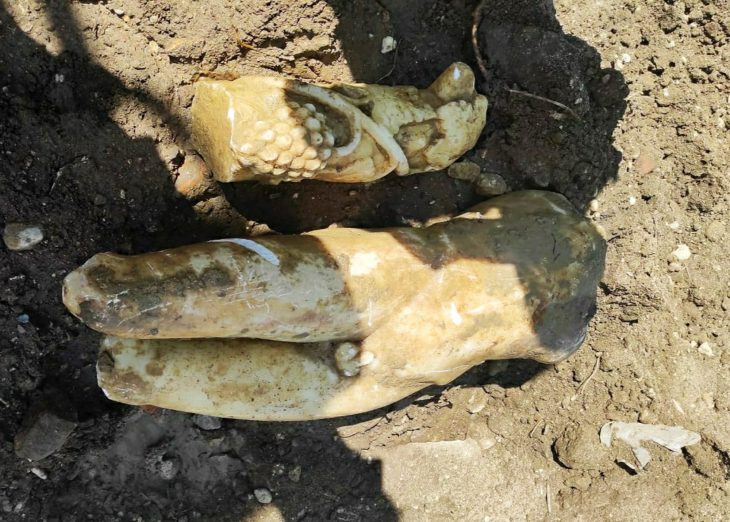
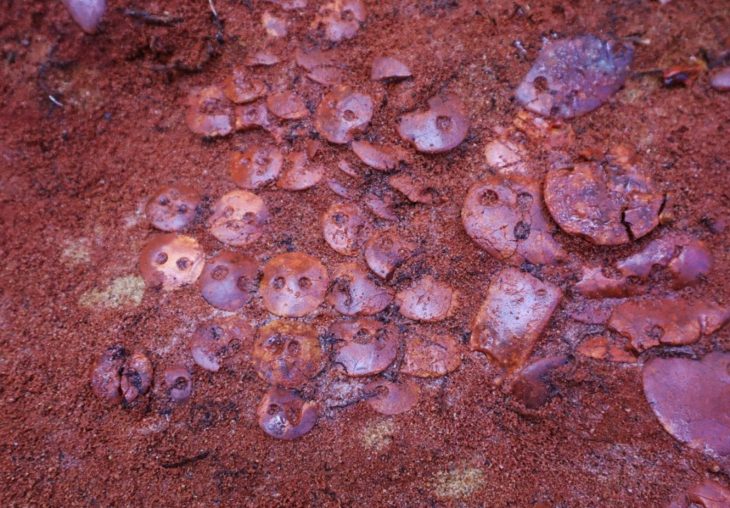
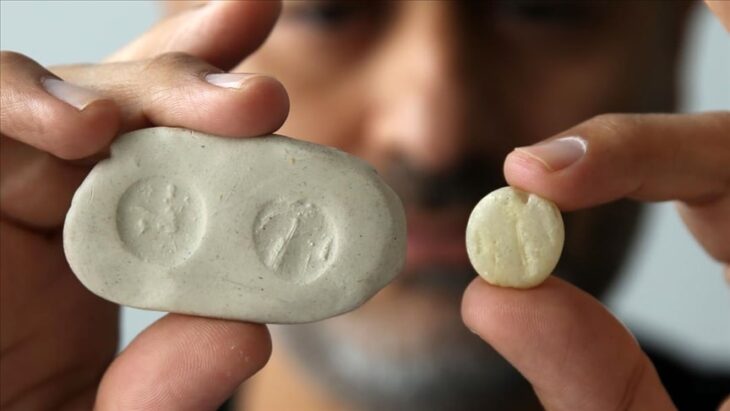
A terracotta whistle believed to be 2,000 years old from the Roman era and placed as a gift in a child’s grave was discovered during excavations at the 7,000-year-old Assos Ruins in the village of Behramkale, in the Ayvacık district of Çanakkale, in northwest Turkey.
