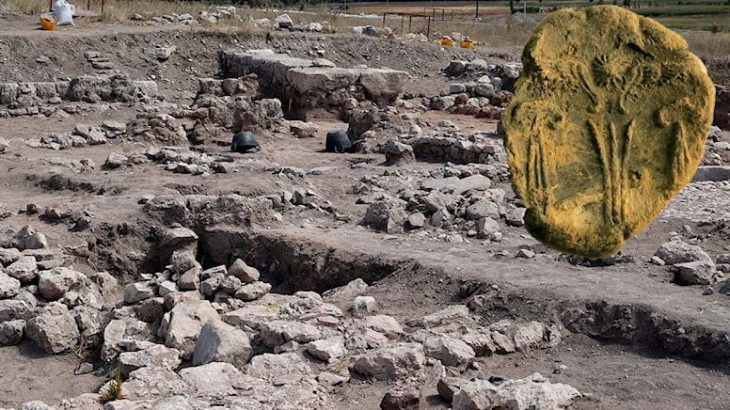
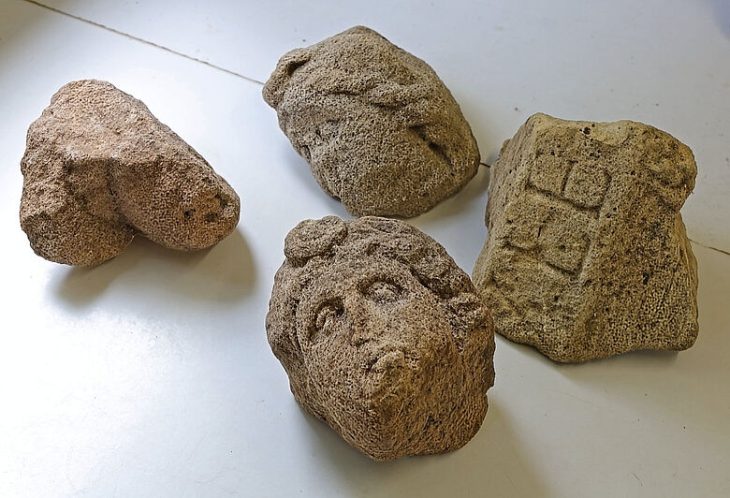
Rescue excavations are starting again on Giresun Island, where the first examples of human settlement in the Black Sea Region in northern Turkey are seen.
Giresun Island Rescue Excavations will be carried out by a group of archaeologists and art historians in September, October, according to a written statement by the Governorship of Giresun.
Giresun Island, a Subject of Many Legends and Myths
Giresun Island, which has traces of human life since the 2nd millennium BC, has been the subject of many legends and myths. The legend of “Hercules and the golden fur” is one of the most well-known narratives. In the written statement that there is a legend that Amazon women organized expeditions to the island and established a living space here, the following information was given about the cultural assets that Giresun Island hosts.
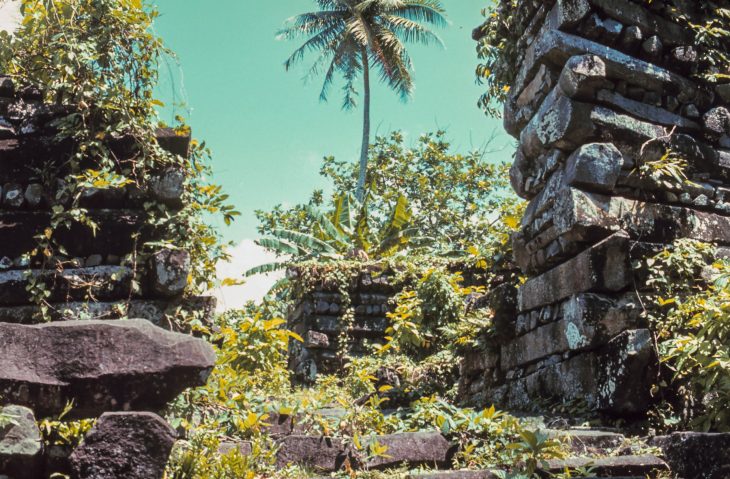
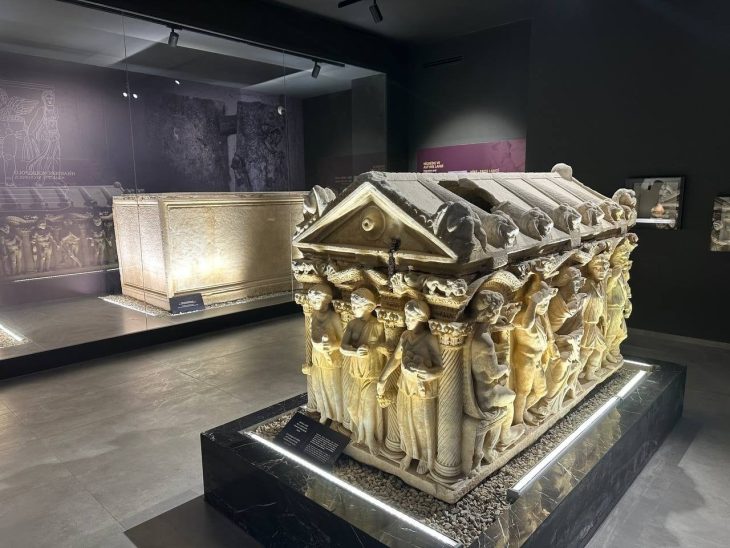
