Sanxingdui, which literally means “Stacks of Three Stars”, is a cultural relic of the Kingdom of Shu in ancient China. This name refers to 3 earth mounds on the site.
The location is located in Guanghan City, Sichuan Province in southwestern China. Excavation work has been going on for nearly 100 years since it was first discovered in the late 1920s.
As a result of long-term studies, experts unearthed a large number of strange bronze images and animals from the ruins, such as bronze masks, standing bronze figures, and goldenrods. The findings also piqued the interest of scholars around the world for the importance of the ancient Shu civilization in southwestern China.
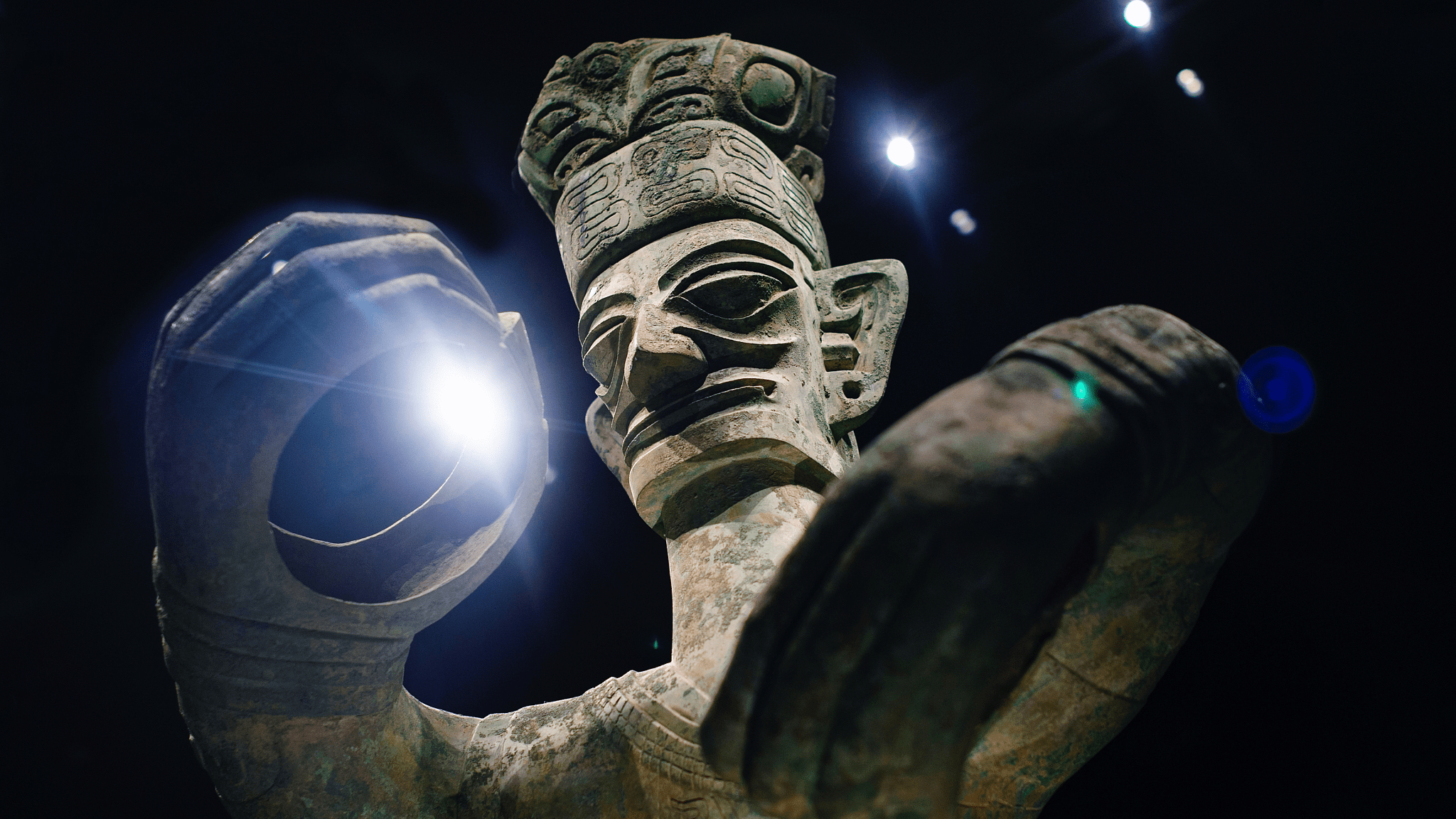

The Sanxingdui Ruins, are considered to be among the most important ancient remains found in the 20th century.
