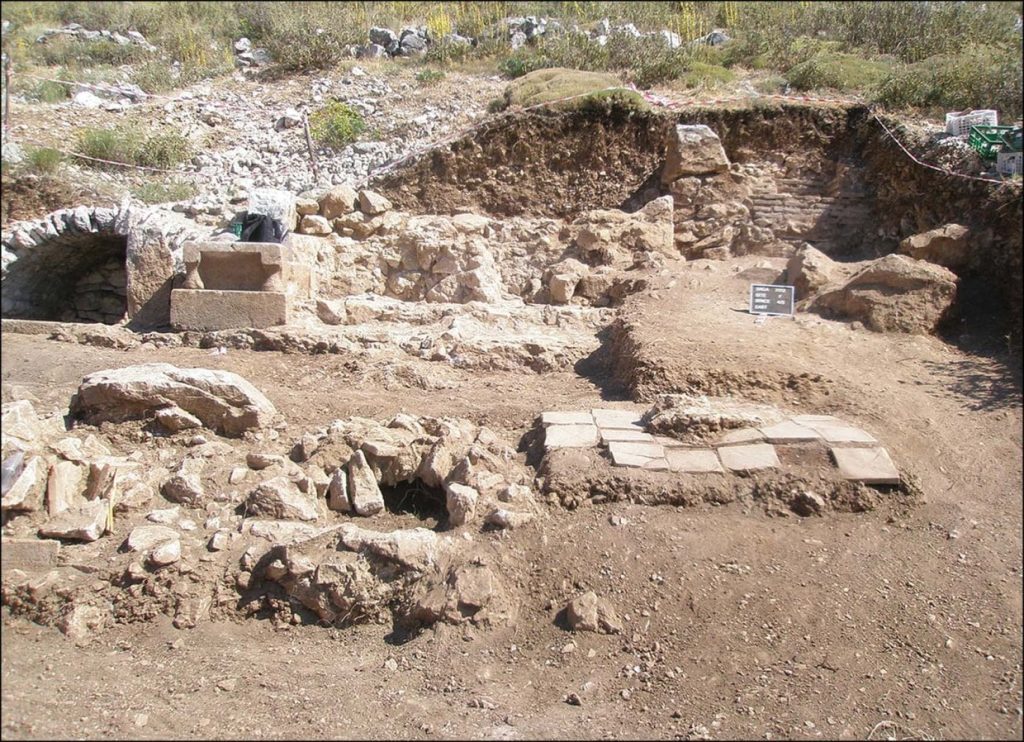
In the ancient city of Sagalassos in southwestern Türkiye, archaeologists have identified an unusual burial practice from the early Roman imperial period, consisting of deliberately bent nails, covering tiles, and a layer of lime.
A team of archaeologists from KU Leuven and the Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences, both in Belgium, have published their new work in the journal Antiquity.
Unearthed at the famed archaeological site of Sagalassos in the Türkiye’s southwest, the tomb, which dates back to A.D. 100-150, contains evidence to suggest that the people of the time were terrified that the dead might rise up from the grave to haunt the living.
Each of these characteristics, which were also present in other ancient Mediterranean burials, points to the possible use of magic to prevent the dead from interfering with the lives of the living.
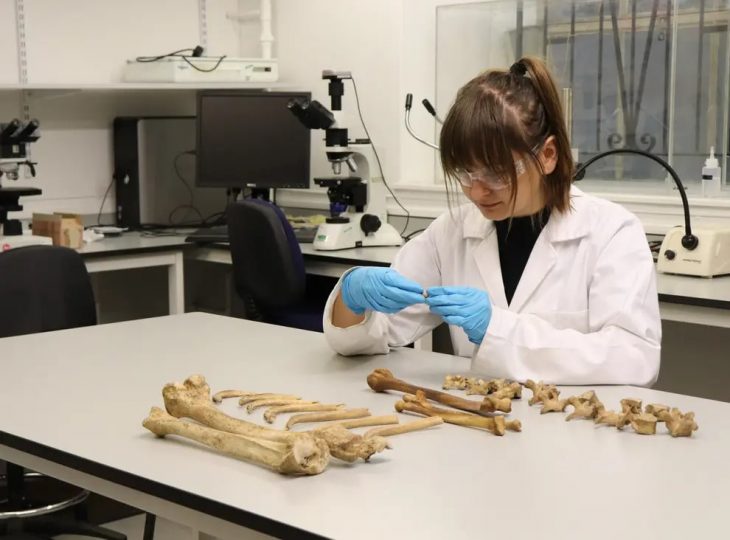
The artifacts revealed that the people of the time had performed cremations differently than others of the Roman era—instead of using a funeral pyre, collecting the remains, and moving them somewhere else, the people in Sagalassos performed their cremations in place.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
