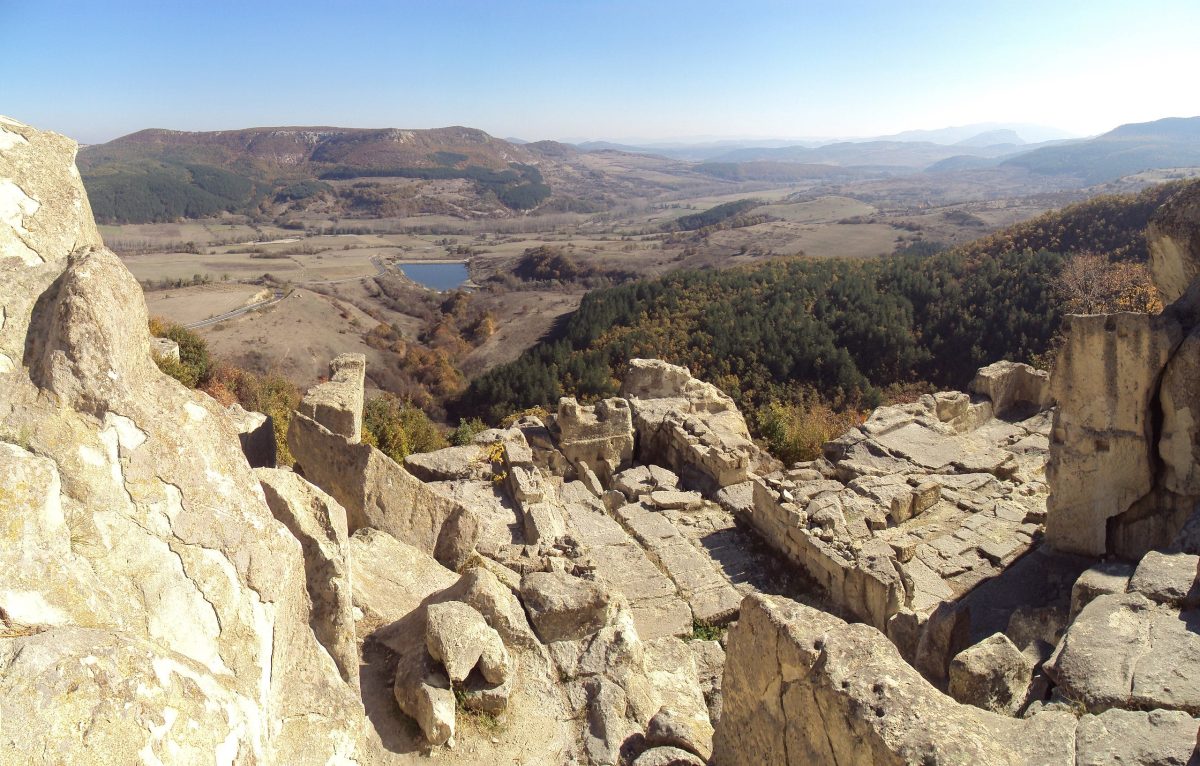
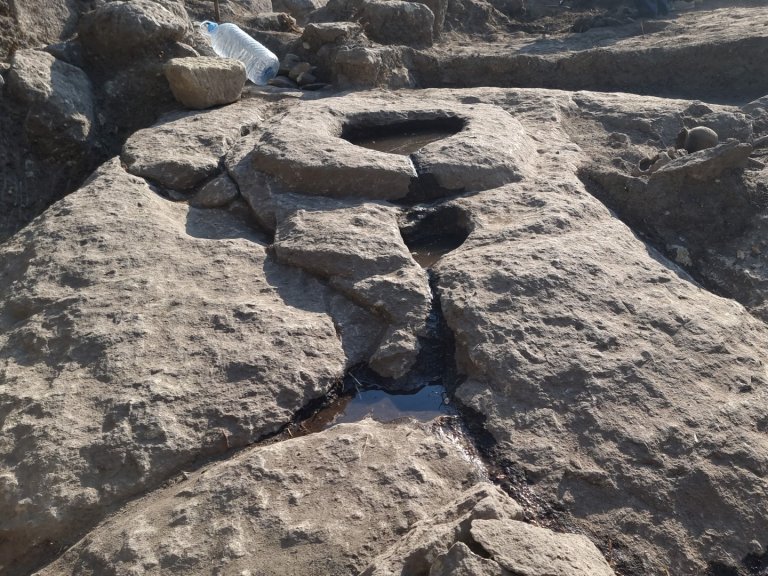
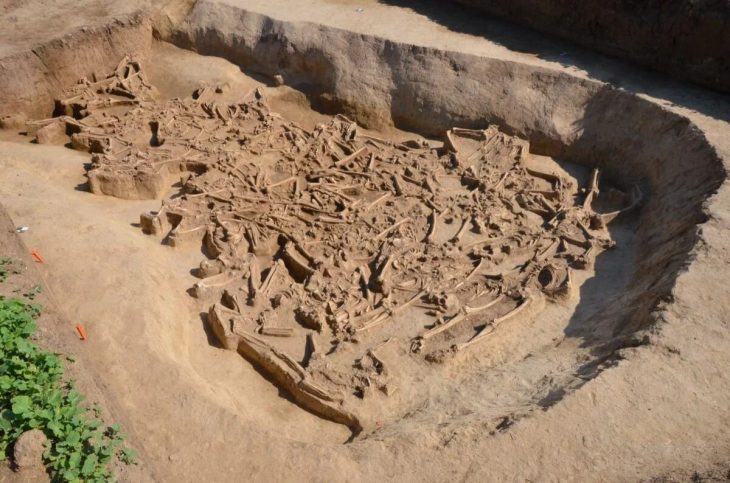
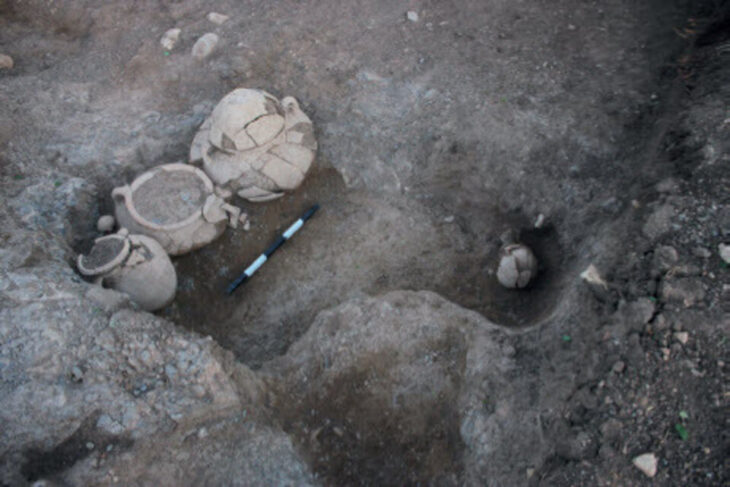
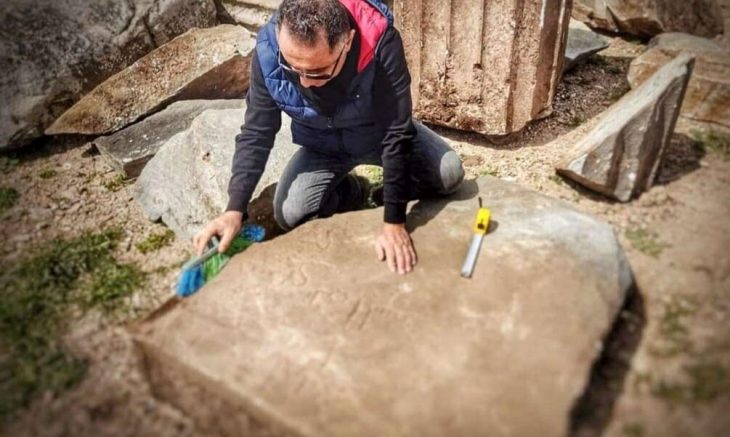
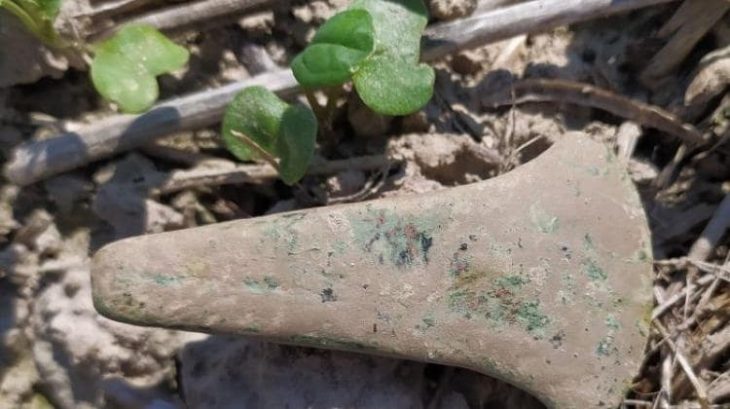
