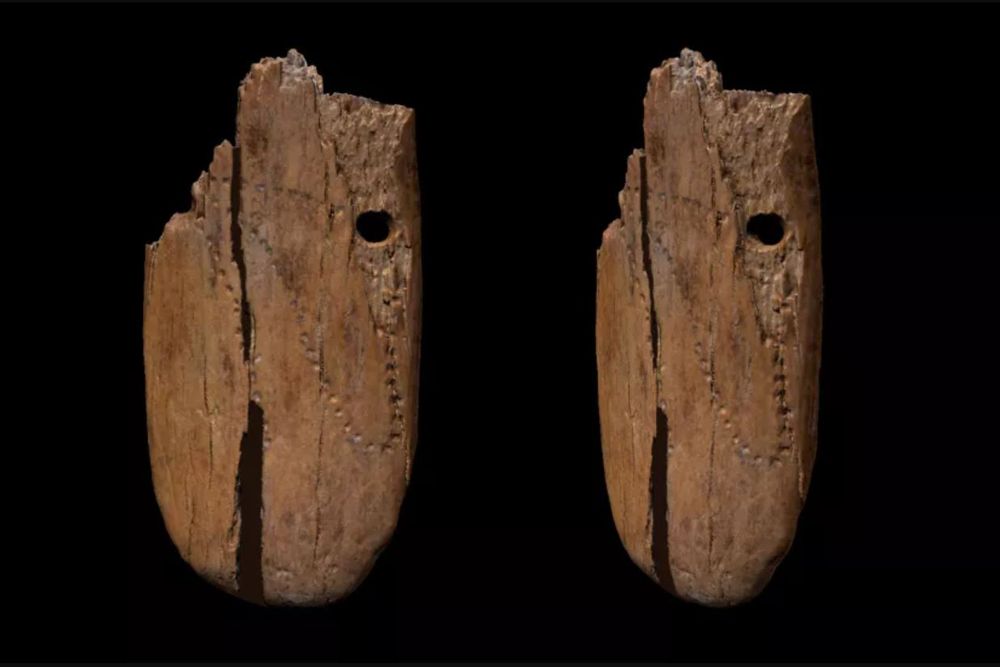
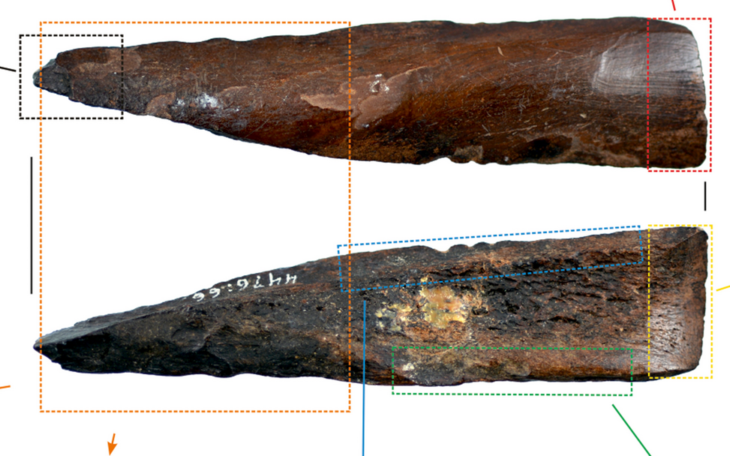
The fragments of an ancient pendant made of mammoth ivory were unearthed in Poland, and are regarded to be the oldest known example of intricate jewelry ever uncovered in Eurasia.
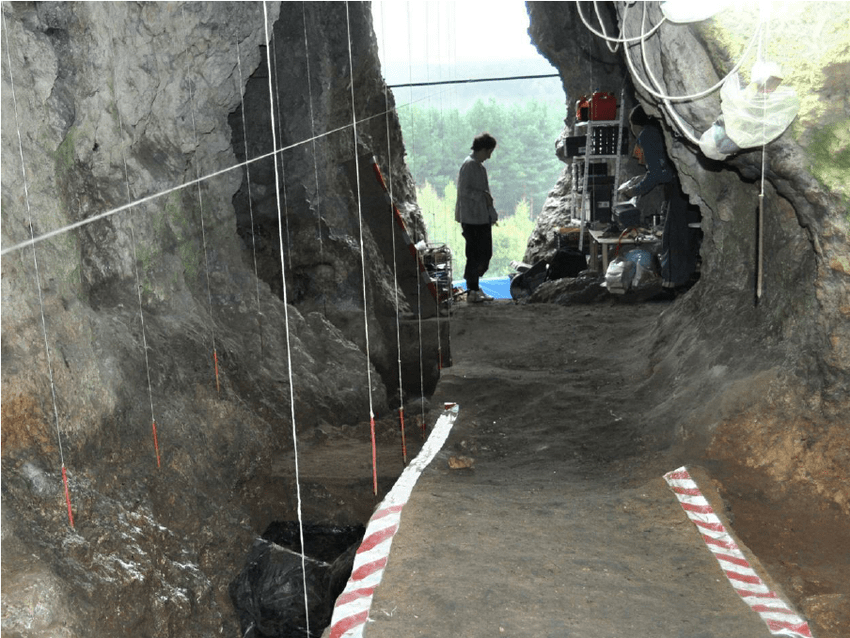
Archaeologists discovered it in the Stajnia cave in southern Poland in 2010, and new radiocarbon analysis has dated it to roughly 41,500 years ago from when Homo sapiens were in Europe.