“Numerous remains and traces of life belonging to the Hellenistic, Roman, and Byzantine periods have been found. The wall ruins surrounding the island and the ruins of the temple dated to the 2nd century AD, the church, chapel, water well, and many tomb structures known to have been built in the 12th century after AD, reveal the cultural richness of the island.”
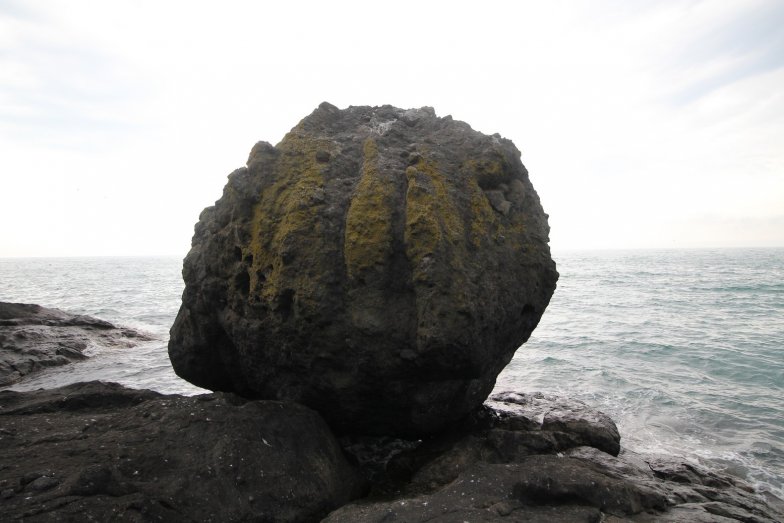

The Hamza Stone, seen as the center of a mystical belief with a history of 4 thousand years, is the most important structure of Giresun Island. The island was declared as a Second Degree Natural and Archaeological Site by the Trabzon Cultural Heritage Regional Board Directorate on 17.05.1991.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Selcuk University Archeology Department Made Excavations
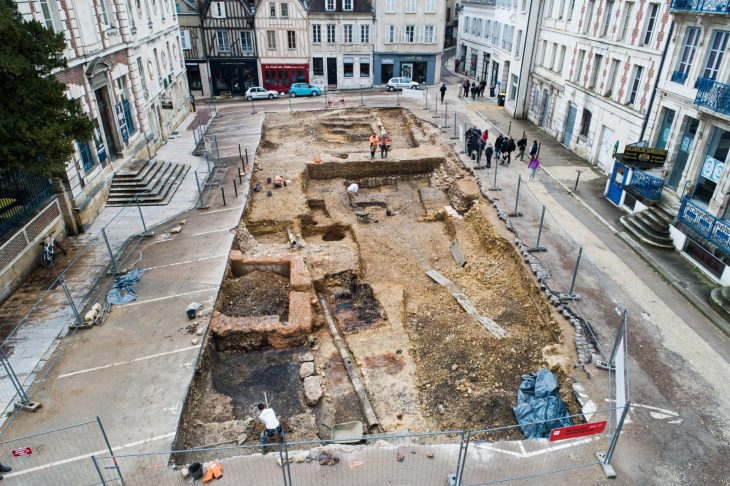
The archeology department of Konya Selçuk University first conducted surveys on Giresun Island between 2009-2010. Archeological excavations on Giresun Island were carried out by again Konya Selçuk University Archeology Department between 2011-2012 under the Presidency of Giresun Museum.
