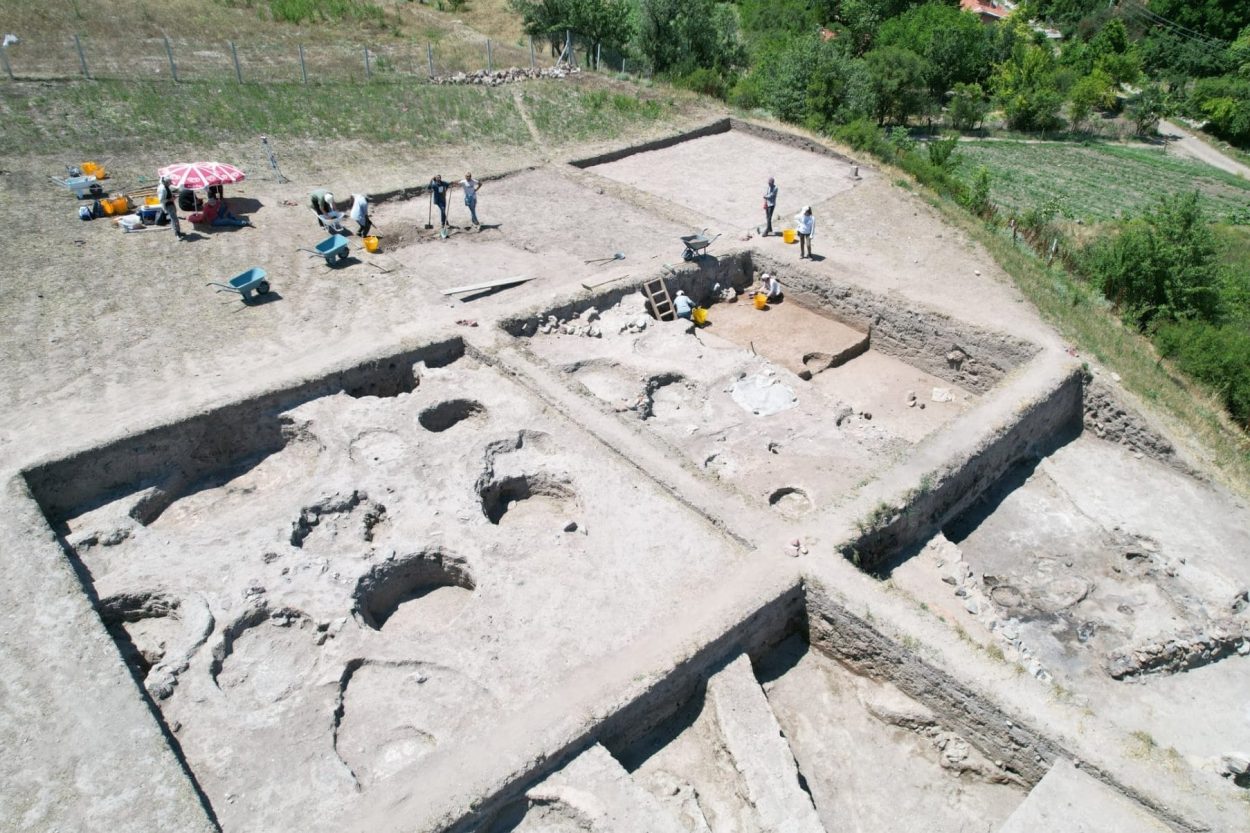
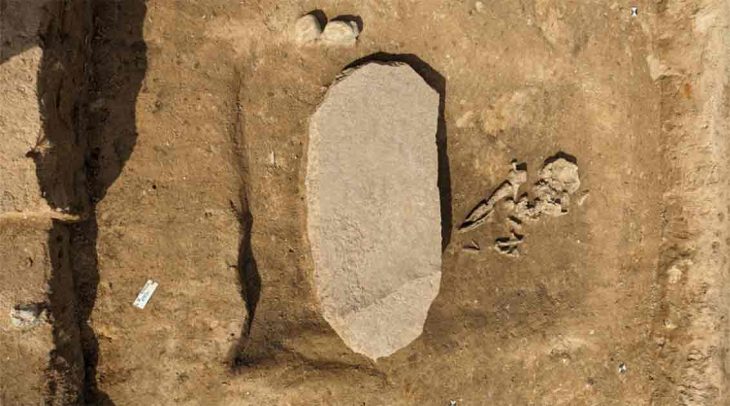
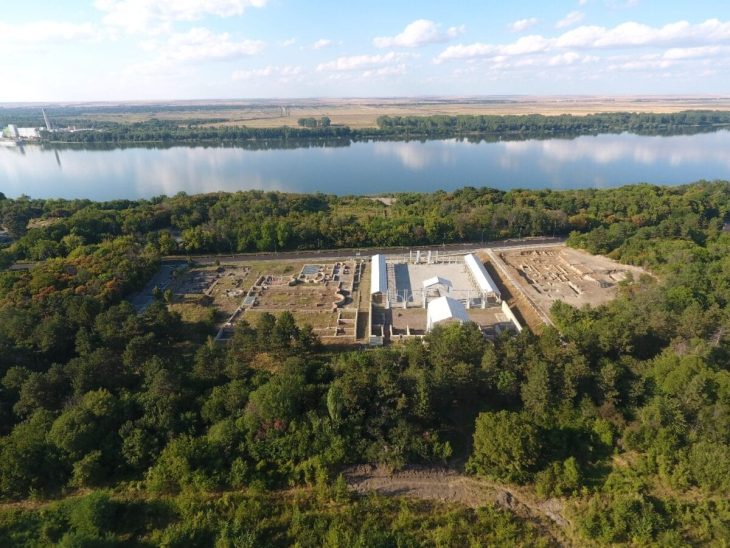
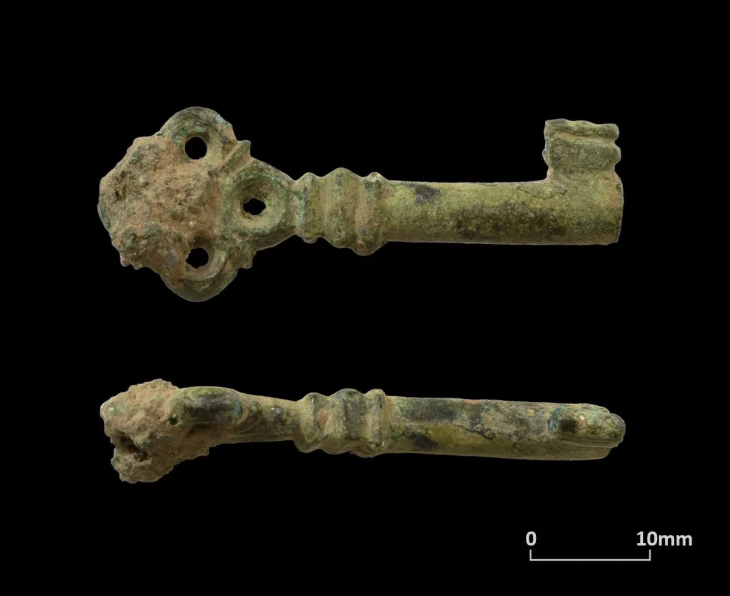
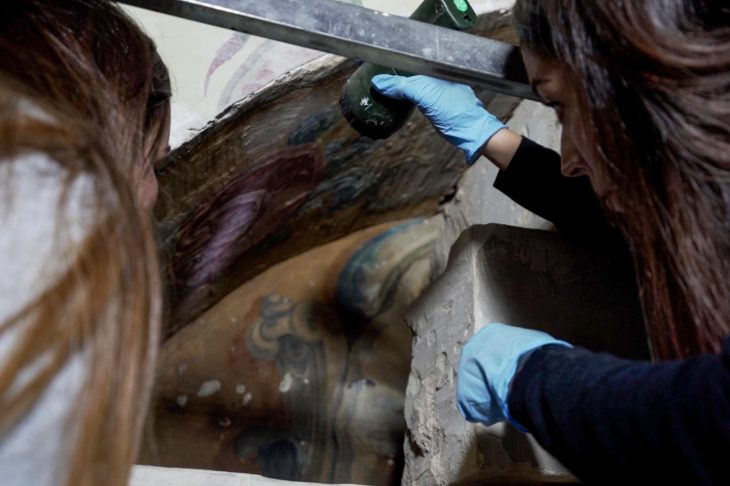
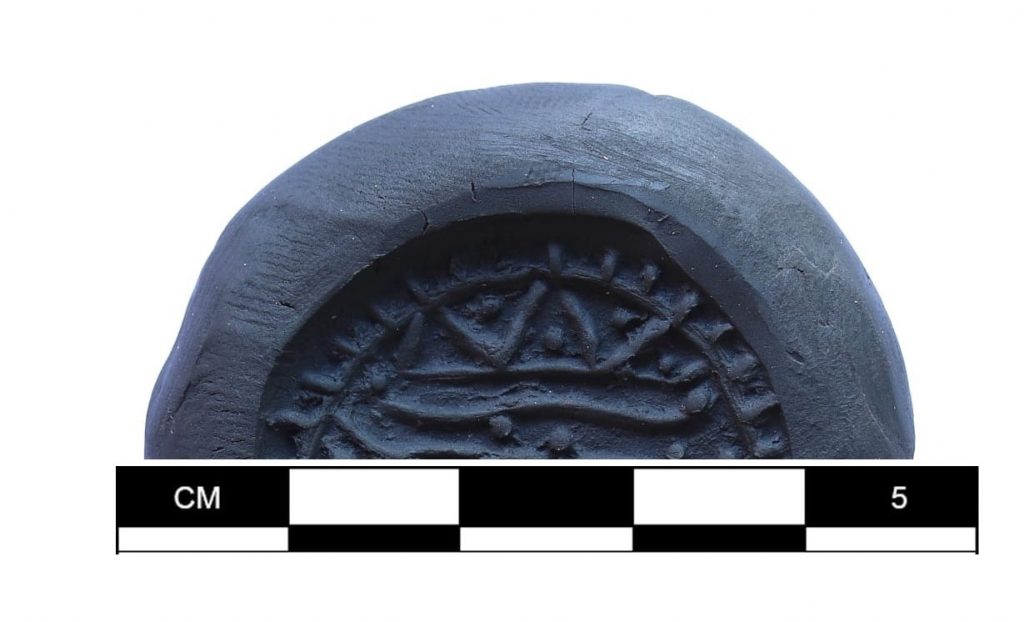
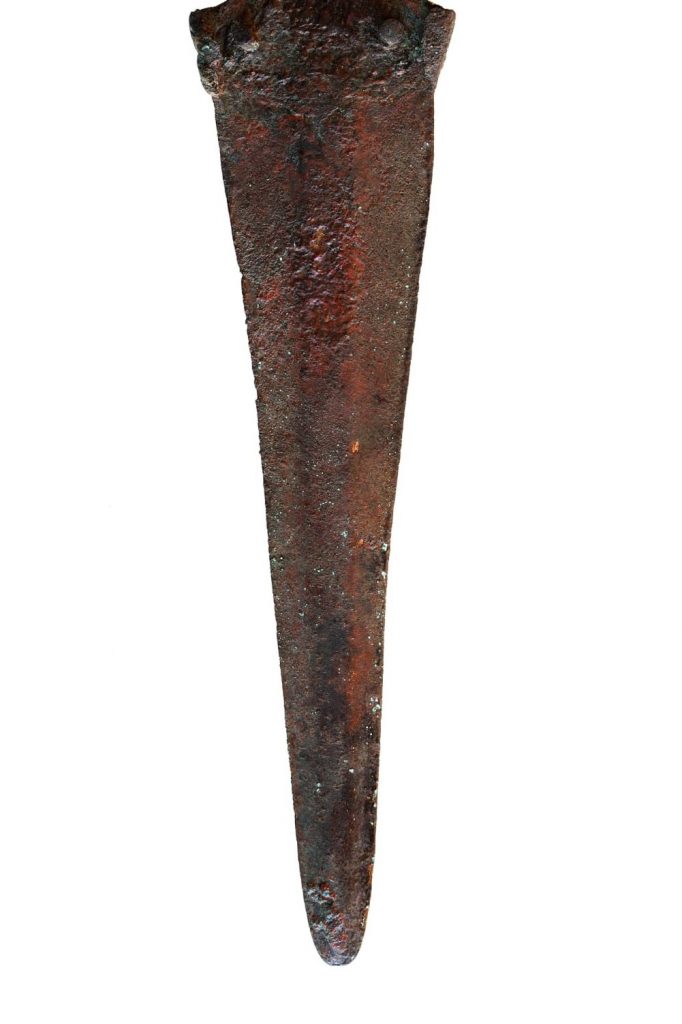
A unique 3300-year-old seal and a sword/dagger reminiscent of Mycenaean swords were unearthed during the excavations of Tavşanlı Höyük (Tavşanlı Mound), the oldest known settlement in Kütahya, dating back 8000 years.
The excavations started in Tavşanlı Höyük, which is called the “Heart of Western Anatolia” because it looks like a heart in aerial shots, and continue in cooperation with the Ministry of Culture and Tourism and Bilecik Şeyh Edebali University.
It was announced that a unique 3300-year-old seal and a sword/dagger reminiscent of Mycenaean swords were unearthed in the excavations of Tavşanlı Höyük, with a post shared today from the official social account of the Department of Excavations and Researchs.
