When it comes to the first establishment of Istanbul, the first to come to mind are the stories of Megarians from Greece, arranged with various legends. Historical narratives must have liked legends that they always used this narrative when a place was being built and destroyed.
One of the best examples of this is Khalkedon, as today’s Kadıköy is the “Land of the Blind”….
The fact that Kadıköy is a “Country of the Blind” is not very logical as a story. As a matter of fact, the fact that the fertile lands targeted by people and the fact that they were established in the place called Kurbağalıdere today show that, on the contrary, it is a completely planned and conscious choice. Taking advantage of the large and fertile lands here is a very smart choice for agricultural residents. It may even be considered that the settlers were experienced in agriculture. (It is also taken into account that it is established by the stream will facilitate irrigation.)
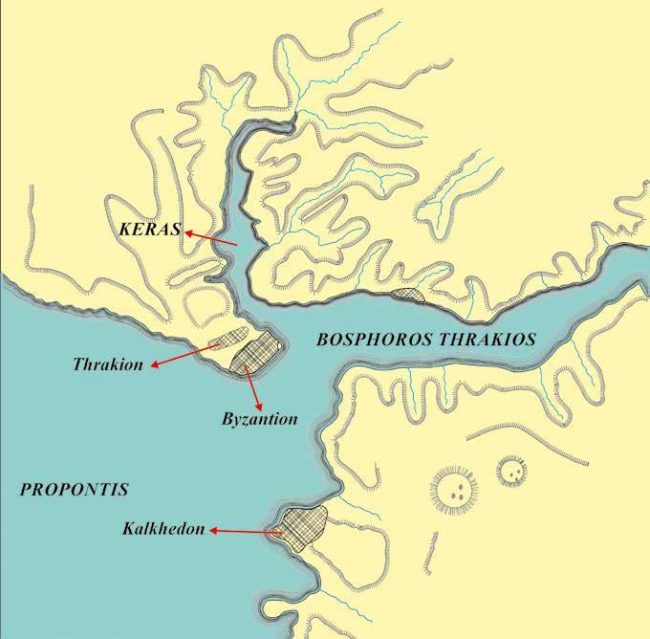
It is asked why those who settled in Chalcedon did not settle in Byzantion on the opposite side. Is this question to cover up the fact that there are already residents in Byzantion in this place is it for?
To date the settled order of Istanbul as late as 675 BC! It should be considered whether it is a deliberate pull forward. Are those who think that there was no Neolithic period in Anatolia until recently and those who attractors the history of Istanbul forward are they the same people? I guess it would not be wrong to ask.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
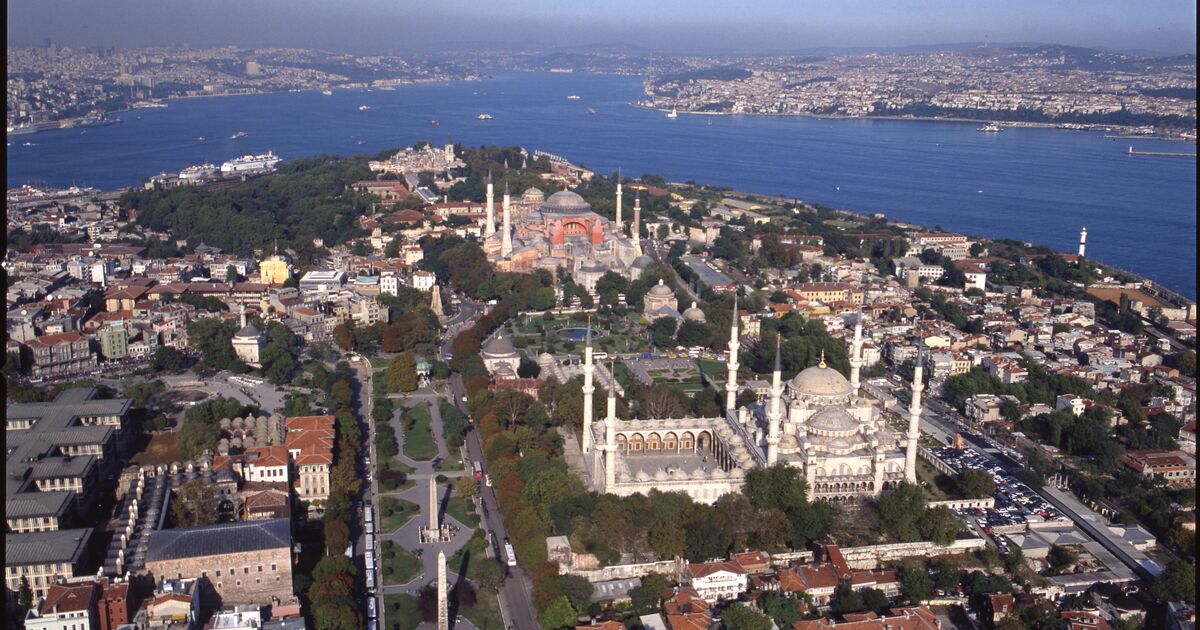
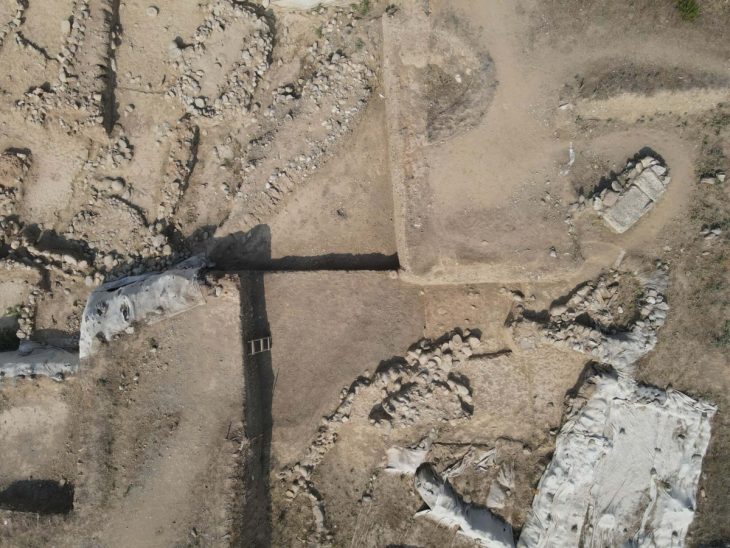
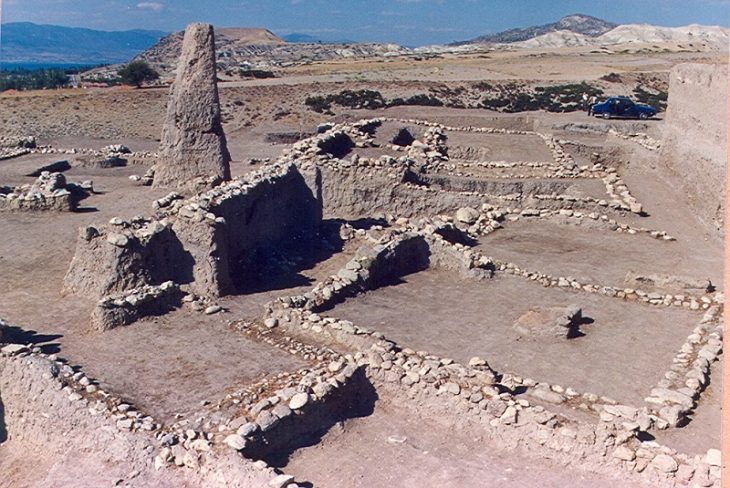
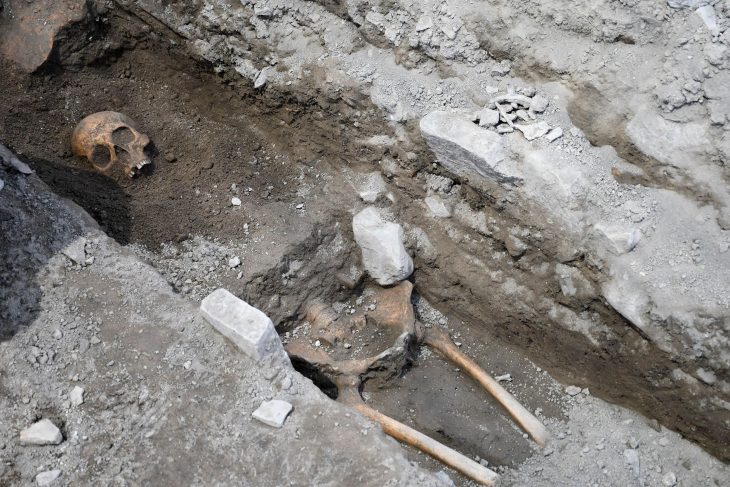
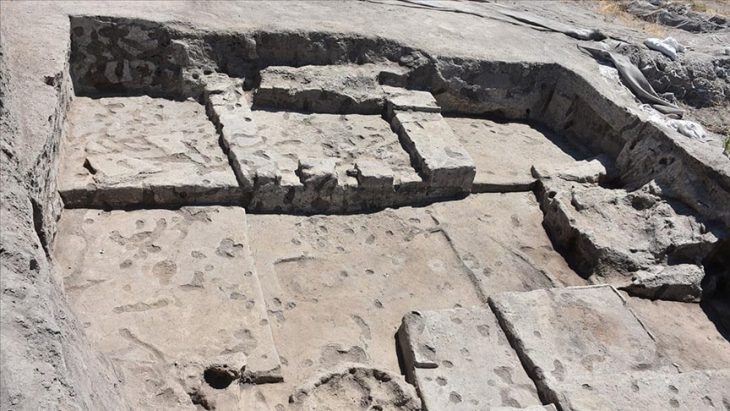
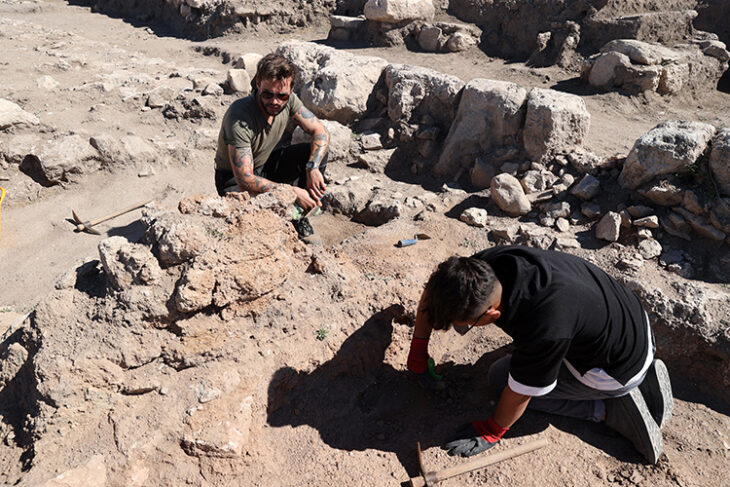
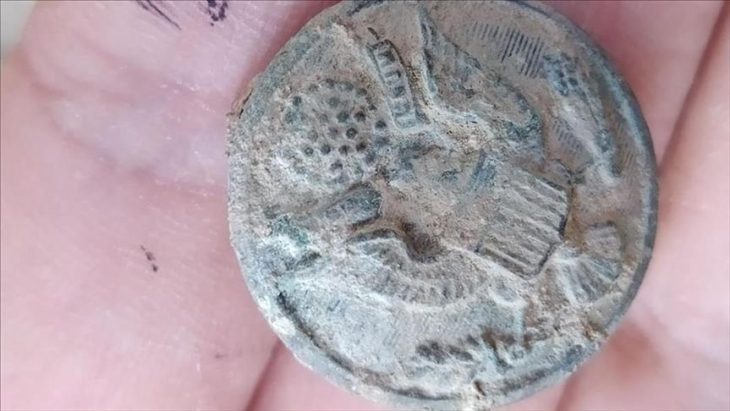
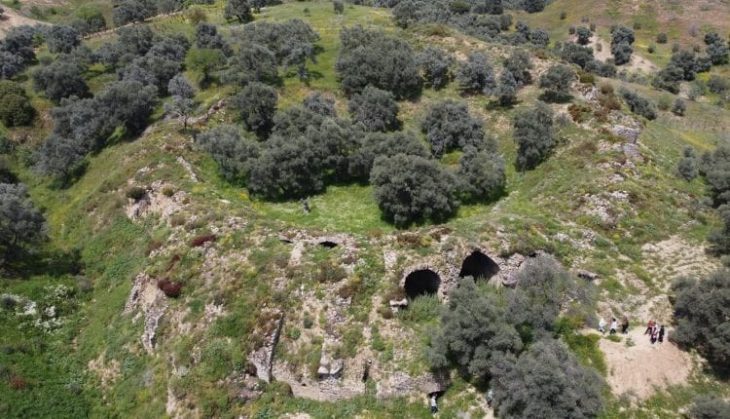
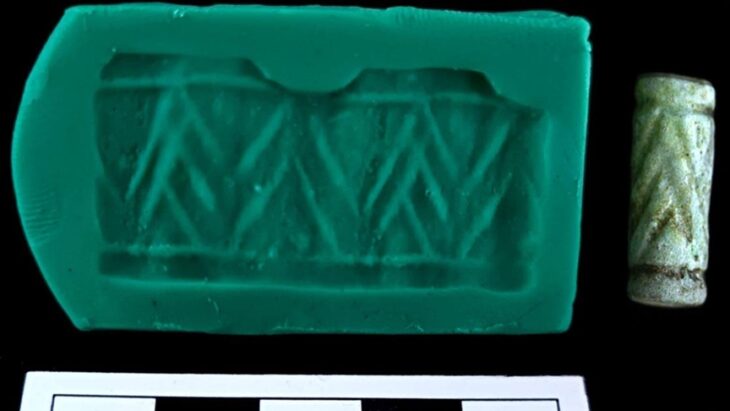
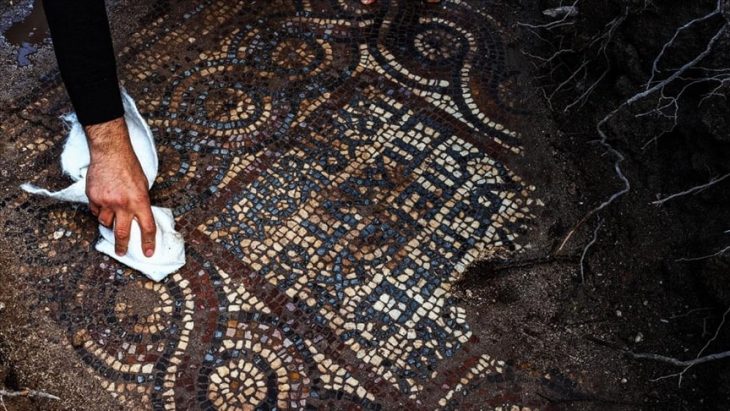
Our knowledge about the first settlements of Istanbul is increasing day by day. Especially the contribution of the recently discovered artifacts to this is great. The excavations carried out within the scope of infrastructure works in Yenikapı and Sultanahmet took the settlement history of Istanbul until back to the Neolithic period of 6500 BC.
As a result of the dense and irregular construction of Istanbul, the lack of areas where in-depth excavations can be made in the city walls and other areas made it difficult to find the location of many old settlements.
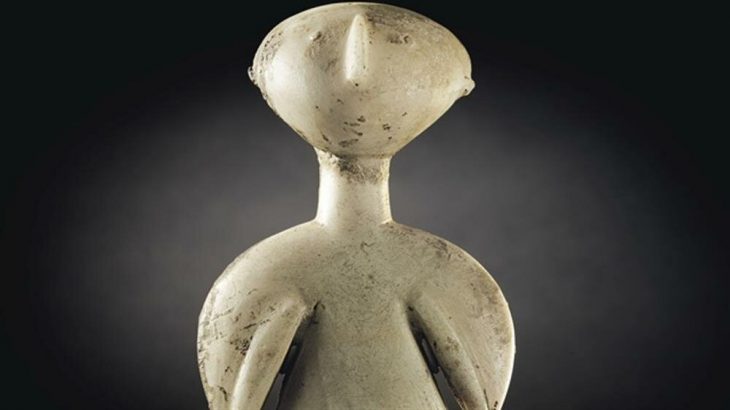
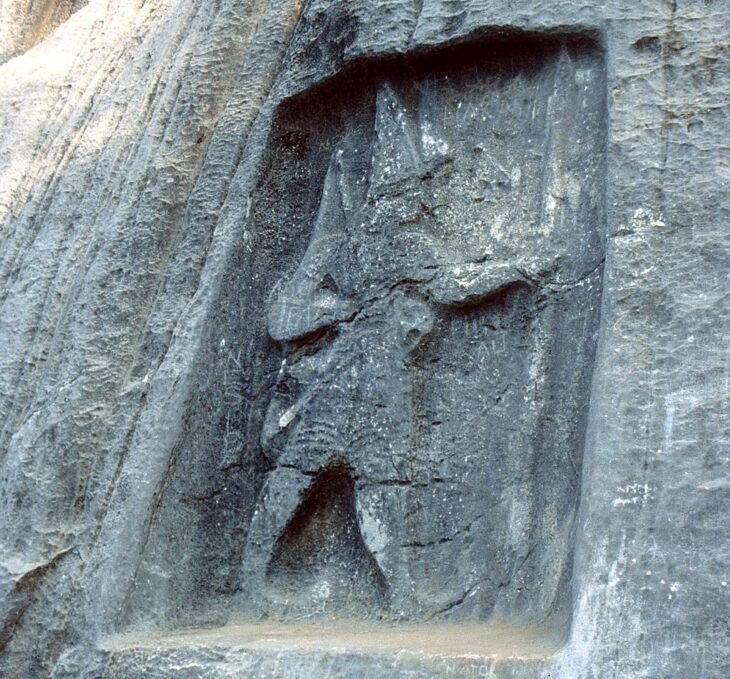
The iron age findings found around Hagia Sophia and Sultanahmet are the oldest living here and the people thought to be the main owner of this region, the Thrako-Phrygians. Thrakion was in this region before Byzantion.
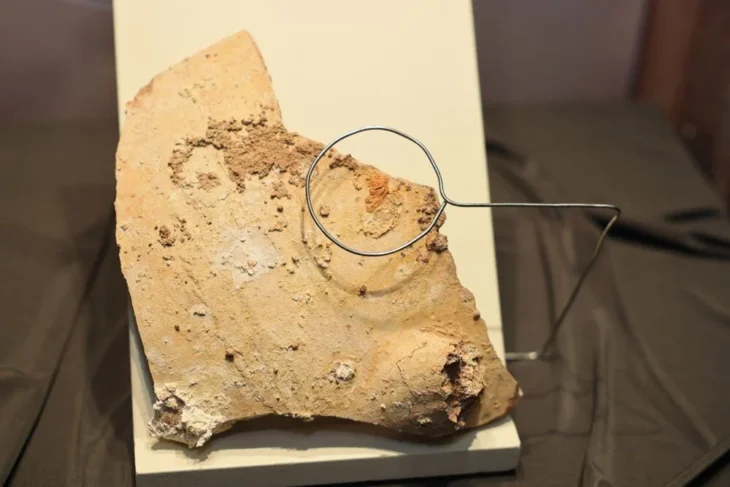
The gray colored pottery pieces found in excavations in Hagia Eirene are proof that this region was inhabited before Byzantion.

We would also like to point out that the article written by our teacher Prof. Dr. Afif Erzen in an old article about the results of these excavations has not been taken into consideration so far. It is worth remembering the fact that the historical peninsula was a part of ancient Thrace.
Proceeding in the light of archaeological and scientific findings rather than legends are more reliable sources and proofs for accurate writing of world history.
It is an important possibility that the Thraco-Phrygian origin peoples lived in this region until the early iron age (1200-1000 BC) until the Megarians came (7th century BC) on the Sultanahmet (Horse square) flat.
In the light of the prominent developments, it is an issue that needs to be studied more deeply that Istanbul had a settlement before the Megarians. Anyway, it is impossible to think that there is no settlement in such a region in an earlier period.
Another issue that has been ignored until today is about the commander who is said to have founded Byzantion. Again, Afif Erzen specifically mentioned this issue in his article written years ago, but it was ignored. Afif Erzen particularly mentioned that the name Byzas is of Thracian origin. This name, which is transmitted as the founder of the city, is of Thrak origin.
History has the ability to reveal the facts with the hands of a science like archeology. I am sure that time will give us the opportunity to write the true story of this establishment.
Source: Dönmez,Ş. 2017, “Şehr-i Istanbul’un Kuruluş Ezberlerine Arkeoloji Darbesi”, Tarih Dergisi, S:34
