The Stajnia Cave is one of the most important archaeological sites due to the finds of the first remains of Neanderthals in Poland, and several tens of thousands of flint artifacts from the Middle Palaeolithic.
Researchers said the Stajnia Cave plate is a piece of personal ‘jewelry’ that was fashioned 41,500 years ago (directly radiocarbon dated). It is the earliest known of its sort in Eurasia, and it marks a fresh beginning for a practice that is closely related to the expansion of modern Homo sapiens in Europe.
The oldest evidence of body decoration in Europe is found about 46 ka BP in the Initial Upper Paleolithic strata of Bacho Kiro, where multiple carnivore teeth were fashioned into pendants.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

A new novel accessory—the alignment of punctuations—appeared on certain ornaments in south-western France and figurines in the Swabian Jura (Germany) as part of these revolutionary accessories. Researchers wrote, so far the majority of these distinctive adornments have been found during earlier digs, with little identification of site formation histories or post-depositional disruption. They said As a result, rather than direct dating, their chronological attribution has relied only on stratigraphic context.
Reporting their discovery in Scientific Reports, the archaeologists said The first news: “The decoration of the pendant included patterns of over 50 puncture marks in an irregular looping curve and two complete holes.”
They added that each puncture could represent a successful animal hunt or cycles of the moon or sun.
Sahra Talamo, who led the study, said: “Determining the exact age of this jewelry was fundamental for its cultural attribution, and we are thrilled with the result.
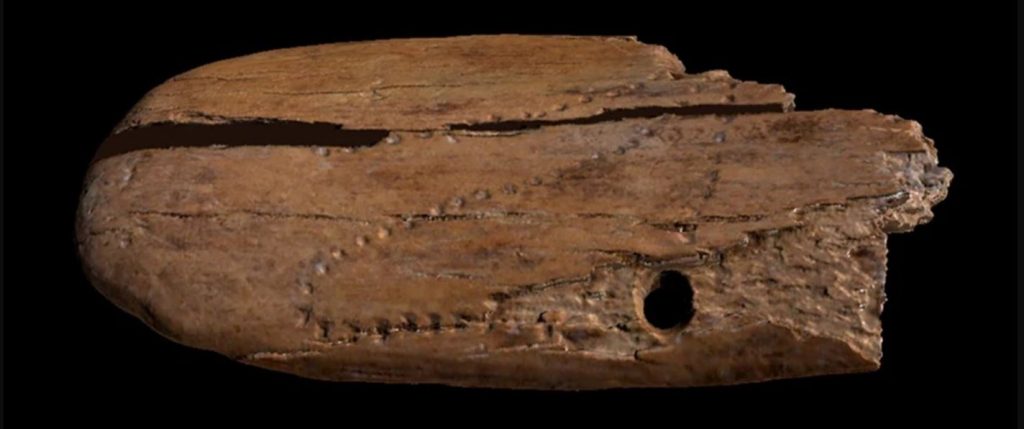

“This work demonstrates that using the most recent methodological advances in the radiocarbon method enables us to minimize the amount of sampling and achieve highly precise dates with a very small error range.
“If we want to seriously solve the debate on when mobiliary art emerged in Palaeolithic groups, we need to radiocarbon date these ornaments, especially those found during past fieldwork or in complex stratigraphic sequences.”
Co-author Wioletta Nowaczewska added: “This piece of jewelry shows the great creativity and extraordinary manual skills of members of the group of Homo sapiens (Homo neanderthalensis) that occupied the site.
“Plakanın kalınlığı yaklaşık 3,7 milimetredir ve delikleri ve onu takmak için iki deliği oyma konusunda şaşırtıcı bir hassasiyet gösterir.”