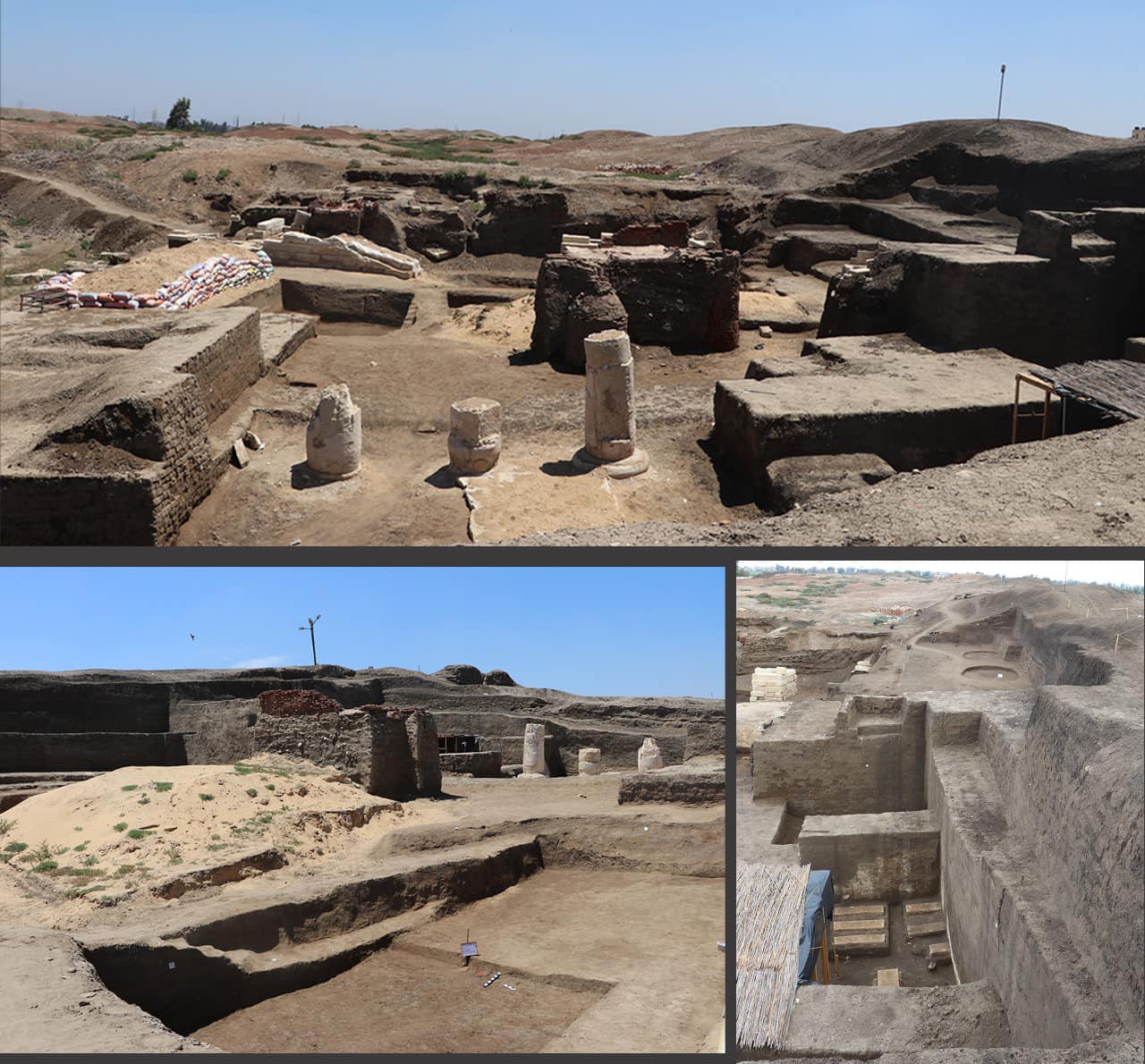
Archaeologists in Egypt unveiled the first and largest astronomical observatory from the 6th century BCE in the Buto Temple at Tell El-Faraeen archaeological site located in Kafr El-Sheikh Governorate.
The discovery was announced on the social media account of the Egyptian Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities.