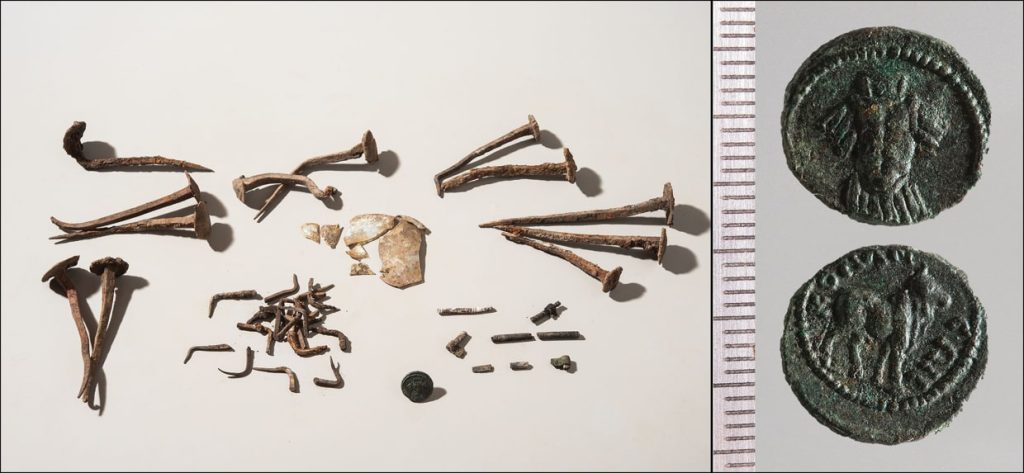
There was no need to move them as a result. They also found that items, such as intentionally bent nails, buried with the remains were unique.

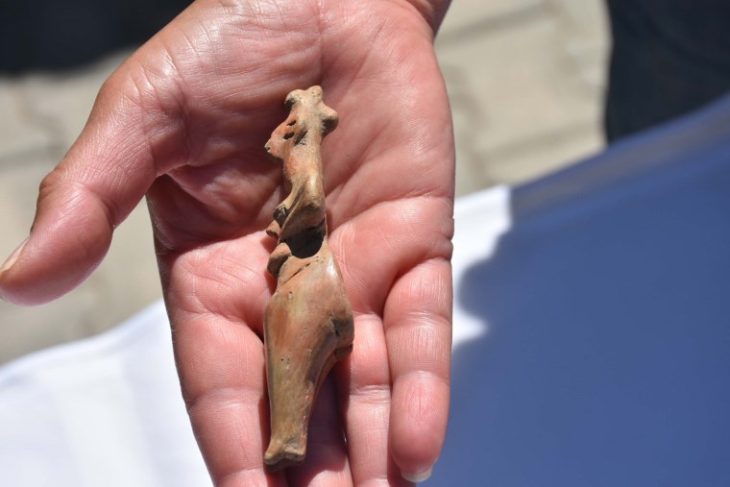
41 broken and bent nails discovered along the burn area’s edges are extremely unusual. Twenty-five nails were bent at a 90° angle and their heads were twisted off. Sixteen of them were deliberately bent or twisted but still had their heads. They could not have been used for a practical purpose, and their distribution around the pyre’s perimeter indicates that they were placed.
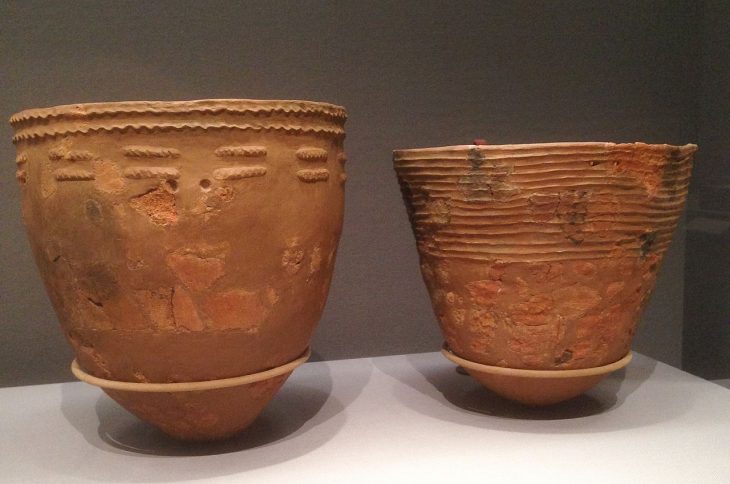
Grave goods discovered include a coin from the second century, a few little ceramic urns from the first century, two blown glass urns, and a hinged object.
According to the research team, unique burial rites were performed in order to prevent the deceased from escaping. Those burying them were apparently afraid of retaliation of some kind, so they used every means possible to keep the deceased person safely buried.