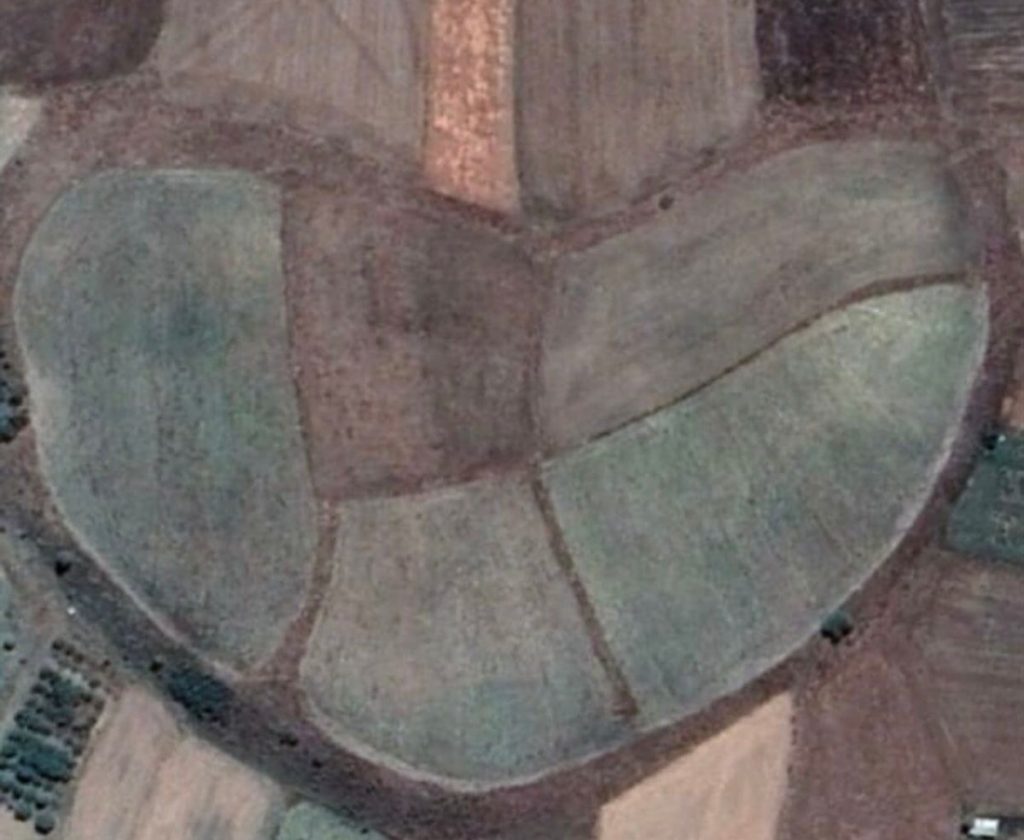

Since Tavşanlı Höyük is located on the transition route between Western Anatolia and Central Anatolia regions, the studies carried out here are crucial in terms of understanding interregional communication.
The excavations of the mound, which spans an area of 45 hectares, are carried out by the Archeology Department of Bilecik Şeyh Edebali University. A team of 25 local and foreign experts accompanies the research carried out under the chairmanship of Associate Professor Erkan Fidan.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
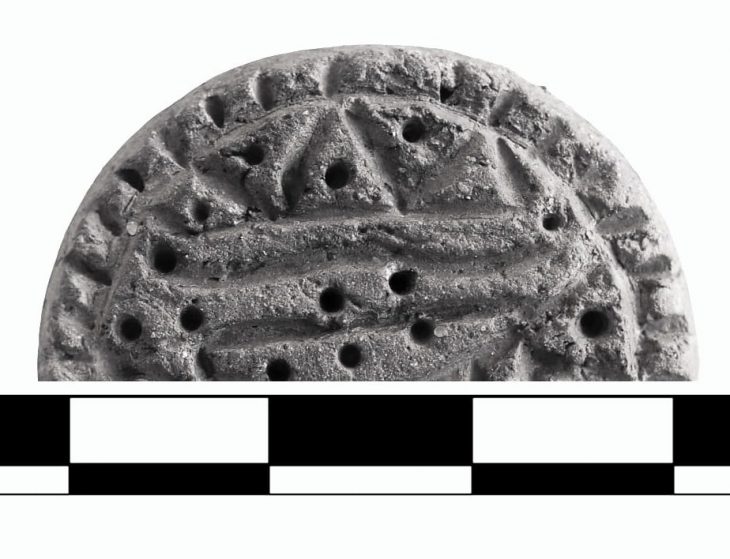


The researchs determined that the settlement started to urbanize about 5000 years ago and became a big city 4000 years ago. With this settlement, the existence of a settlement that was contemporary with the last periods of the Hittite Empire, which was seen only in a few archaeological centers in Western Anatolia, was detected for the first time.
Tavşanlı Höyük is thought to be the capital of an unknown kingdom with an area of 50 hectares.

The head of the excavation, Associate Professor Erkan Fidan, in a statement last year: “It is known that the peoples defined as Hatti in Central Anatolia and Luwi in Western Anatolia lived in this period. I can say that the Hittite civilization in Hatti and later is well known, but we do not have any information about the Luwian cities. I think that Tavşanlı Höyük may be a city belonging to the Luwians, which is seen as a missing link in Anatolian history,” he said.
According to the results of carbon 14 analyzes carried out in Tavşanlı Höyük, which is the oldest known settlement in Kütahya, it was determined that settlement began in this area 8,100 years ago.