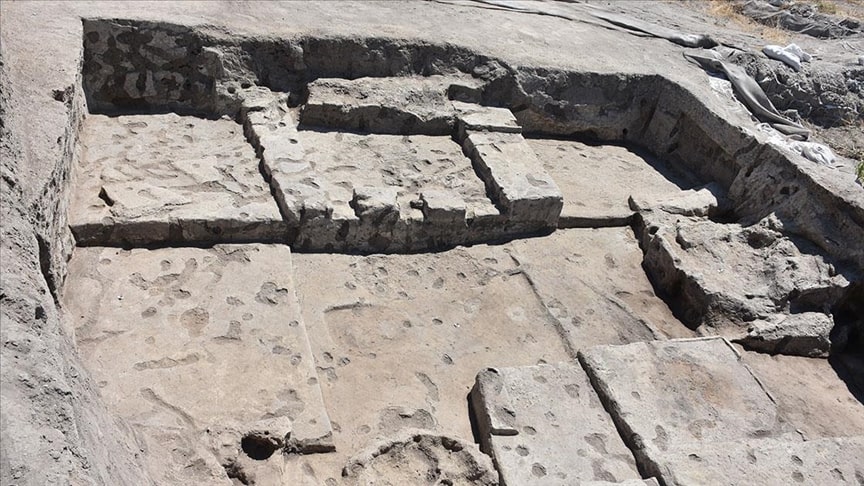
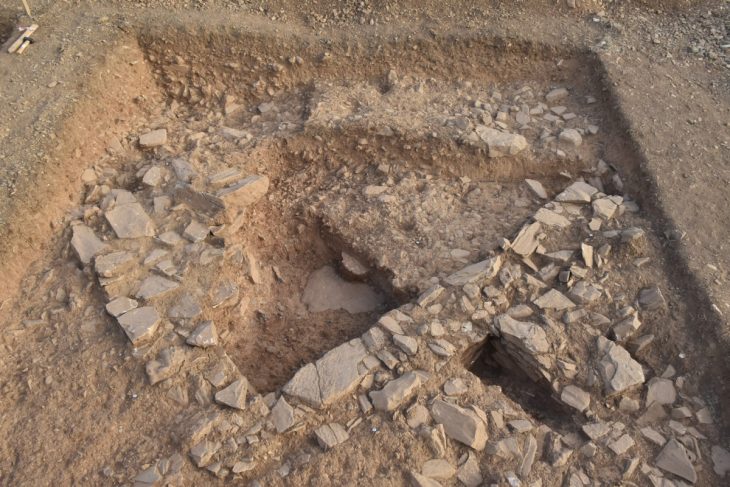
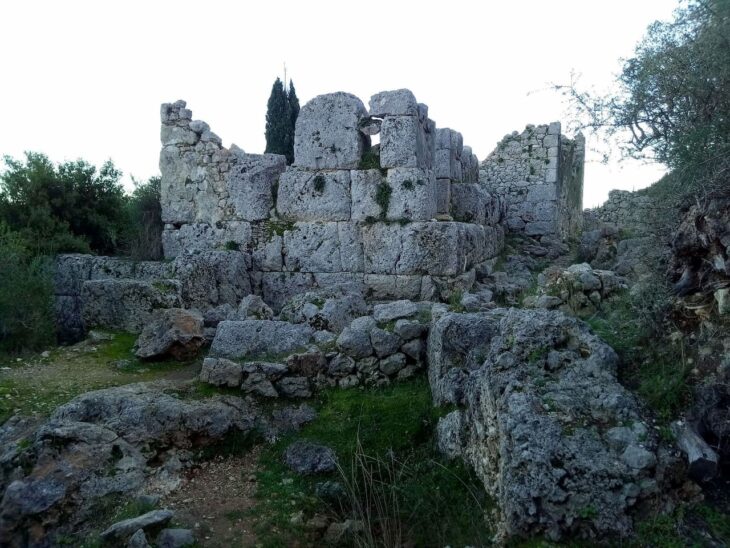
An 8,200-year-old temple structure was found during the 30th excavation season of the excavations at Çatalhöyük, one of the first urbanization models in Anatolia and the world.