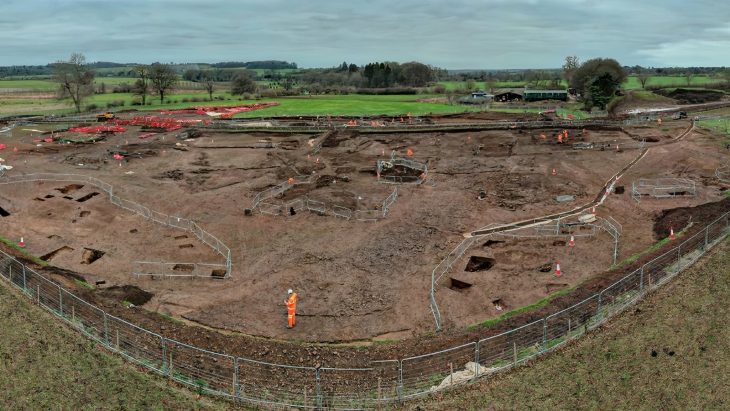
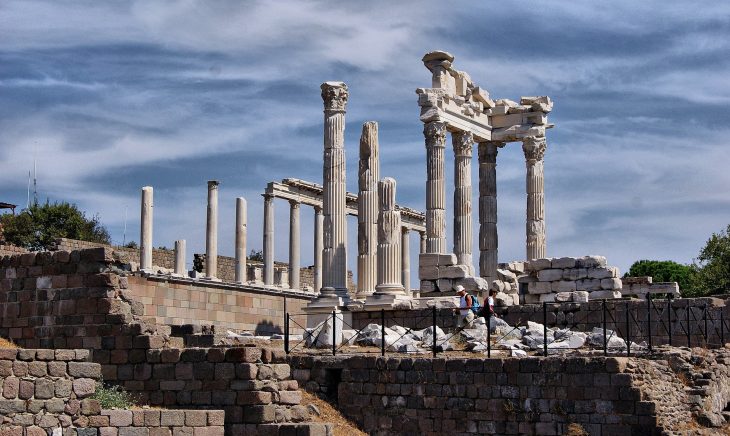
Assos Ancient City’s history dates back to the sixth century B.C. The city faced to the sea and people were climbing down via terraces to the sea. The city was built on an extinct volcanic hill, between andesite rocks and 236m high from the sea. The ruins are listed on UNESCO’s World Heritage Tentative List.
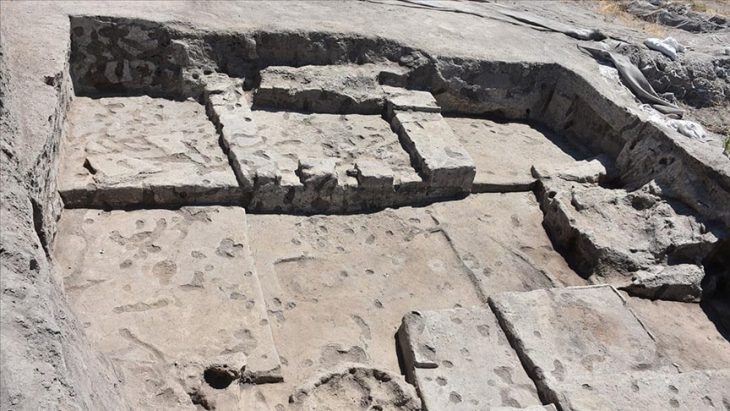
