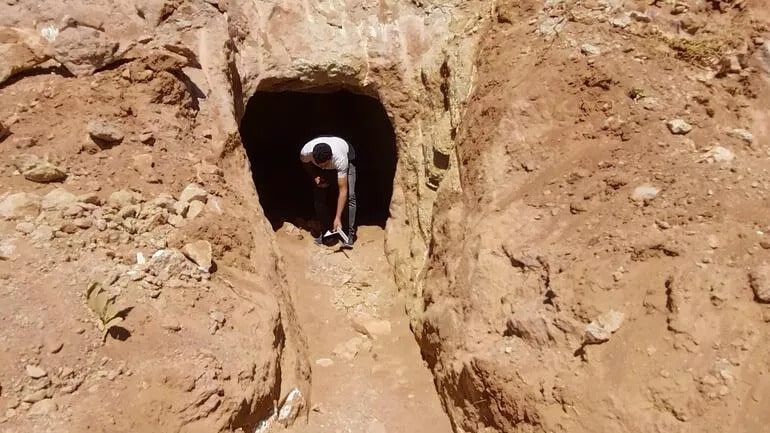
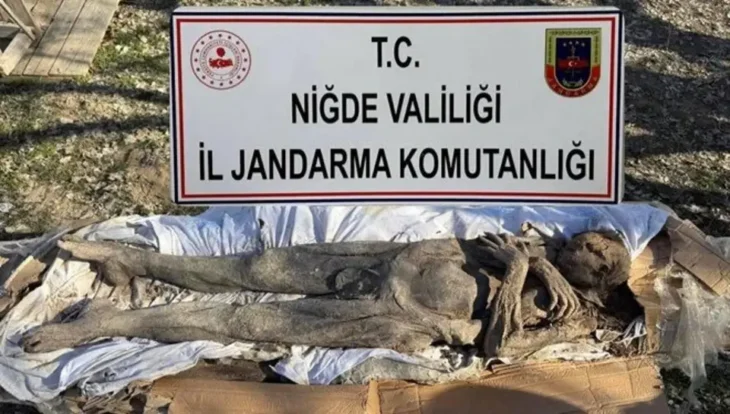
A total of 27 skeletons were found in a burial pit carved into the rocks in Adıyaman province, an important culture, and tourism city in Southeast Turkey.
The finds came to light after locals notified authorities of an illegal dig by treasure hunters in a rural part of the Gölbaşı district.
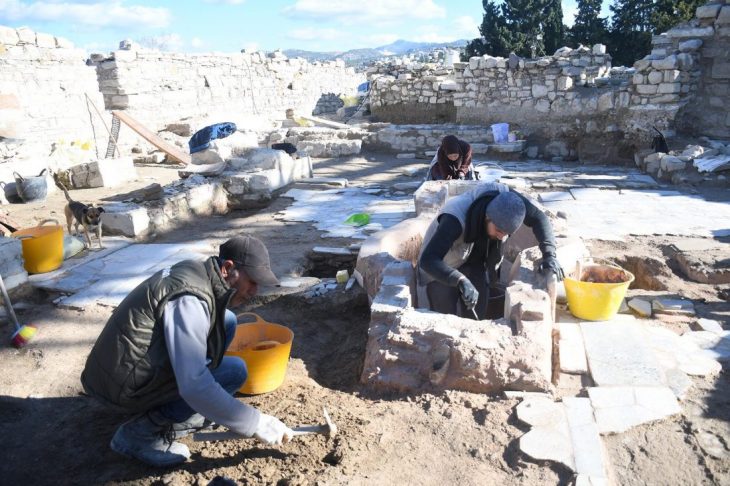
The incident occurred in the Örenli village of Gölbaşı district of Adıyaman. It turned out that the 1,700-year-old historical burial chamber, the entrance part of which was opened by treasure hunters with construction equipment and illegal excavations, was a mass grave.