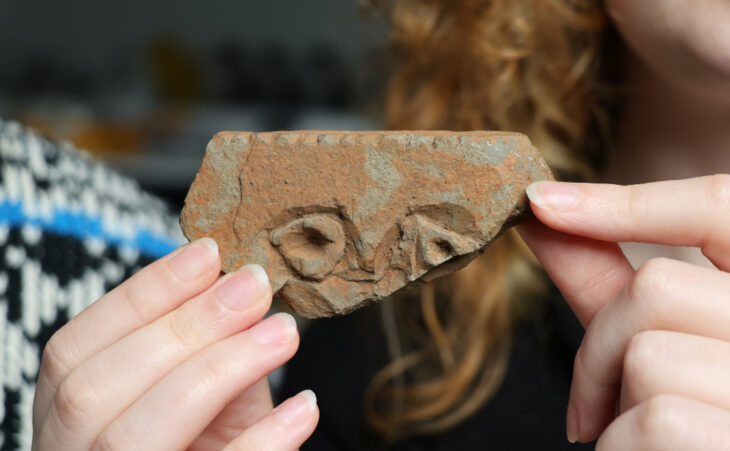
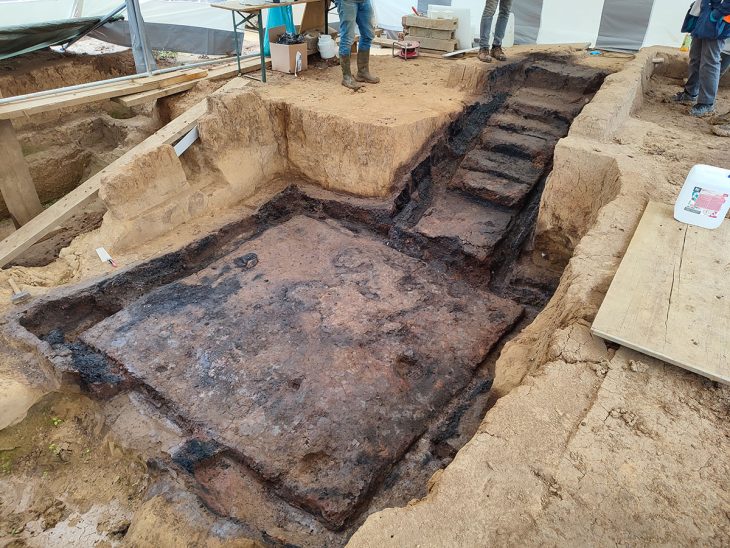
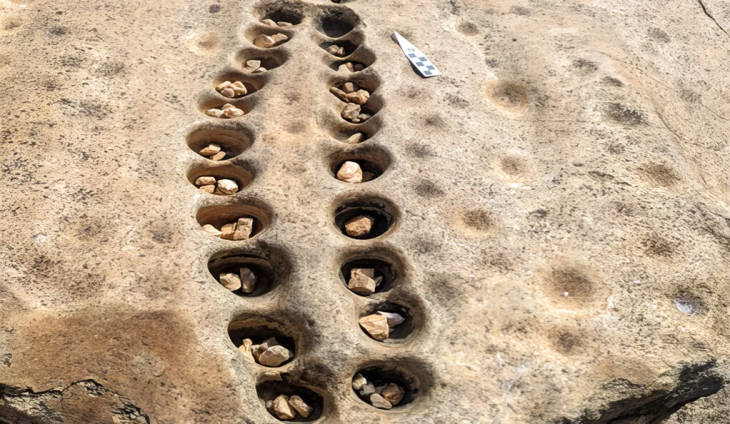
The explanation, which mentions that some structures were partially unearthed on the island surrounded by walls with these studies, said: “Along with structures such as churches, towers, administrative buildings, chapels, and cisterns built on the medieval settlement, the harbor area and offering pits belonging to the Classical and Hellenistic periods were identified.”
Giresun Island archaeological excavations continued in 2015-2016-2017, and in these excavations, areas where various ceramics, frescoes, mosaics, used as wine cubes, Byzantine period coins, and many skeletons were unearthed.