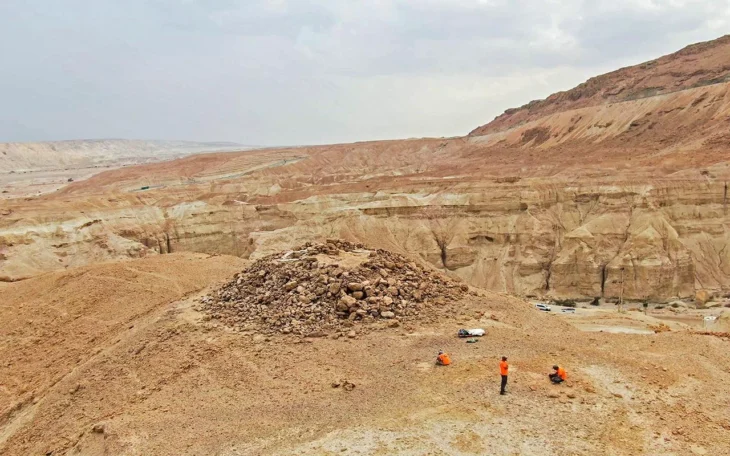
The observatory, which was made of mud brick, was crucial for monitoring the movements of the sun and stars. This astounding discovery demonstrates the ancient Egyptians’ profound understanding of and proficiency with astronomy.
“It highlights the advanced astronomical knowledge of the ancient Egyptians, including their ability to determine the solar calendar and significant religious and agricultural dates,” said Mohamed Ismail Khaled, Secretary-General of the Supreme Council of Antiquities (SCA).
The structure also gives an insight into the sophisticated techniques employed by the ancient Egyptians using simple tools, he added.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
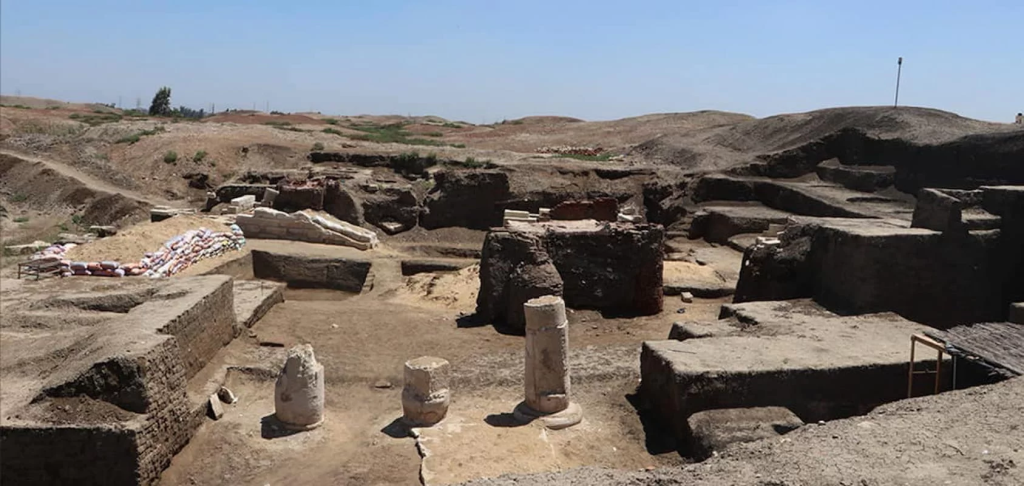

The head of the Egyptian Antiquities Sector at the Supreme Council of Antiquities, Ayman Ashmawy, said that the astronomical observatory building covers approximately 850 square meters.
It consists of an entrance facing east where the sun rises, he added, with a central columned hall open in the shape of the letter “L” preceded by a huge, high wall of mud bricks with an inward slope, resembling the style of the Egyptian edifice known in temple entrances.
Ashmawy said that the mission also found five mud brick rooms likely used to store tools, four small mud brick rooms, and a small stone room representing the observatory tower.