While the first findings showed that the burial chamber of about 10 square meters from the Roman Period was 1,700 years old, archaeologists took the findings into the examination.
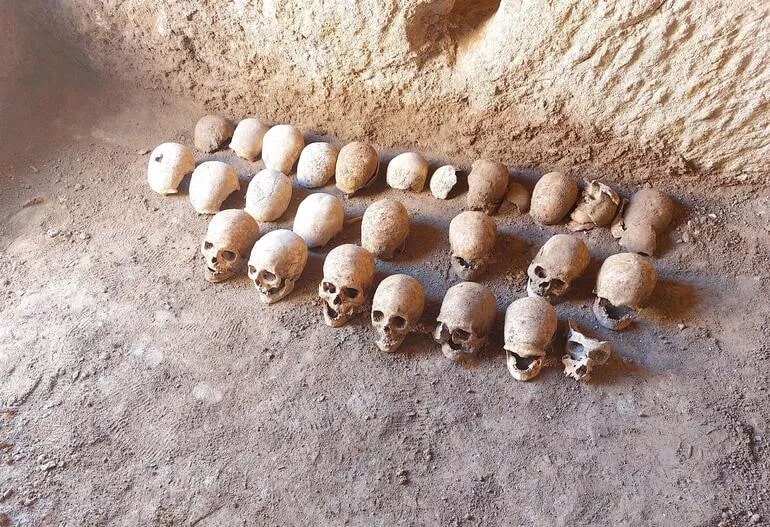

Adıyaman Museum Directorate officials encountered an interesting situation during their excavation in the tomb belonging to the Roman Period, which was destroyed by treasure hunters. 27 Skeletons were found in the room with only 1 rock tomb.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Regarding this unusual situation, Museum Directorate officials stated that such a number of skeletons had never been seen in a chamber tomb before.
Along with skeletons, broken lachrymatory bottles, a staple of ancient Roman tombs, and three intact spindle whorls, usually found in ancient graves of women, were discovered in the grave. The skeletons found in the burial chamber were cleaned and brought to the Adıyaman Museum Directorate.
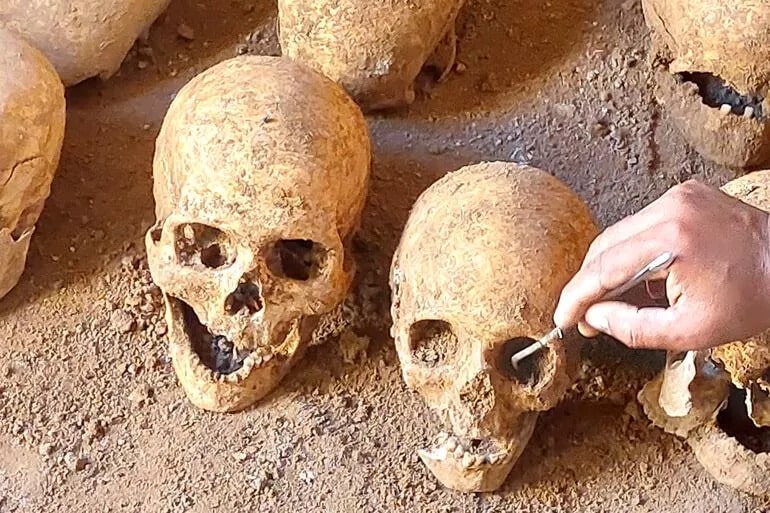

While suspects are still at large, an investigation into the unlawful excavation is being conducted.
The history of Adıyaman, which is one of the oldest settlements in the world, dates back to the first ages. It has been home to the Hittites, Mittans, Urartians, Assyrians, Med, and Komagene Kingdoms throughout history. It was dominated by the Great Seljuk Empire in the 11th century and later by the Anatolian Seljuk State.
Hellenistic, Roman, Byzantine, and Turkish-Islamic works can be seen in the region. The Romans arrived in the Adıyaman region around 72 A.D.
Cover Photo: İHA