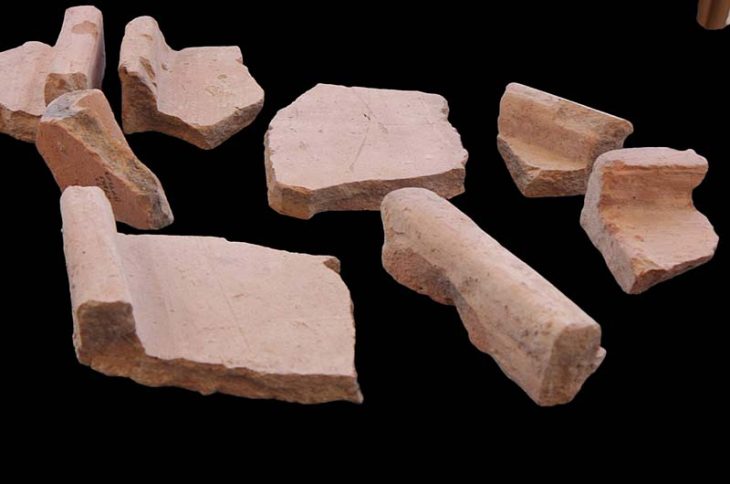
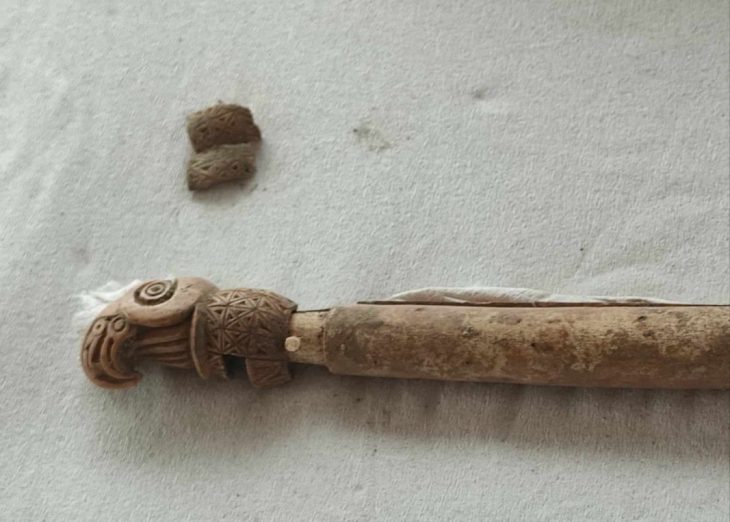
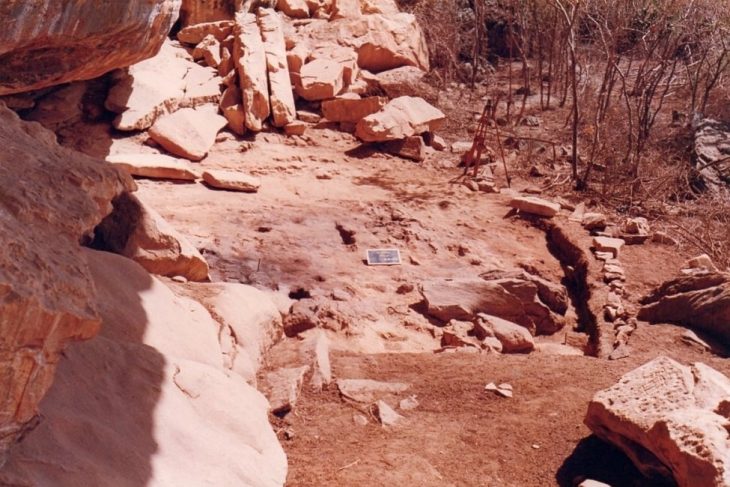
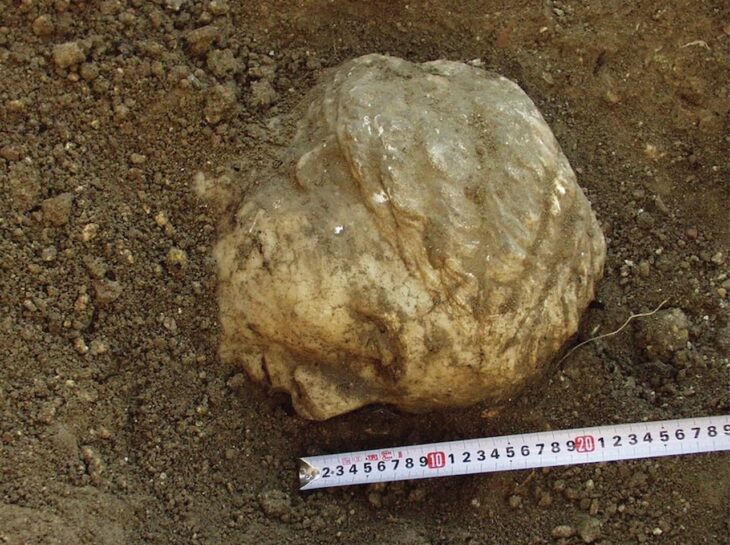
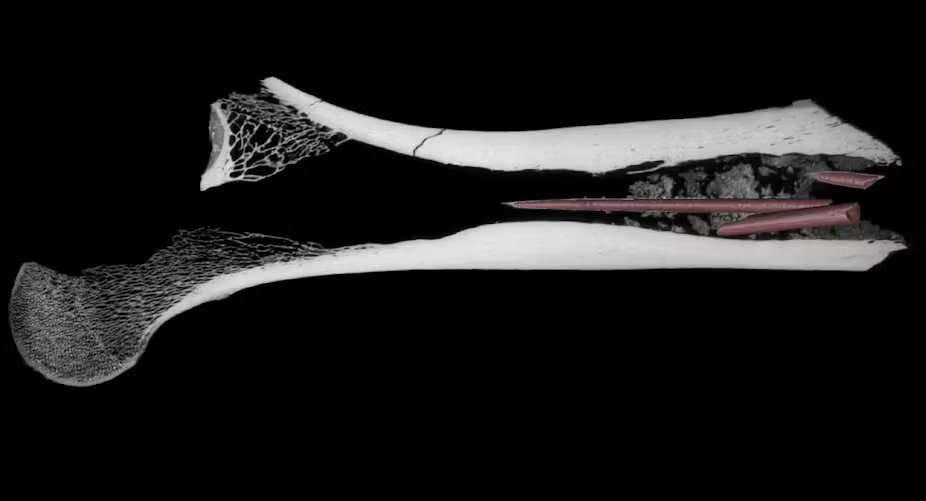
In a groundbreaking discovery, archaeologists excavating Kruger Cave in South Africa have identified what may be the oldest confirmed multi-component arrow poison in the world, dating back 7,000 years. The femur bone of an unspecified antelope, found during a 1983 excavation, contained three modified bone arrowheads embedded in its marrow cavity.
After lying in storage at the University of the Witwatersrand for nearly four decades, renewed archaeological investigations in 2022 prompted scientists to re-examine the femur and its contents. A team from the University of Johannesburg, led by Associate professor Justin Bradfield focused on organic materials, conducted a detailed analysis of the chemical matrix surrounding the arrowheads.
The research revealed a complex recipe combining at least two toxic plant ingredients, including cardiac glycosides known to disrupt heart function. Notably, digitoxin and strophanthidin were identified, alongside ricinoleic acid, a by-product of the toxic lectin ricin. The presence of these compounds suggests that ancient peoples were adept at mixing various plant toxins to create effective hunting poisons.
Interestingly, none of the plant species containing these toxins are native to the Kruger Cave area, indicating that the ingredients may have been sourced from distant locations or through established trade networks. This finding challenges previous assumptions about the movement of non-domestic plants in southern Africa during this period.
