealed and recorded in the presence of witnesses.
Kulakoğlu said, “If you want to withdraw your share of the company’s capital before the due date, you will be given about 4 kilos of silver instead of 1 kilo of gold. If you withdraw your capital before its due date, you are making a loss. In other words, it is guaranteed that the capital will remain in place for a long period of 12 years.”
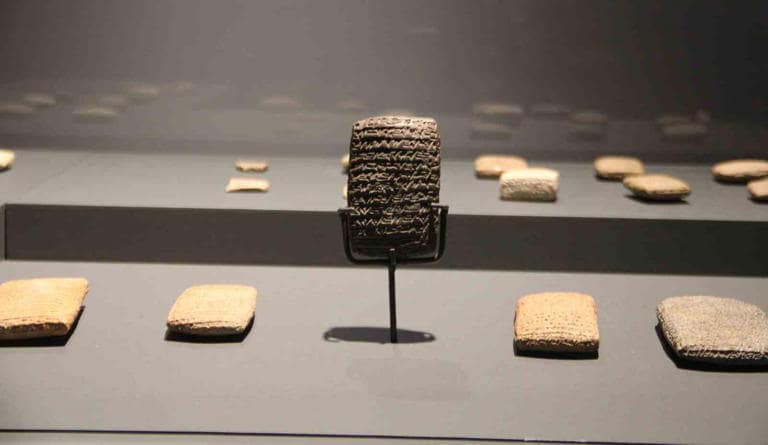

“The tablets found here are dated to the period after the 1950s BC. This is the period when writing first started in Anatolia. Naturally, it is the first declaration of the first company in Anatolia, in a sense, a company deed. It appears here for the first time in Anatolia,” he said.
Clay tablets do not only contain commercial information. Many social life details such as marriage contracts, divorces, inheritance documents, and notary procedures are also included in these tablets. This shows that Kültepe is a great source for us to understand the social and economic life of the period.
Cover Photo: İHA