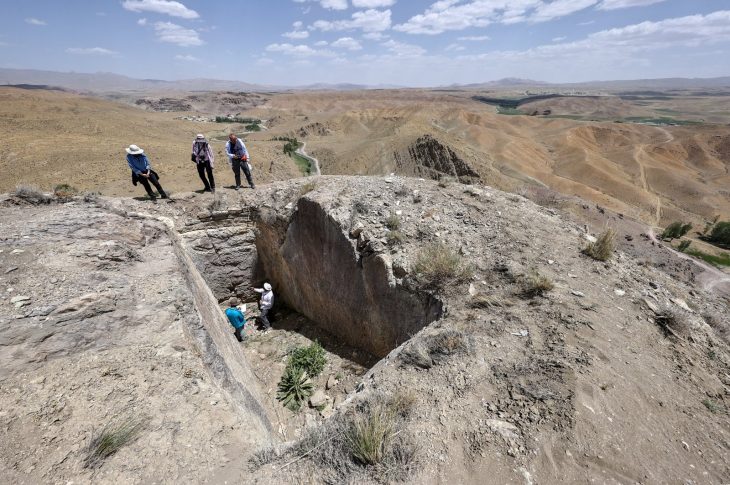
In the Steinacher area (Canton of Aargau) on the Limmat there was a Roman settlement that was significantly larger than long assumed. Before the remains are destroyed for housing development, the cantonal archeology department carries out large-scale excavations.
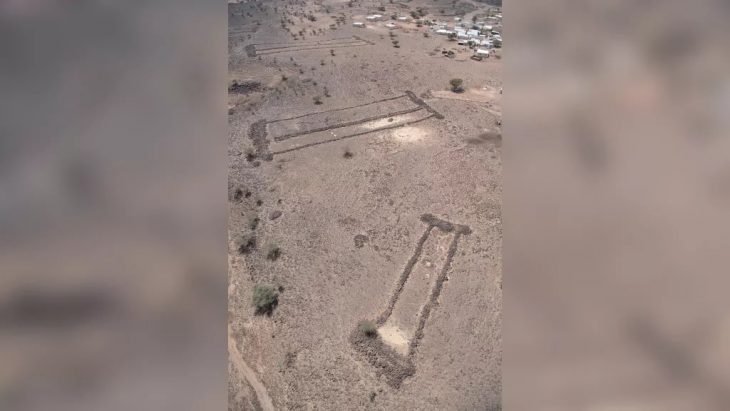
It has long been known that Romans once lived in what is now the Steinacher area of Gebenstorf. The first finds were made in the 17th century, and in 1856 the graves of Roman legionnaires came to light during the construction of a railway line. Until recently, however, it was not known that there was even a large Roman settlement on the site on the Limmat.
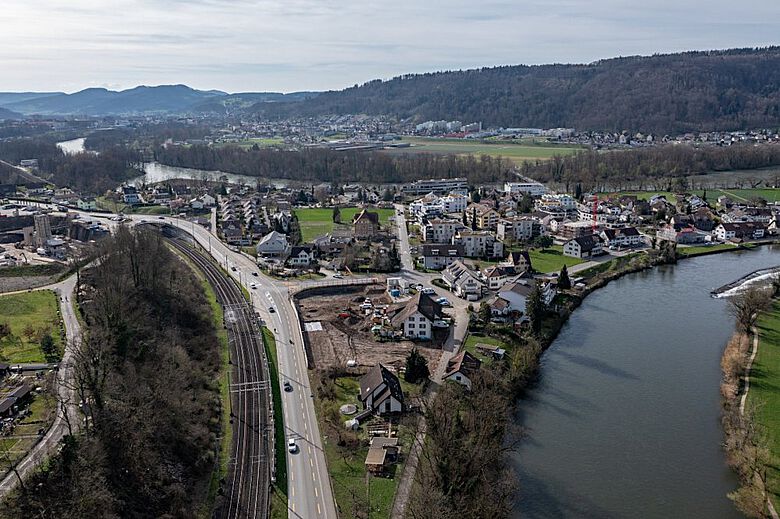
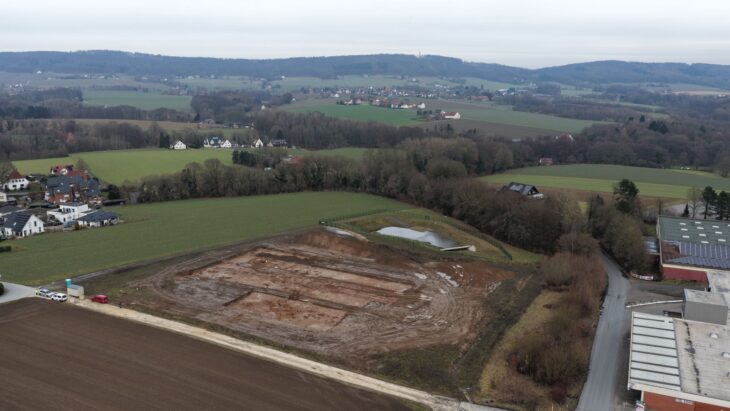
During the preliminary excavation in advance of the planned excavation, the first wall foundations and Roman building rubble, as well as individual finds, came to light on the building plot between Limmatstrasse and Vogelsangststrasse. Here in Gibstorf in the “Steinacher”, about 2.2 kilometers from the Roman legionary camp in Vindonissa, a residential development with an underground car park is planned. Even before construction begins, Cantonal archeology (Die Kantonsarchäologie) is now documenting the archaeological remains before they have to make way for new living space. The rescue excavation began at the beginning of April.