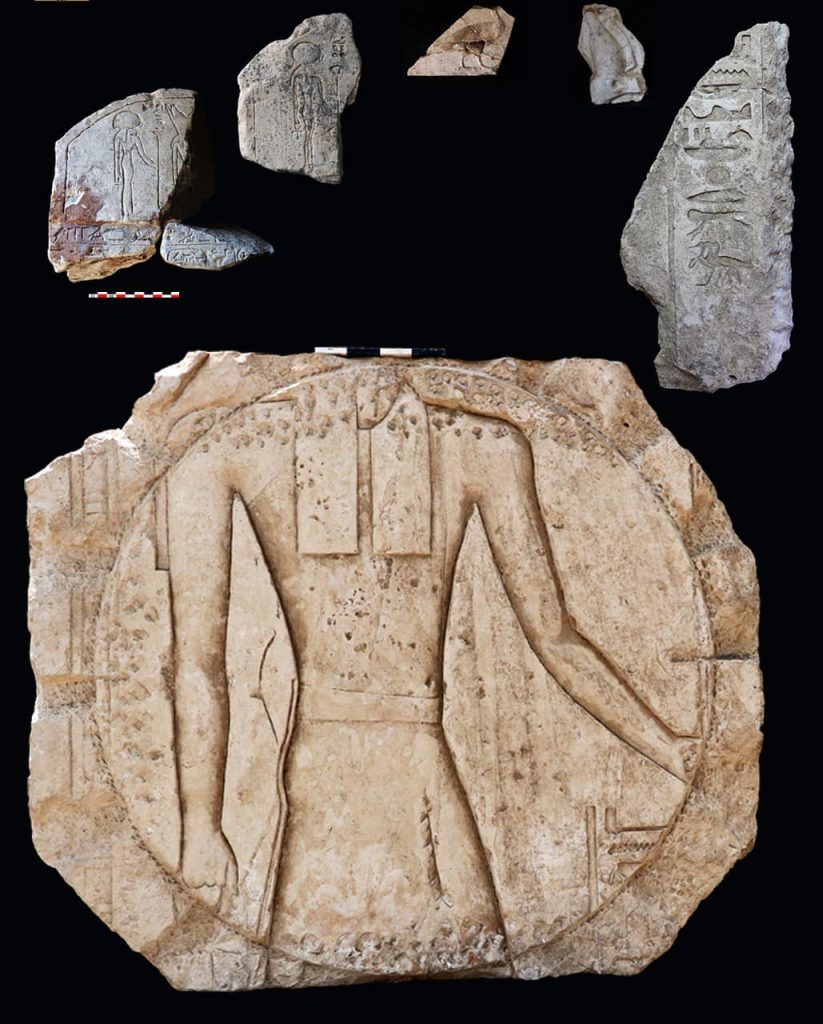

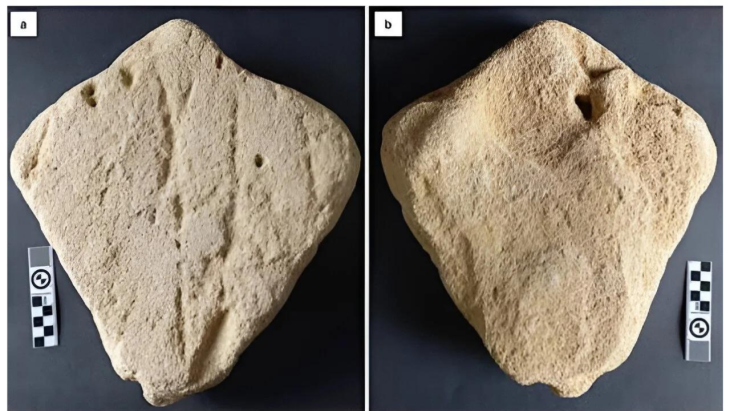
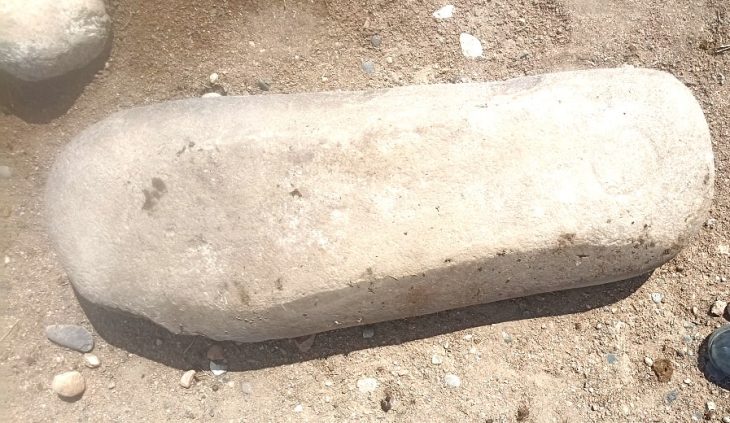
Among the key discoveries is a rare slanted stone sundial, referred to as a shadow clock, of its kind from that era. This sundial is made up of a 4.80-meter-long row of straight limestone slabs. On top were five flat blocks of limestone, two horizontal and three vertical. These slabs most likely had inclined lines on them that were used to gauge the sun’s shadow and angle, which made it easier to track the sun’s movements throughout the day.
Archaeologists also discovered a stone fixed to the floor of a circular chamber inside the observatory and two additional circular stones used to measure the sun’s inclination.