Çatalhöyük, which is on the UNESCO World Heritage List, is located in the Çumra district of Konya province in the central part of Turkey.
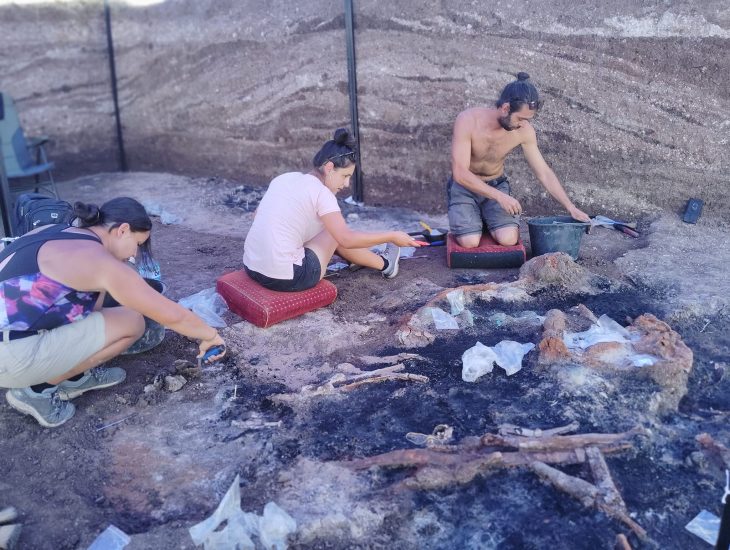
Continuing their work on the eastern skirt of the mound in the 9,000-year-old Neolithic City of Çatalhöyük, the excavation team reached a special religious structure of approximately 30 square meters.
Head of the Excavation Delegation and Anadolu University Faculty Member Associate Professor Ali Umut Türkcan reminded the AA correspondent that a new neighborhood and street were found in the northern mound last year and that excavations are continuing in this area.
Professor Arkadiusz Marciniak, a lecturer at the Poznan University Institute of Prehistory in Poland, said that he started work on the eastern area of the southern mound in 2018 and that the area, which contains traces of the last periods of Çatalhöyük, gave a surprise this year.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
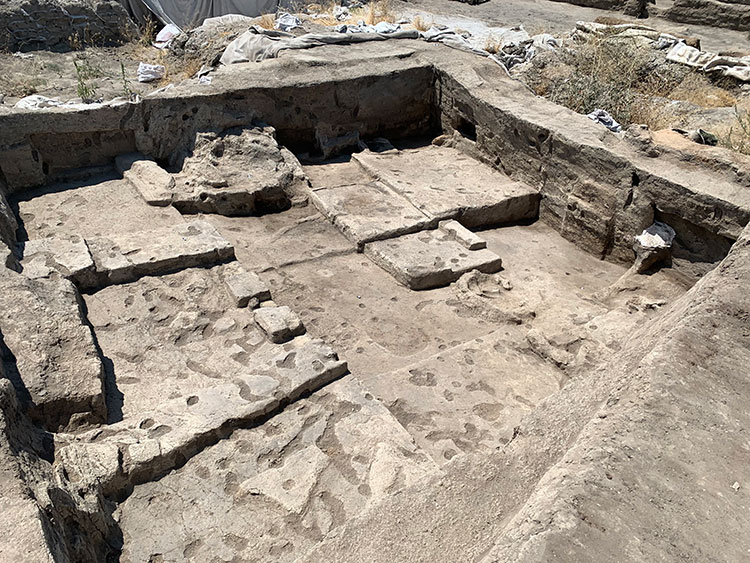

Associate Professor Ali Umut Türkcan stated that 48 of the 150 structures excavated in the first period in the 1960s were cult or belief structures called “shrines”, “We had not seen any of these structures since the 1960s until 2008. In 2008, there was only Building 77 in the northern area. There were murals and reliefs in a building measuring approximately 30 square meters, and we know that that building was specially covered. There were bull-heads and altars. We are now taking this area under protection with special techniques. We will examine it in more detail next year,” said.
