A deep neural network trained to restore ancient Greek texts can do so with 72% accuracy when used by historians, suggests a Nature paper.
The findings could assist with the restoration and attribution of newly discovered or uncertain inscriptions with improved speed and accuracy, advancing our understanding of ancient history.
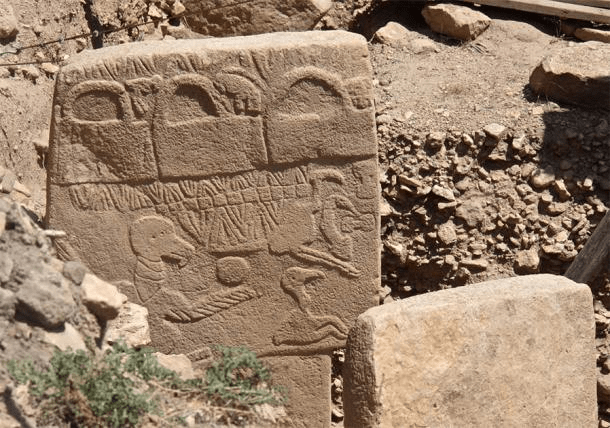
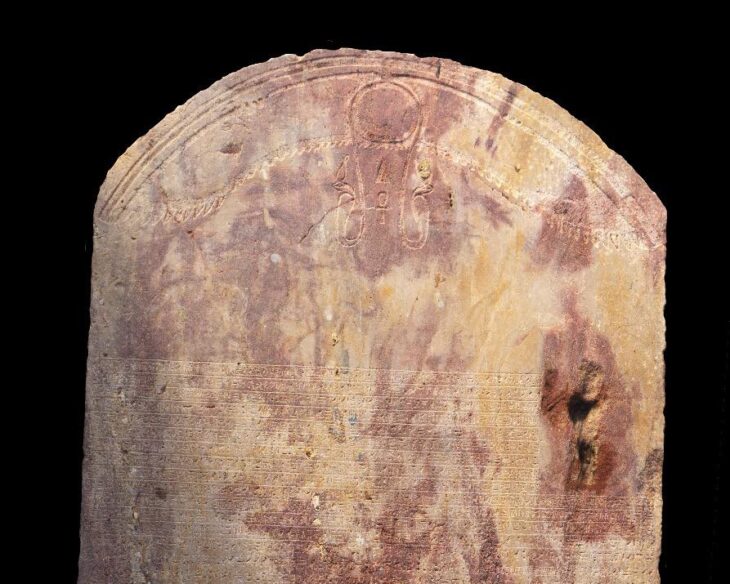
Ancient history relies on disciplines such as epigraphy—the study of inscribed texts known as inscriptions—for evidence of the thought, language, society, and history of past civilizations.
To understand the history of ancient civilizations, historians study the inscriptions created by past individuals, written directly on materials — such as stone, pottery, or metal — that have survived until today. However, over the centuries, many inscriptions have been damaged to the point of illegibility, transported far from their original location, and their date of writing is steeped in uncertainty. Specialists in the study of inscriptions, known as epigraphers, can reconstruct missing texts, but their traditional methods are highly complex and time-consuming.

To overcome the constraints of current epigraphic methods, Yannis Assael, Thea Sommerschield and their colleagues tested a deep neural network (named Ithaca), a type of artificial intelligence that was trained to restore, date, and place ancient Greek inscriptions. Ithaca’s architecture focuses on collaboration, decision support, and interpretability.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The authors found that Ithaca could achieve 62% accuracy when used alone to restore damaged texts, and 72% accuracy when it is used by a historian. Additionally, Ithaca could also help to determine inscriptions’ place and date of writing; in their experiments, it attributed inscriptions to their original locations with 71% accuracy and dated them to less than 30 years from the date ranges proposed by historians.
Ithaca is the first model to tackle the three central tasks in the epigrapher’s workflow holistically. Not only does it advance the previous state-of-the-art set by Pythia, but it also uses deep learning for geographical and chronological attribution for the very first time and on an unprecedented scale.

To demonstrate the creative potential of Ithaca, the researchers applied the model to a current discussion of dating a group of inscriptions central to the political history of classical Athens.
Historians disagree on whether these decrees should pre- or post-date 446/5 BC depending on the (dis)belief in using specific letterforms as dating criteria (the three-bar sigma dating convention). In recent years, the validity of this dating convention was called into question—the dates of many decrees have been pushed to the 420s BC, therefore profoundly influencing our understanding of Athenian imperialism.
Ithaca’s predictions for these held-out texts independently align with the most recent dating breakthroughs, therefore overturning the conventional historical reading based on the sigma dating criterion. More specifically, whereas the I.PHI labels are on average 27 years off the ‘lower’ dating proposed by modern re-evaluations, Ithaca’s predictions are on average only 5 years off the newly proposed ground truths.
The findings could unlock the cooperative potential between artificial intelligence and historians, and improve our understanding of human history.
doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04448-z