Recent findings have revealed that the long-distance transport of non-domestic plants in Africa may have occurred much earlier than previously thought. While researchers have long known that the transport of seashells as ornaments and currency was common throughout the continent well before 7,000 years ago, the movement of non-native plants at such an early date was unexpected.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

This discovery highlights the advanced knowledge of ancient peoples regarding plant acquisition and usage. The ability to identify which plants to gather, where to locate them, and how to utilize them effectively underscores the depth of traditional pharmacological knowledge systems that have existed for millennia. This insight not only reshapes our understanding of ancient trade practices but also emphasizes the sophistication of early human societies in their interactions with the natural world.
The study also highlights the significance of traditional pharmacological knowledge among ancient populations, as well as the potential of archaeobotany and organic chemistry to enhance our understanding of historical practices. The ability to create complex recipes for poisons, adhesives, and medicines reflects advanced cognitive capacities of the makers.
This discovery adds to the growing body of evidence regarding the use of poisons in hunting technology, which has been documented across various cultures worldwide. The findings at Kruger Cave illuminate ancient hunting practices while also demonstrating the advanced understanding of natural resource utilization by early human societies.
Bradfield, J., Dubery, I. A., & Steenkamp, P. A. (2024). A 7,000-year-old multi-component arrow poison from Kruger Cave, South Africa. iScience, 27(12), 111438. doi:10.1016/j.isci.2024.111438