China’s National Cultural Heritage Administration will announce important archaeological discoveries at the 3,000-year-old Sanxingdui site on Saturday.
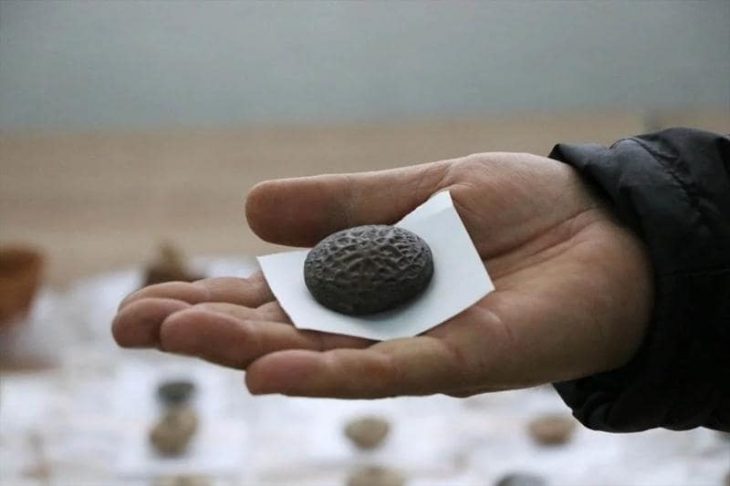
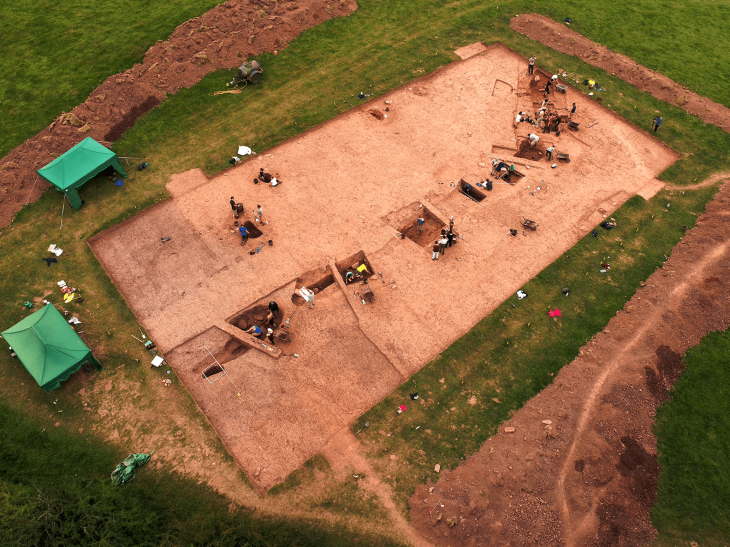
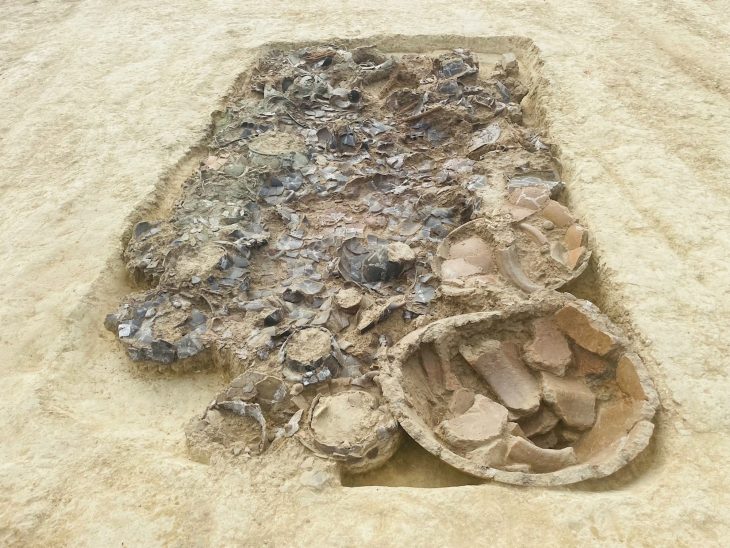
From October 2019 to August 2020, archaeologists discovered six new sacrificial pits at the site. Since September last year, the Sichuan Provincial Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology has cooperated with many national organizations to officially launch archaeological excavations. The meeting on Saturday will It will announce major developments and new discoveries.