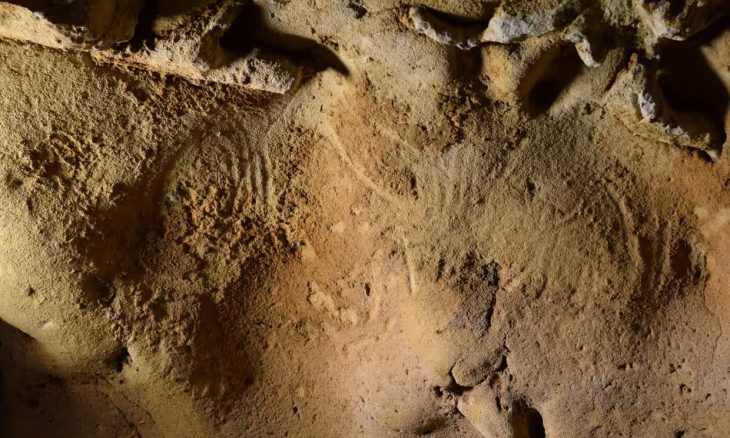
In the ancient Thracian city of Perperikon, partly carved into the rock in the Eastern Rhodope Mountains of Bulgaria, two altars were unearthed, one of which was used for sacred winemaking and the other for animal sacrifices.