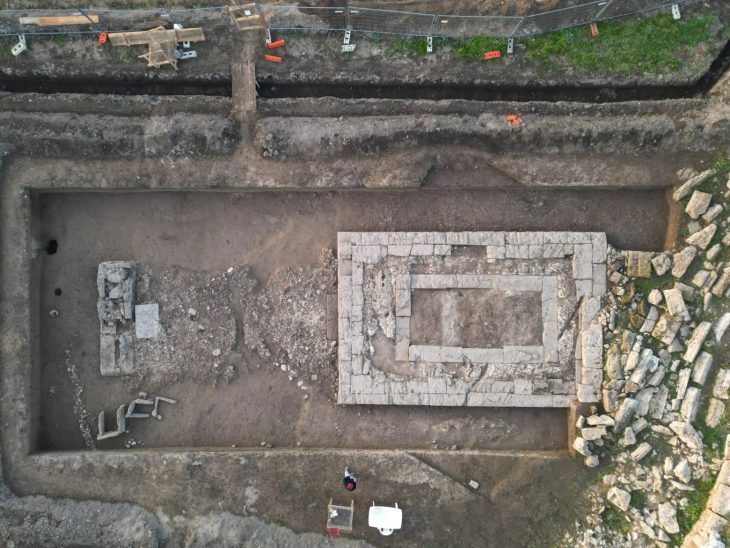
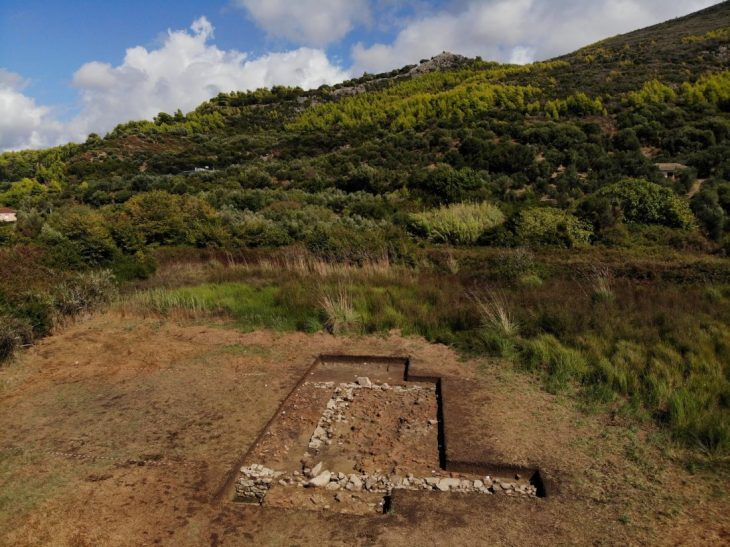
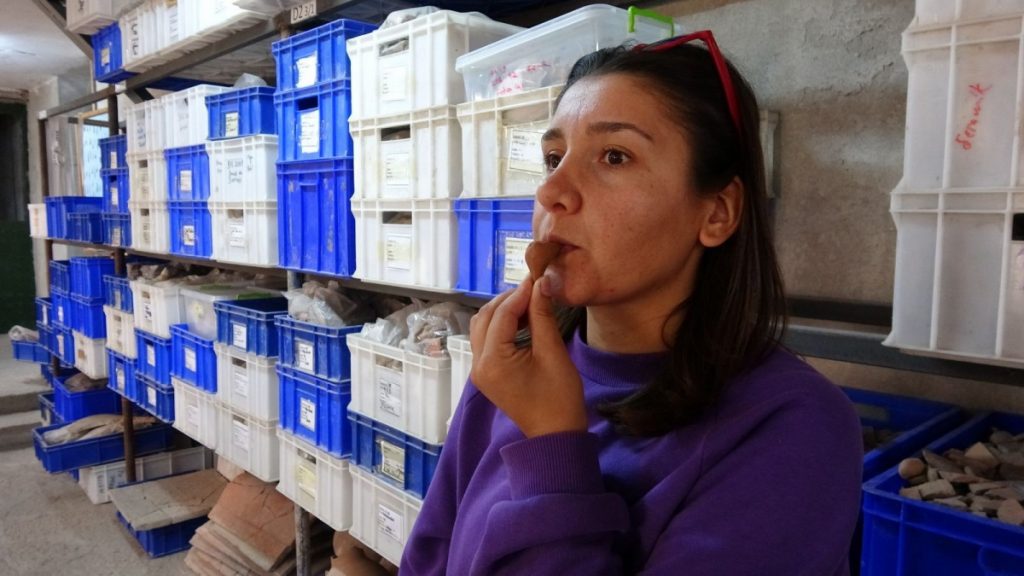
Çanakkale Onsekiz Mart University’s (ÇOMÜ) Archeology Department lecturer professor Nurettin Arslan with a team of 25 people continue excavations in the agora and gymnasium of Byzantine Period Ksenedochion (guesthouse) structures built in the Hellenistic period at the ruins.