The bent nails, for example, were most likely used as a “magic barrier,” going all the way around the charred bones and ashes of the remains. Lime appeared to have been used by those involved in the burial to keep the person, or their spirit, from escaping from the ground, rather than for aesthetic reasons.
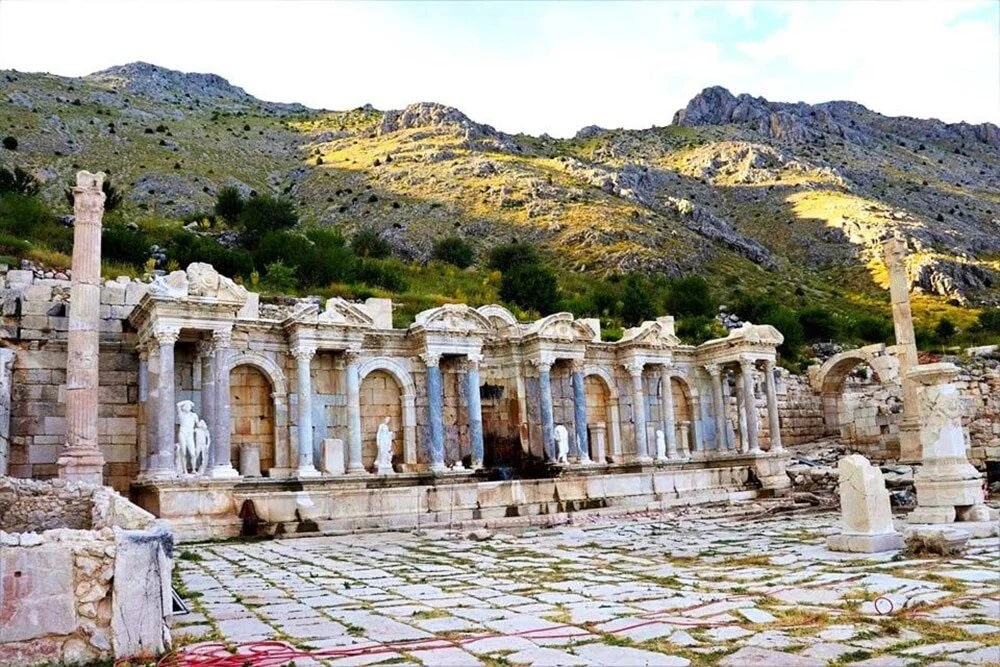
The archaeological site of Sagalassos is located in southwest Türkiye, near the present town of Ağlasun (Burdur province); roughly 110 km to the north of the well-known port and holiday resort of Antalya.
Sagalassos was a city-state of the Hellenistic Attalid Kingdom by the 2nd century B.C. It was founded in the late 5th century B.C., when the area was still a part of the Achaemenid Empire, and it passed to the Roman Republic in 133 B.C. The city flourished during the Roman Imperial era after Augustus included it in the Roman province of Galatia in 25 B.C. The city declined in importance in late antiquity.

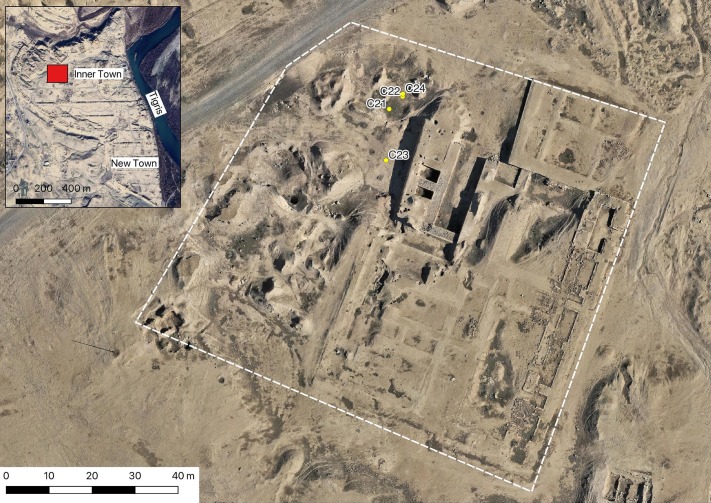
The Catholic University of Leuven has been systematically excavating the site since 1990. The Sagalassos Archaeological Research Project of KU Leuven began a fresh investigation of the city’s northeastern edge in 2010. The area was originally dedicated to agricultural terracing, but as the city expanded in the Hellenistic period, it began to be used for funerary purposes. In the end, the excavation turned up inhumation and cremation graves that dated from the late Hellenistic (c. 150–25 B.C.) through the Late Roman (c. 300–450/475 A.D.) periods.