Professor Nikolay Ovcharov, head of the Perperikon excavation team, announced the discovery of two altars, one designated for blood sacrifices, that mark the boundaries of a “sacra” area in the southern section of the archaeological site.
Prof. Nikolay Ovcharov, who has been leading excavations at the site for nearly 25 years, told BTA that these altars fully prove the fact that the great temple of Dionysus was located in the complex.
The priestesses of Thrace’s renowned Dionysus Oracle foretold the glorious futures of Alexander the Great and Augustus, the first Roman Emperor. This is what ancient historians tell us. However, none of these ancient sources have provided a precise description of the shrine’s location, other than to say it was on Thrace’s highest mountain, in the lands of the Satri tribe. So far, historians have claimed that the seer lived primarily in the Rhodope and Stara Planina mountains, where he competed with the Delphi-based Apollo Oracle in prestige and prophecy accuracy.
However, Perperikon is the largest megalithic settlement in the Balkans and has a history of 8,000 years. Over time it was used by various civilizations such as the Thracians, Romans, Byzantines, and the medieval Bulgarian Empire.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
In Perperikon, numerous rock-cut altars and sanctuaries that may have been used for religious rituals honoring Dionysus have been discovered by archaeologists. These altars, carved directly into the rock, often feature basins that may have been used for libation. Dionysus was central to the Orphic Mysteries, a collection of religious practices that began in Thrace.
Some scholars also suggest that the Thracian god Zagreus, son of Zeus and Persephone—who was dismembered by the Titans and reborn—was sometimes identified with an Orphic Dionysus, linked to mystery cults and the cycle of life and death. Sabazios, the sky father and horseman, was another deity worshipped in Thrace, and he might have also influenced later interpretations of Dionysus.
“The earliest sacrifices were made 3000-3200 years ago, at the end of the Bronze Age and the beginning of the Iron Age,” the archaeologist explained, adding: “As the altar is from the Roman era, we are using the data from that era and doing a comparative reconstruction,” said Prof. Nikolay Ovcharov.
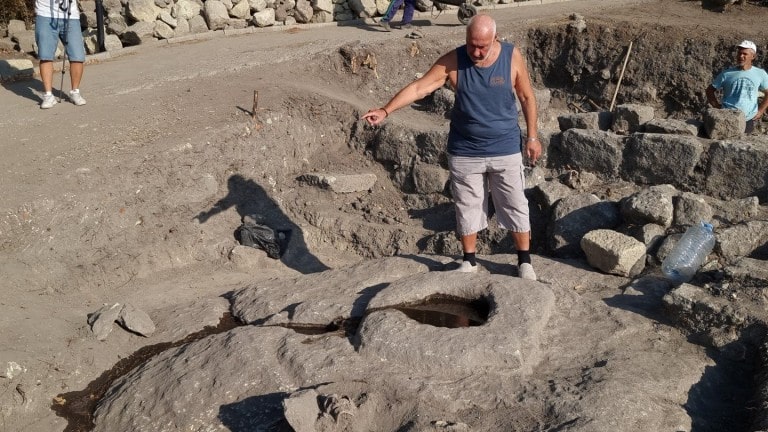

He noted that it was most likely an altar for the underground gods, where it was necessary for people to dress in black and animals to have black fur. He added that it must have been small animals, like goats and sheep, which were brought as sacrifices, and that it was also mandatory the animals were healthy, as well as that the animal itself went voluntarily, and not to be dragged by force.
Ovcharov said that the altar was most likely made as early as the end of the Bronze Age or the beginning of the Iron Age and was abandoned in the Middle Ages. It is related to the temples of the 3rd-4th century, which have been studied in the southern quarter and include the temple of the Eastern god Mithras, the temple of the Ancestors and an unidentified temple. Ovcharov emphasised that the two large sacrificial altars are only the beginning and more finds are to be expected.
The excavations at Perperikon will continue until the beginning of November.
Cover Image: Perperikon, Kardzhali District, Bulgaria