Some archaeologists predict that the newly discovered artifacts from the six pits may bring some new insights.
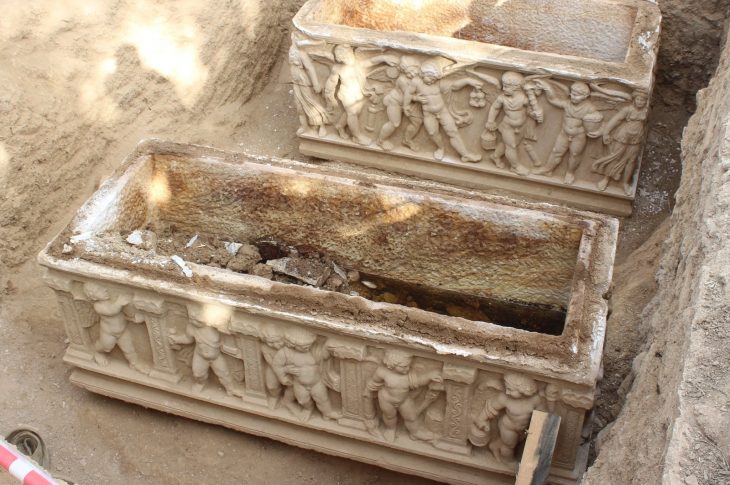
Before that, in 1986, two sacrificial pits filled with over 1,000 national treasures, including golden masks, bronze products, and jade tablets, were discovered, stunning the world with the ancient Shu civilization buried underground for 3,000 years.
Sanxingdui is considered to be one of the most important historical sites in the world for its scale, age, and monuments.
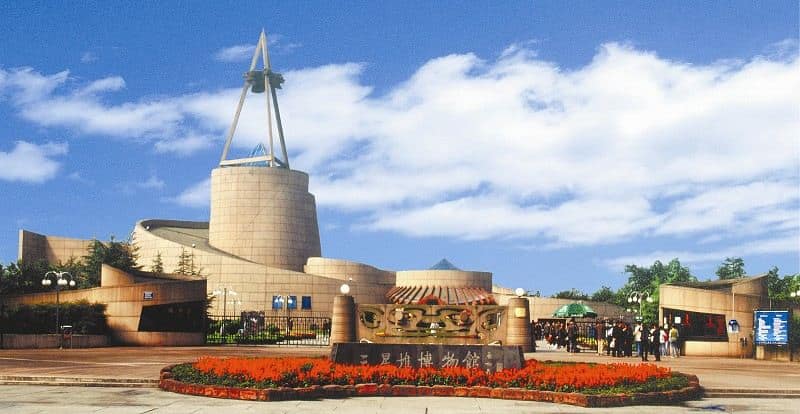
The works found in Sanxingdui are quite remarkable and are exhibited in the Sanxingdui Museum.