New research suggests an ancient trade hub lies beneath Egypt’s Red Sea coast—offering clues to how early civilizations connected Africa to the wider world and influenced patterns of human migration.
What if one of humanity’s earliest international ports is hidden beneath the Red Sea?
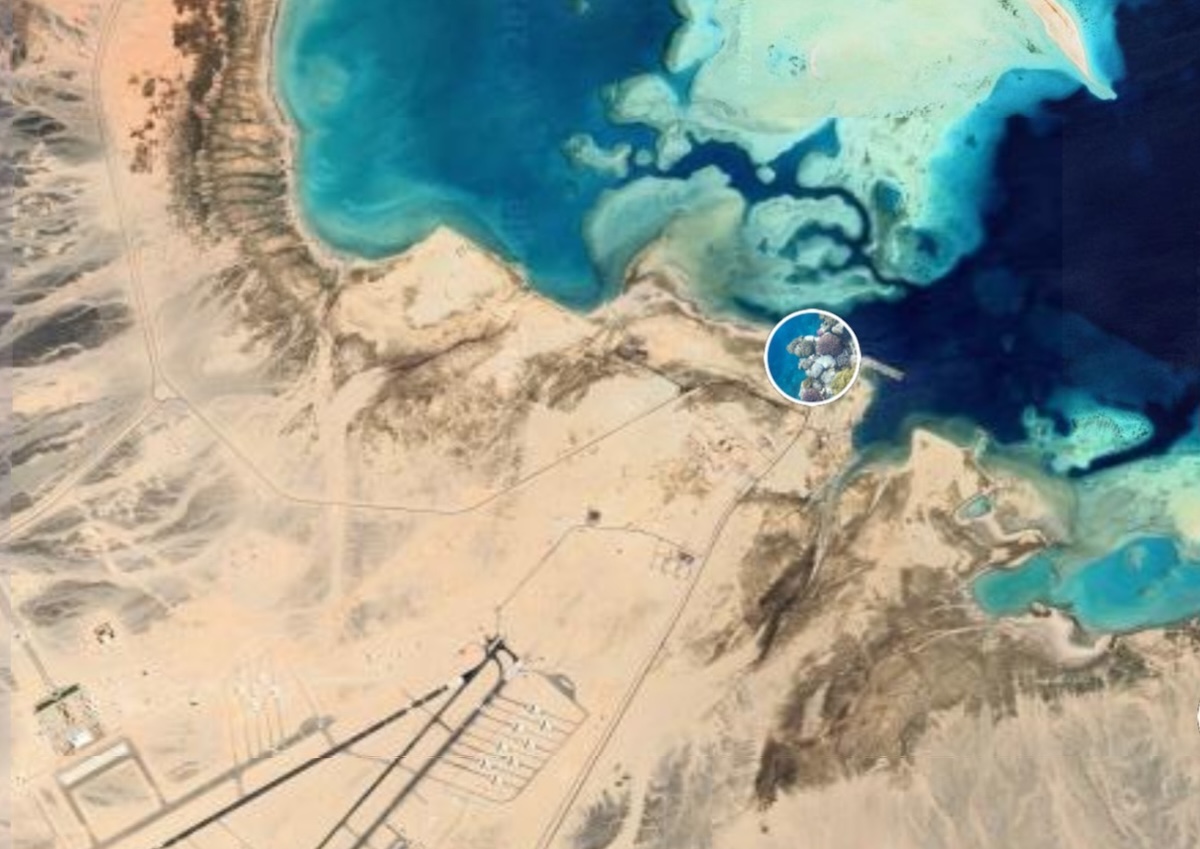
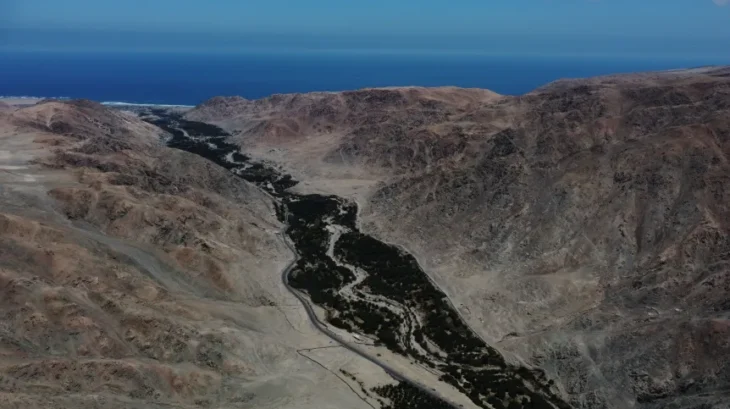
In a discovery that could dramatically reshape our understanding of ancient trade, migration, and civilization, researchers have identified a region along Egypt’s Foul Bay that may have hosted a thriving coastal city—now submerged under the sea. Named Berenice Aquaterra by scientists, this lost port may have once connected Africa to the Mediterranean, serving as a critical crossroads for early human movement and commerce.