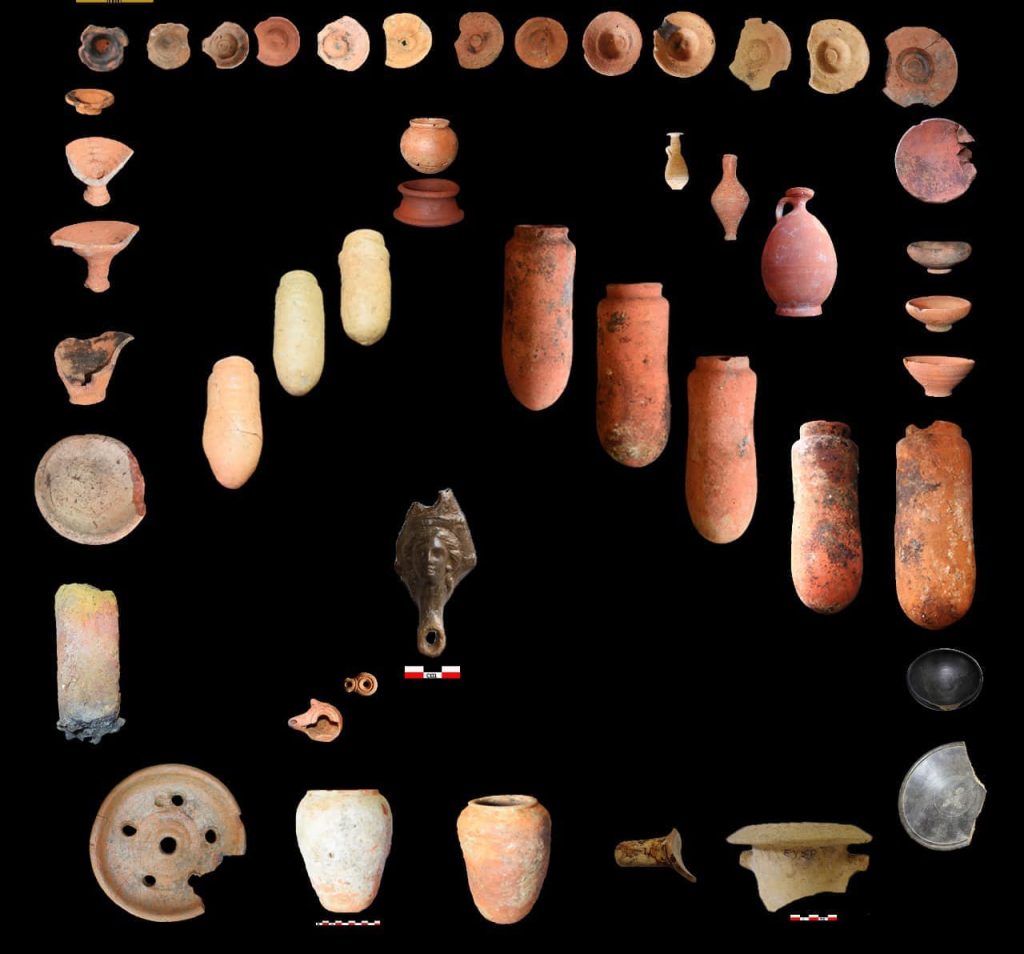

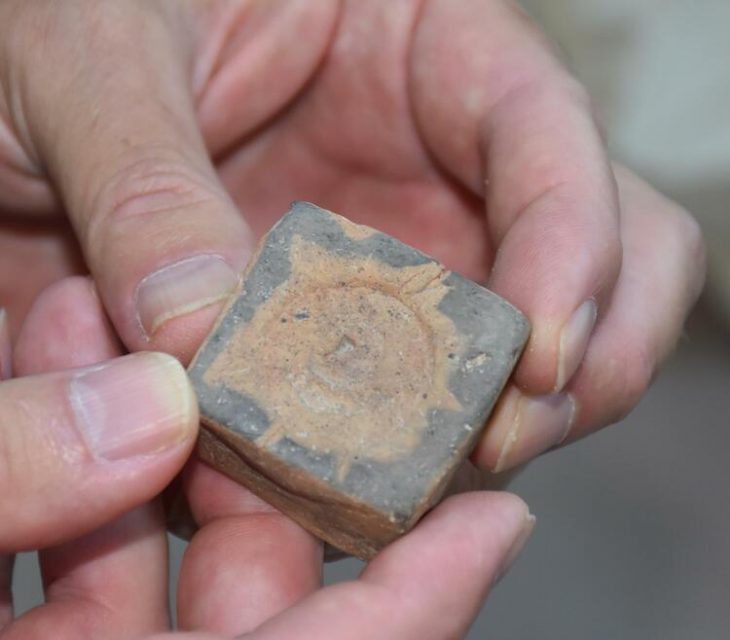
The work uncovered numerous artifacts, including a statue from the 26th Dynasty, a Merkhet measuring tool, and various religious items and pottery related to daily life and rituals, the ministry said in a statement.
The discovery highlights the value of Egyptian archaeological efforts in revealing new facets of the nation’s rich past and offers deeper insights into the scientific and religious practices of the ancient Egyptians.
Egypt Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities
Cover Image: Egypt Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities