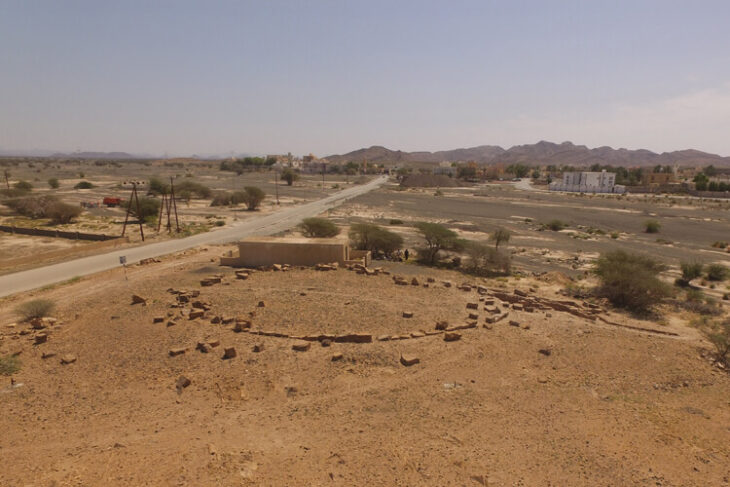
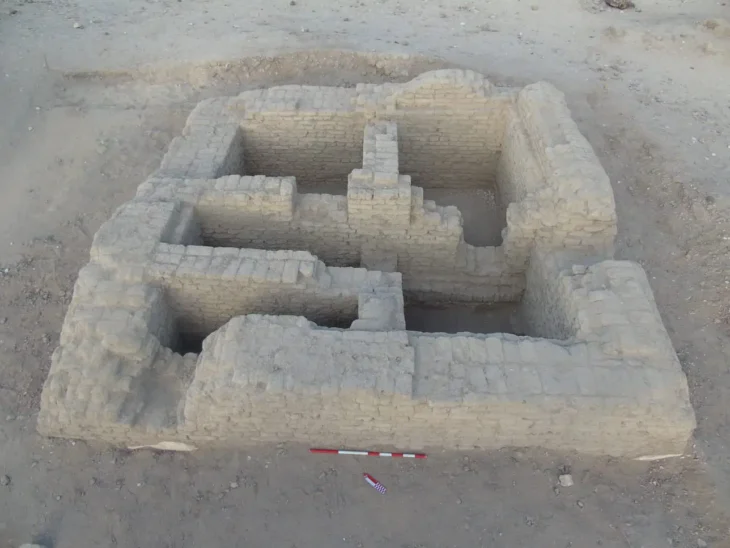
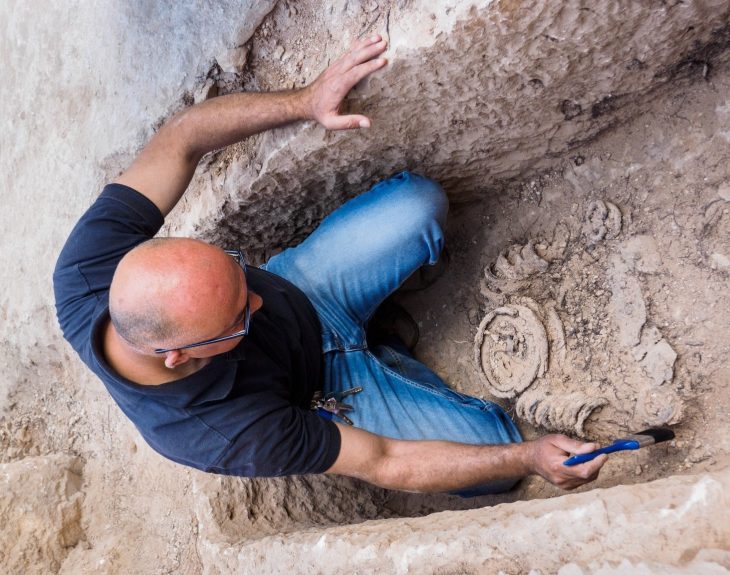
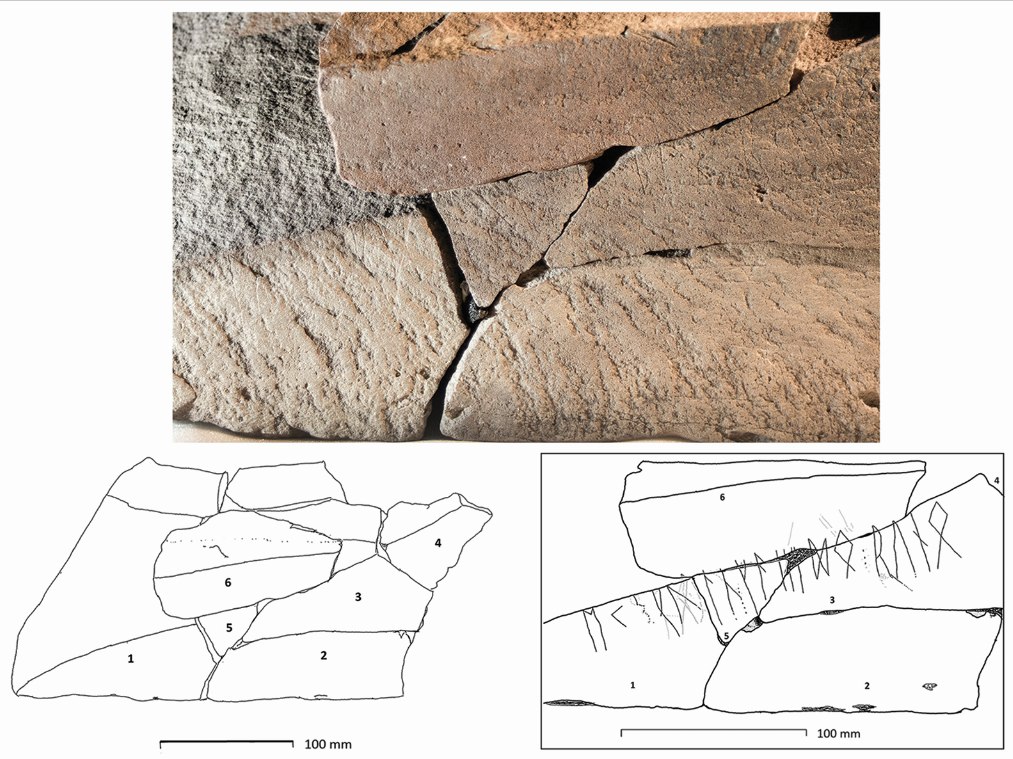
Archaeologists have found fragments of the world’s oldest known rune stone at the Svingerud burial field in Norway and fitted them together like pieces of a jigsaw puzzle. These fragments may have been intentionally separated, shedding light on the diverse pragmatic and ritual aspects of Germanic rune-stones.
A team of researchers has found fragments of the oldest rune stone in the world in the Svingerud burial field, Norway. These pieces, which have been assembled like a puzzle, offer a unique insight into the early uses of runic writing on stone and its possible ceremonial and practical meanings.
Runes were the letters used to write Germanic languages before the adoption of the Latin alphabet, with the oldest examples in use until around AD 700. However, the origins and utilization of these runes remain unclear.
Dr. Kristel Zilmer, a professor of runology at the University of Oslo (UiO) and a member of the research team, emphasizes the complexities surrounding the origins of runic writing, stating, “The development of runic writing and the practice of inscribing runes on stone are difficult to trace.” She further elaborates on the significance of rune-stones, suggesting that they likely served both ceremonial and practical purposes.
“The grave field and the original raised stone indicate a commemorative and dedicatory intent, while their subsequent use in separate burials highlights later pragmatic and symbolic expressions,” Dr. Zilmer explains.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

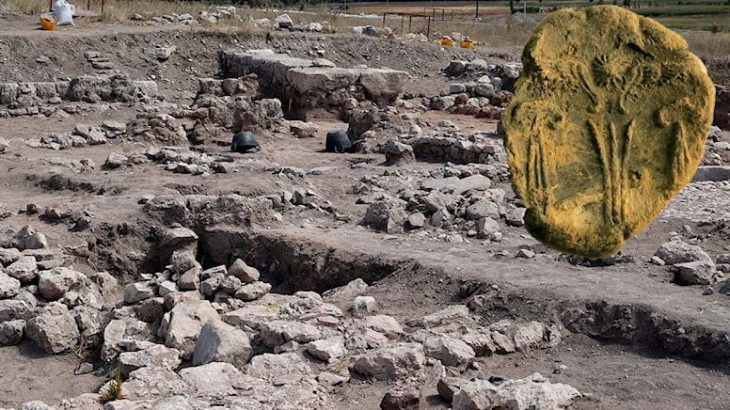
The discovery of several sandstone fragments inscribed with runes at the Svingerud grave field in Norway is particularly exciting, as it illuminates the early use of runic writing on stone and features multiple intriguing sequences of runes alongside other puzzling markings. The archaeological contexts of these finds provide excellent opportunities for dating the rune-stone through radiocarbon dating.
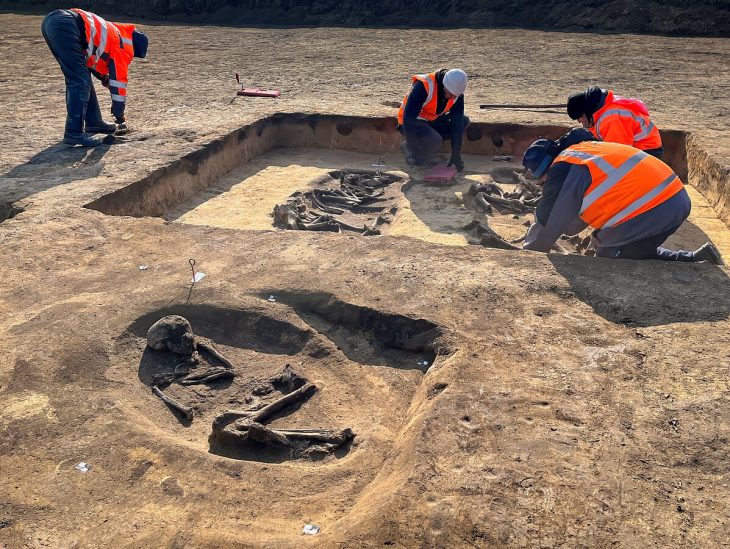
The stone pieces were found in separate graves. Through meticulous archaeological investigations conducted over three field seasons and subsequent laboratory analyses, the research team discovered that the fragments fit together like a jigsaw puzzle.
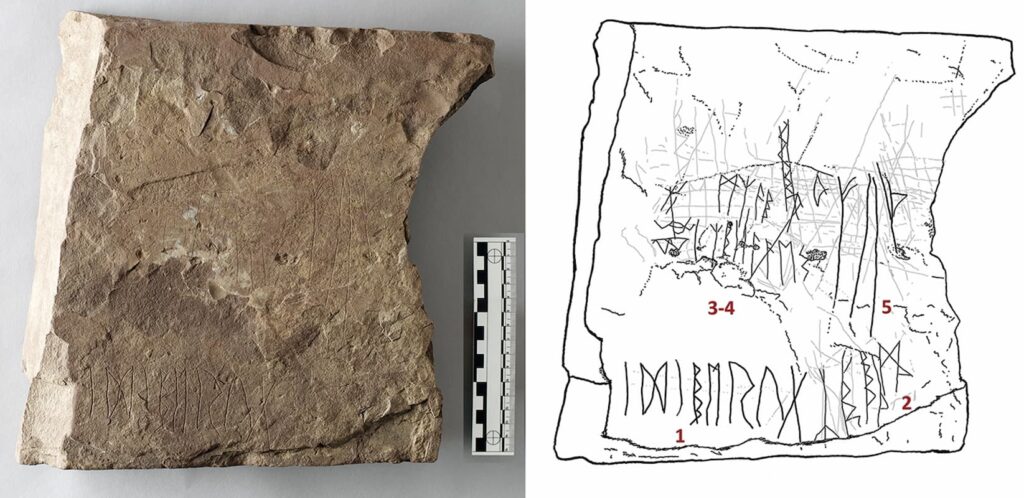
By piecing together the fragments, the team was able to identify several runic inscriptions. Some fragments were carved with multiple runic sequences, while others contained ambiguous markings. This suggests that they may have been engraved at different times by various individuals.
This indicates that the original large stone was intentionally fragmented, scattered, and incorporated into later burials. It is possible that the stone was initially intended to mark one grave but was fragmented to commemorate subsequent burials.
Importantly, as Svingerud is a grave field, the cremated human remains and charcoal found at the site can be radiocarbon-dated, providing a firm date range for the contexts in which the rune-stone fragments were discovered. Radiocarbon dating revealed yet another surprise: the contexts date between 50 BC and AD 275, indicating that these rune-stone fragments are the oldest examples discovered to date.
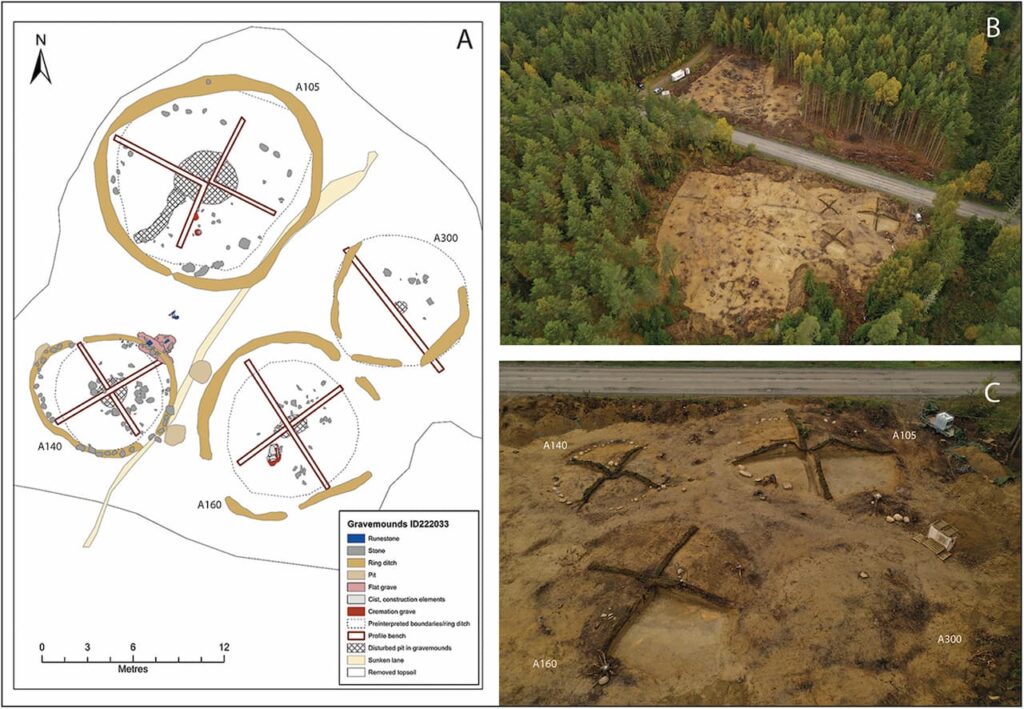
This discovery invites a new perspective on the rune stone, raising intriguing questions about the nature of the unidentified symbols. Could they potentially bridge the gap between ornamental script and early writing? Was the fragmentation and scattering of rune stones a means to connect different graves across the grave field?
Dr. Steinar Solheim, the first author of the study, emphasizes the significance of this finding, stating, “This is a rare example of finding runic fragments in well-preserved, datable archaeological contexts. It is of great importance for discussions on early Scandinavian rune-stones.”
Dr. Steinar Solheim also highlights the importance of this discovery as a reminder for archaeologists to conduct thorough investigations of stone fragments found in burial contexts and to actively search for potential inscriptions. He conveys a sense of optimism regarding future research, indicating that additional investigations of this site and the rune-stone fragments are expected in the forthcoming years.
In conclusion, the discovery and analysis of the rune-stone fragments at the Svingerud grave field not only provide invaluable insights into the early use of runic writing but also open new avenues for understanding the cultural and ceremonial practices of ancient Scandinavian societies, underscoring the significance of continued archaeological research in this area.
Solheim, S., Zilmer, K., Zawalska, J., Vasshus, K. S. K., Sand-Eriksen, A., Kimball, J. J. L., & Havstein, J. A. M. (2025). Inscribed sandstone fragments of Hole, Norway: radiocarbon dates provide insight into rune-stone traditions. Antiquity, 1–18. doi:10.15184/aqy.2024.225
Cover Image Credit: Kristel Zilmer