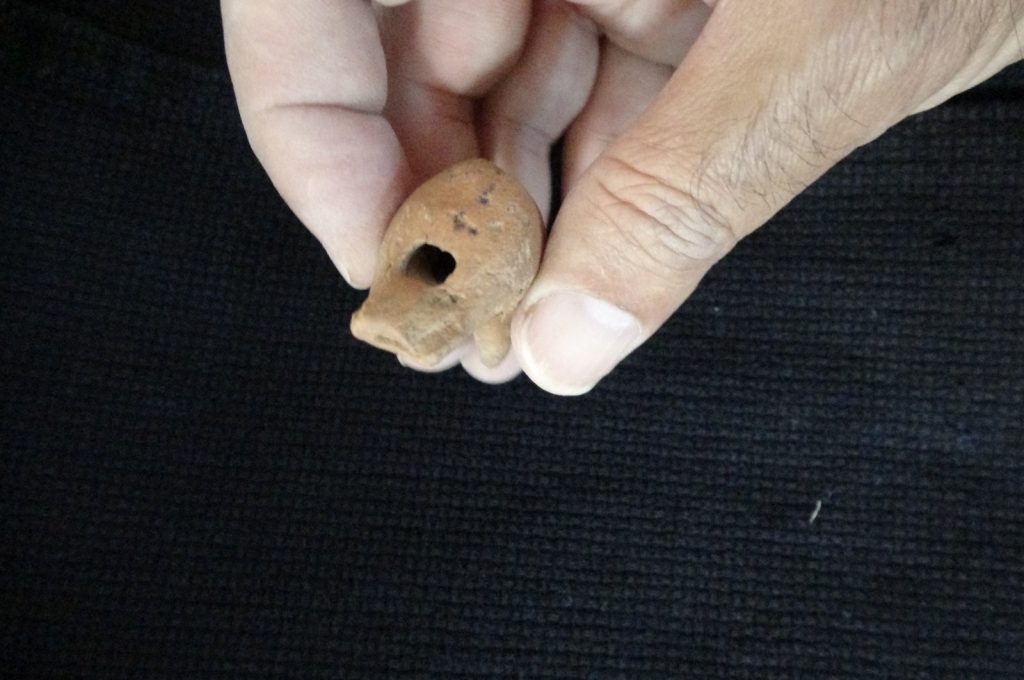

Professor Nurettin Arslan said, “It was understood that the terracotta bird figure found on the surface around the Ayazma Church was a whistle. In ancient times, such objects were used as children’s toys and left as gifts, especially in kids graves. It is known that this object, which still functions as a whistle, was used from the Classical Age to the Roman Age. Since the find layers of this object are not known, it is not possible to give an exact date. “But we guess it’s the Roman period or before,” he said.
In addition, they seem to be causal children’s toys of the time and were placed in children’s graves as a cultural ritual. This particular Roman whistle is estimated to be 2,000 years old.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Assos was one of the most important port cities in the ancient ages and home to many cultural riches such as an ancient theater, agora, necropolis, and ramparts.

The city has been home to many societies for centuries, having been founded on the summit and slopes of a volcanic hill at the southern end of the region, called as “Troas” in ancient times, across the island of Lesbos in Greece.
One of its famous residents was Aristotle who together with the philosopher Xenocrates established a philosophical school at Assos.
It was the first ancient city that U.S. archaeologists excavated in the 1800s. It was excavated in 1981 after a long break.