The finding comes from a study led by Jerome Dobson, professor emeritus at the University of Kansas, and Italian collaborators Giorgio Spada and Gaia Galassi. Published in Comptes Rendus Géoscience, their research uses cutting-edge glacial isostatic adjustment (GIA) models to simulate ancient coastlines from 30,000 years ago to the present. These reconstructions, combined with DNA and archaeological data, suggest vast areas of land now underwater once hosted early human settlements.
“We’re not just looking at abstract coastlines,” Dobson said. “We’re potentially looking at the remains of a city that helped move goods, people, and culture between continents.”
A City Lost to Rising Seas?
During the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) roughly 21,000 years ago, sea levels were up to 125 meters lower than today, exposing large areas along the Red Sea. Foul Bay, now an inlet on Egypt’s eastern coast, was a dry and potentially strategic location—offering a shorter and safer overland route to the Nile River than the longer Suez corridor. Dobson and his team propose that this area could have developed into a port city to facilitate trade between inland Africa and seaborne routes.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
What makes this hypothesis more than just theory is the unusual pattern of coral reefs in Foul Bay—over 300 patch coral formations, many growing on what may be ancient stone foundations. “Coral reefs require hard substrates. If these reefs are sitting on masonry or human-built structures, we could be looking at a submerged archaeological site of global importance,” Dobson noted.
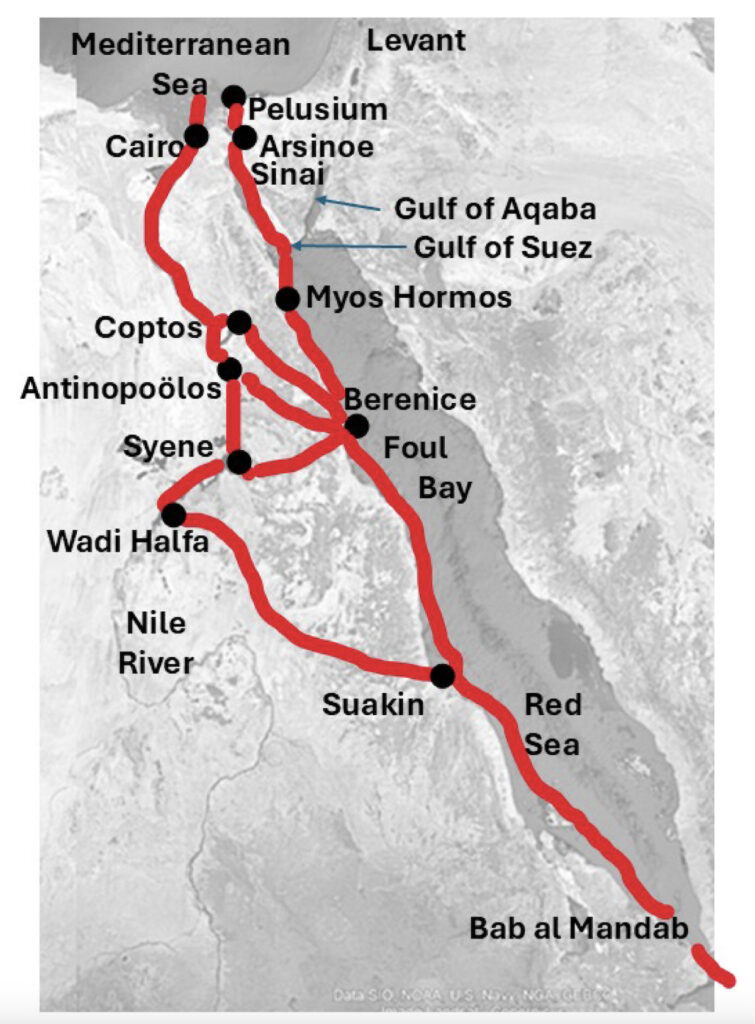
Rewriting the Map of Ancient Trade
The potential existence of Berenice Aquaterra challenges traditional views of how early civilizations moved across and beyond Africa. Instead of relying solely on the narrow Suez land bridge, ancient people might have utilized this southern route when sea levels made it viable—connecting to the Nile and eventually reaching the Mediterranean.
“If proven, this would place Foul Bay as one of the earliest known hubs of human trade,” Dobson said. “It’s like discovering a missing piece of the ancient world’s infrastructure.”