The earthworks affect an archaeologically relevant area of 3,200 square meters. The terrain here will be excavated to a depth of several meters. Finds reported since the 17th century and targeted investigations by the cantonal archaeological service between 2017 and 2023 have revealed an extensive Roman settlement site with well-preserved stone buildings in places in and around the affected plot.
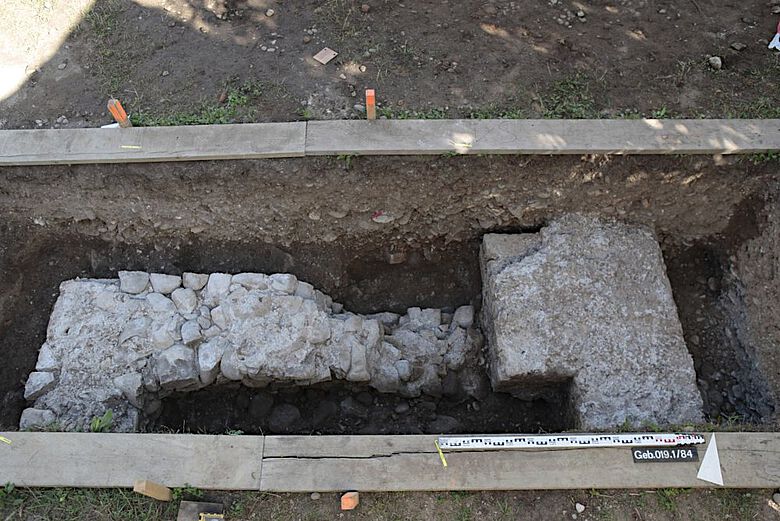

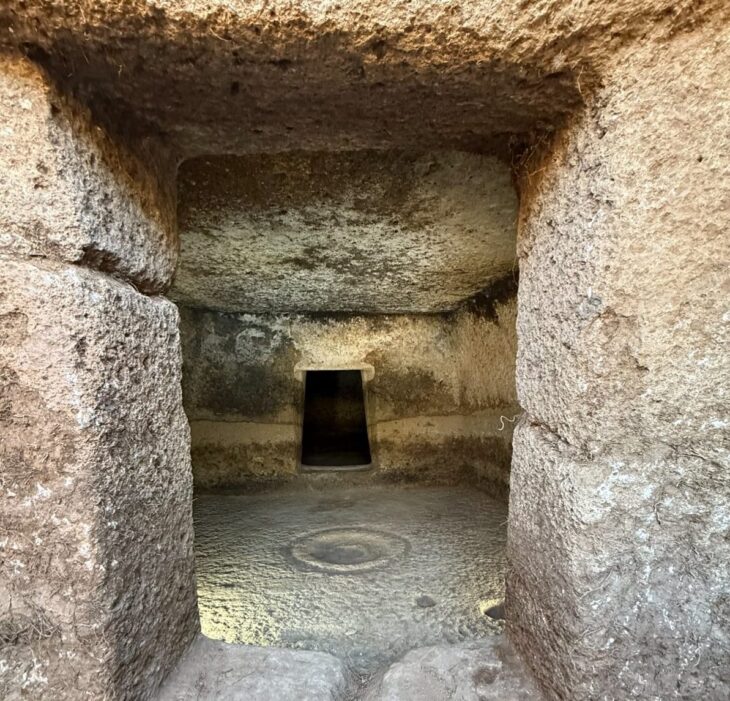
An ancient cemetery with gravestones of soldiers stationed in Vindonissa was located directly to the west of the affected plot 2,000 years ago. As similar constellations in the Roman Empire show, the settlement and cemetery of Gebenstorf were laid out at an apparently legally binding distance – in Latin: “extra leugam” – from the associated garrison town of Vindonissa. The leuge is a Roman mile and corresponds to 2.22 kilometers, which is exactly the distance between the legionary camp and the settlement site in Gebenstorf.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
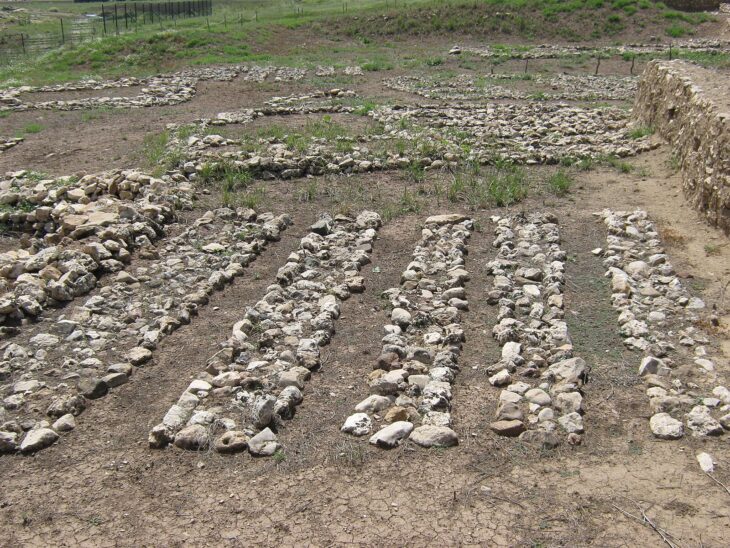
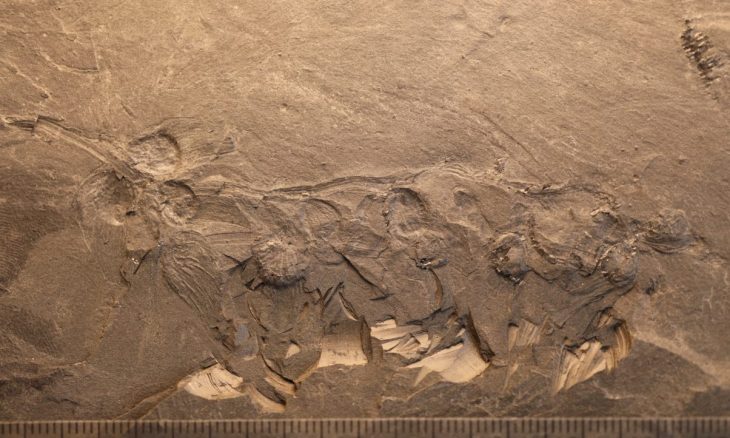
As early as 2019 and 2020, when there was no concrete construction project yet, the cantonal archeology conducted its field course with volunteers in the Steinacher in Gibenstorf. Under the direction of cantonal archeology, the volunteers documented the walls of a large stone building, the construction of which, with projecting buttresses and pilaster foundations, indicates a granary or a warehouse. A monumental building with an administrative function is also conceivable. The majority of finds were amphora shards, which most likely suggest a kind of reloading station immediately south of the Limmat.