“It is important in terms of showing the continuation of the worship tradition”
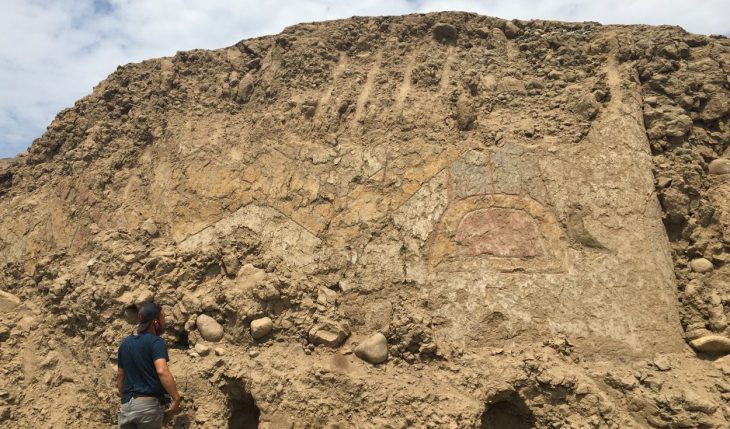
Emphasizing that the last temple found in Çatalhöyük is important in terms of showing the continuation of the worship tradition, Türkcan said that there is an altar area, benches decorated with bull heads, narrow private entrances, wall paintings, and reliefs.
Türkcan pointed out that the area was quite solid since the area was filled by the people of Çatalhöyük when the area was abandoned. ” Excavations at Çatalhöyük are carried out in two different areas. There are some unresolved questions at Çatalhöyük. We are trying to understand this. There was the phenomenon of no street, we found a street last year. Çatalhöyük covers an area of 14 hectares and we think that this settlement exceeded 7 thousand people at its greatest time. Considering that 6 to 10 percent of the area has been excavated for 61 years, the number of graves found is 830. If we multiply this by 9-10, the number will come out,” he said.
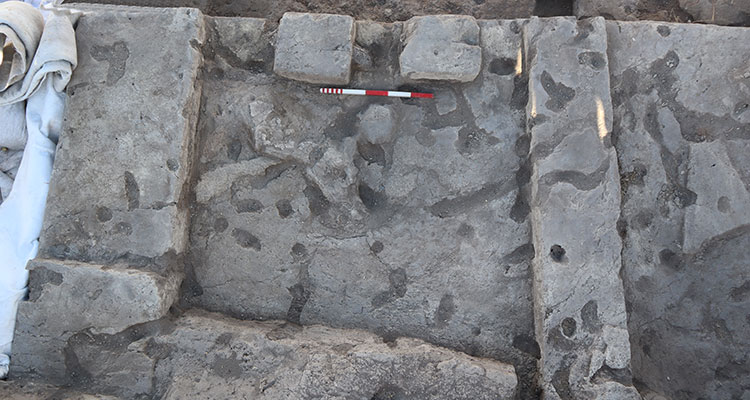

“We understand that this area is a special structure made entirely for rituals”
Professor Arkadiusz Marciniak, who carried out the excavations at the site, said that he was able to give the plans of the structures beneath when 5-10 cm of the surface was scraped in Çatalhöyük, and that he had an idea about the structures as a result of the scraping he made in the area in 2018.
Explaining that he always thought that such a structure could exist in the area, Marciniak continued:
“This building is similar to the structures that were called a temple in the previous periods, but it belongs to else a late period. It is very important that the settlement was in a phase of abandonment. The feature that distinguishes this building from the buildings used as houses is that it does not contain any elements related to domestic use. There is only a hearth. The locations of the hearths are also in a different place. The square pillars you see here look like an altar area where bull heads are displayed. There is a raised fire place in the middle. It is also noteworthy that there is a narrow entrance on both sides that can be passed by crouching. We understand that this area was a special structure entirely built for rituals. We are very meticulous. In such structures, large boards and paintings come,”
Explaining that they know that there are at least three successive phases in this structure, Marciniak said, “We don’t have radiocarbon dating yet. When we make a relative date, the building belongs to the late periods of Çatalhöyük, according to the material found here. A belief structure of 8 thousand 200 years. We should not forget that Çatalhöyük is a settlement dating back to 1200 years. It is a rare settlement in the world with a long process with early, middle, and late stages.” used the phrases.