The area’s historical counterpart, Berenice Troglodytica, became a major Greco-Roman port 2,000 years ago. But this new research suggests that Foul Bay’s significance predates that by thousands of years.
Underwater Archaeology’s Next Frontier
Despite centuries of archaeological interest in ancient Egypt, much of the region’s submerged coastline remains unexplored. The researchers are calling for underwater surveys to investigate the coral-covered seabed of Foul Bay.
“Just because something hasn’t been found doesn’t mean it never existed,” Dobson noted, referencing how the famed Lighthouse of Alexandria remained hidden for centuries—only to be rediscovered underwater near its original location.
The open-access GIA datasets provided by the team make it easier for researchers across disciplines to pursue their own investigations into humanity’s submerged past.
“This isn’t just about one city,” Dobson emphasized. “It’s about recognizing that massive portions of human history might be lying just beneath the waves, waiting to be rediscovered.”
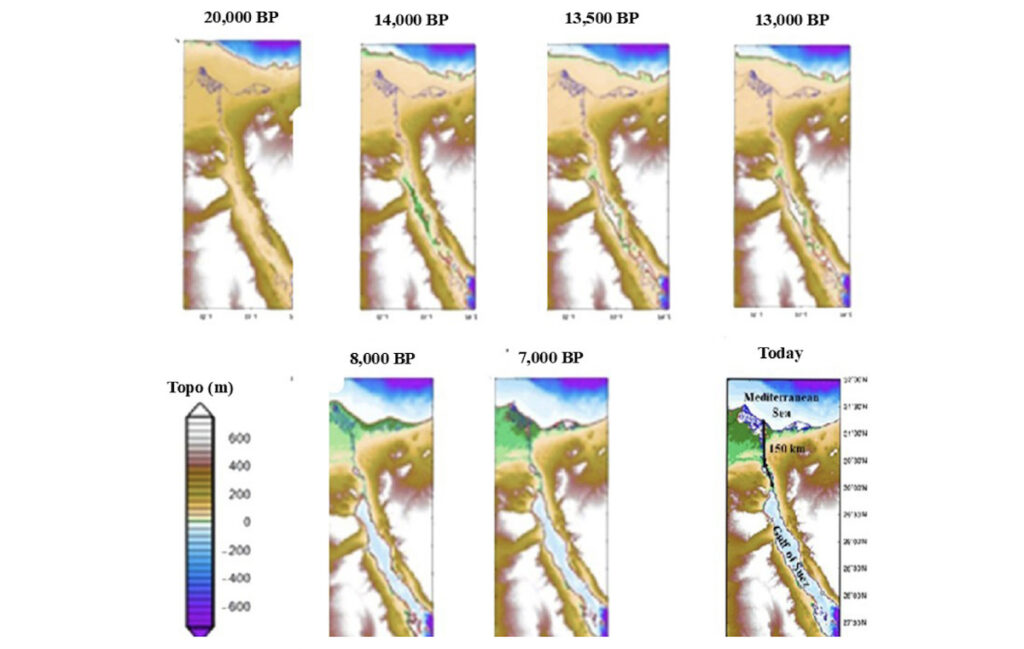
As climate change continues to reshape our own coastlines, the lessons from Berenice Aquaterra could be more relevant than ever—offering a glimpse into how ancient humans adapted to a world in flux and how much we’ve yet to uncover about our shared origins.
Jerome Eric Dobson, Giorgio Spada, Gaia Galassi, Alternative crossings into and out of Africa since 30,000 BP. Comptes Rendus. Géoscience, Volume 357 (2025), pp. 1-24. dx.doi.org/10.5802/crgeos.273
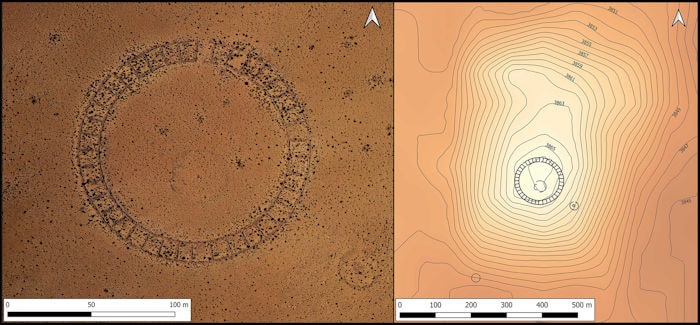
Cover Image Credit: Satellite image of Berenice, an ancient port, on the Red Sea coast. A KU researcher asserts new information about Berenice should prompt reexamination of migration into the Nile Valley before or during the Last Glacial Maximum. Coral reefs near Foul Bay might hold more clues, according to Jerome Dobson. NASA