Archaeologists and AI experts uncover a 3,000-year-old hymn praising Babylon‘s grandeur, revealing rare insights into ancient urban society, education, and gender roles.
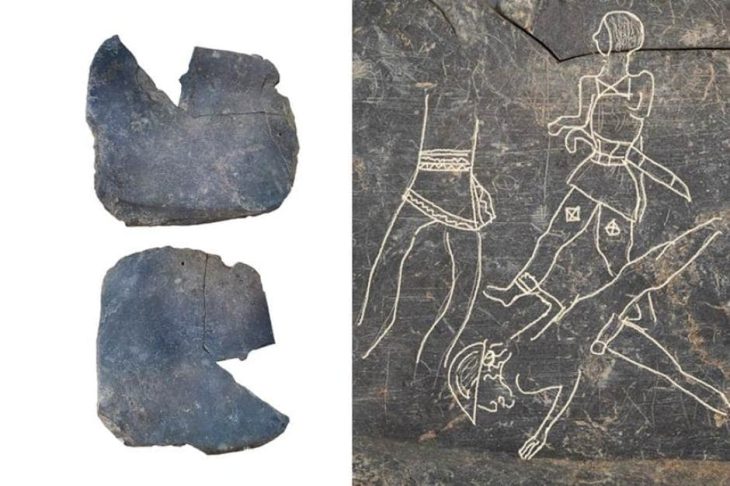
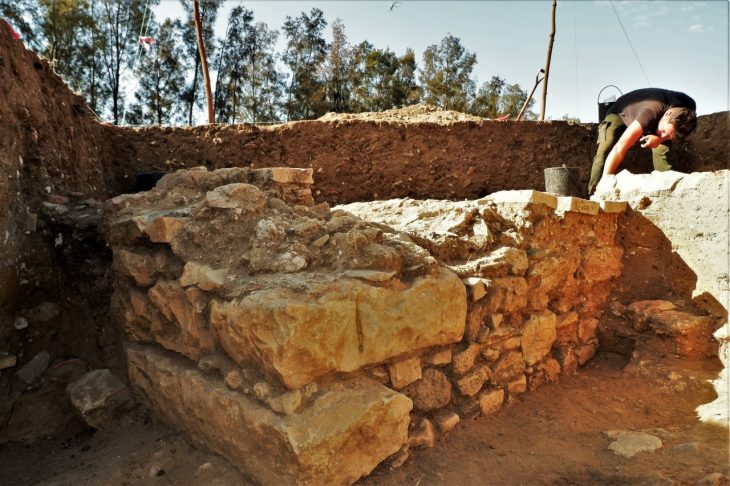
In a collaboration between Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (LMU) and the University of Baghdad, scholars have uncovered a lost Babylonian hymn of praise that dates back to around 1000 BCE. Thanks to the use of artificial intelligence and digital archaeology, this remarkable literary artifact has been pieced together from over 30 separate cuneiform tablets.
The rediscovery, led by Professor Enrique Jiménez of LMU’s Institute of Assyriology, marks a major advancement in our understanding of Babylonian culture, urban society, and religious devotion. The hymn, which extols the beauty of the city and its people, was widely copied by schoolchildren and revered across centuries — yet was lost for over a millennium.
AI Unlocks the Past: Reconstructing the Hymn
Using the Electronic Babylonian Library, a digital platform that aggregates and analyzes ancient Mesopotamian texts, researchers used AI to match fragments of clay tablets from libraries and collections worldwide. What would have once taken decades was completed in a fraction of the time.
“Using our AI-supported platform, we managed to identify 30 other manuscripts that belong to the rediscovered hymn,” said Professor Jiménez. The team was then able to reconstruct most of the hymn’s 250 lines — a significant feat, given the fragmentary nature of cuneiform records.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Babylon in Its Glory: Praise, Nature, and Justice
The hymn paints a vivid picture of Babylon, the capital of Mesopotamia and once the largest city in the world. It praises the city’s architecture, religious sanctuaries, and the life-giving waters of the Euphrates River, which fertilized the surrounding fields.
“The Euphrates is her river – established by wise lord Nudimmud –
It quenches the lea, saturates the canebrake,
Disgorges its waters into lagoon and sea,
Its fields burgeon with herbs and flowers,
Its meadows, in brilliant bloom, sprout barley,
From which, gathered, sheaves are stacked,
Herds and flocks lie on verdant pastures,
Wealth and splendor – what befit mankind –
Are bestowed, multiplied, and regally granted.”

These lines are especially significant because Mesopotamian literature rarely describes natural phenomena in such detail. Only one other known text from the period features a similar description of the spring season.
A Window into Ancient Urban Life and Education
What astonishes scholars is the hymn’s widespread use in schools. It was regularly copied by students — a rare survival for a text so broadly disseminated in antiquity yet unknown until now.
Its content offers unexpected glimpses into Babylonian society. It describes the city as a place of justice and cultural refinement, where citizens were said to protect the humble and respect foreigners — particularly foreign priests living among them.
The hymn also includes one of the few surviving references to Babylonian women, acknowledging their religious roles and social standing. Though described in terms typical for the era — focusing on devotion and discretion — these lines remain invaluable to historians studying gender roles in ancient Mesopotamia.
From Lost Text to Global Treasure
The original hymn appears to have been written by a Babylonian deeply devoted to his city and its gods. It opens with praise for Marduk, Babylon’s patron deity, and moves on to celebrate the temple Esagil, the grandeur of the city’s gates and walls, and its founding myths.
Its tone may read like ancient propaganda — comparing Babylon to precious stones and gardens — but its poetic richness and cultural value are undeniable. That the hymn survived in so many copies over centuries shows how deeply it resonated with the people.
Preserving Ancient Knowledge for the Future
This rediscovery is part of a larger mission by Jiménez and his team to digitize every known cuneiform fragment. With AI assistance, they aim to reconstruct lost literary works and preserve the cultural heritage of ancient Mesopotamia for future generations.
As Professor Jiménez aptly noted: “It’s unusual that such a popular text in its day was unknown to us before now.”
Anmar A. Fadhil und Enrique Jiménez: Literary texts from the Sippar Library V: A hmyn in praise of Babylon and the Babylonians. Doi:10.1017/irq.2024.23 In: IRAQ 2025, Cambridge University Press.
Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (LMU)
Cover Image Credit: Anmar A. Fadhil, Department of Archaeology, University of Baghdad. With the permission of the Iraqi Museum and the State Board of Antiquities and Heritage