The planned construction measures include in-depth excavation for the basement and ground floor, earth interventions for factory lines and systems, removal for construction site installations and changes to the terrain as part of the surrounding design. As a result, the Roman remains preserved in the ground are destroyed, which is why cantonal archeology, in accordance with the legal mandate, scientifically examines the areas beforehand, documents them and secures the finds.
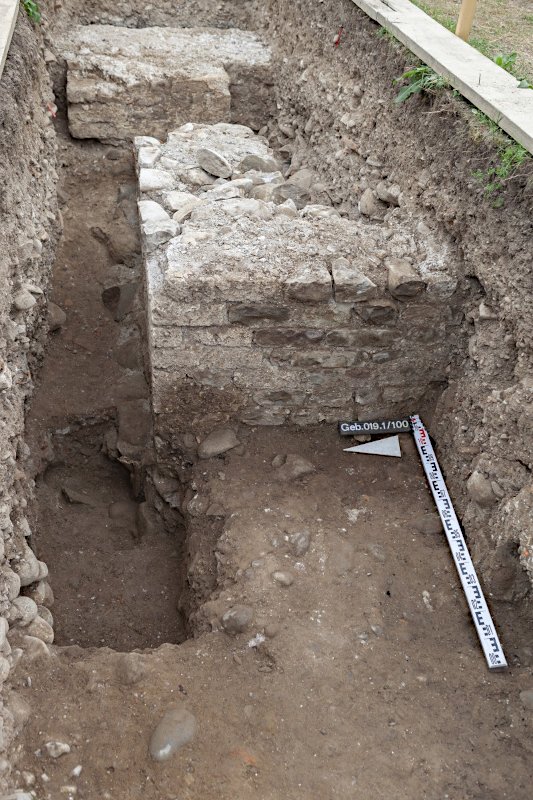

The rescue excavation will take place in two excavation stages from April to November 2024 and March to May 2025. The building perimeter will be released for the new building at the beginning of June 2025, and the western part will be released in autumn 2024. Here, the excavation and the construction project are closely linked. The scientific and conservational follow-up work on the recovered small finds will then extend until November 2025.
The excavation in Gibstorf not only secures the archaeological remains but also enables knowledge of the history of Vindonissa to be gained. From a scientific point of view, the complex of this “planned settlement” is of great importance, as here, in a largely undisturbed area, essential statements can be made on the question of the relationship between Roman military camps and their civilian settlements, which is intensively discussed in international research.
The results of the excavation will be conveyed during the further course of the investigation with excavation tours. We can look forward to the coming weeks.