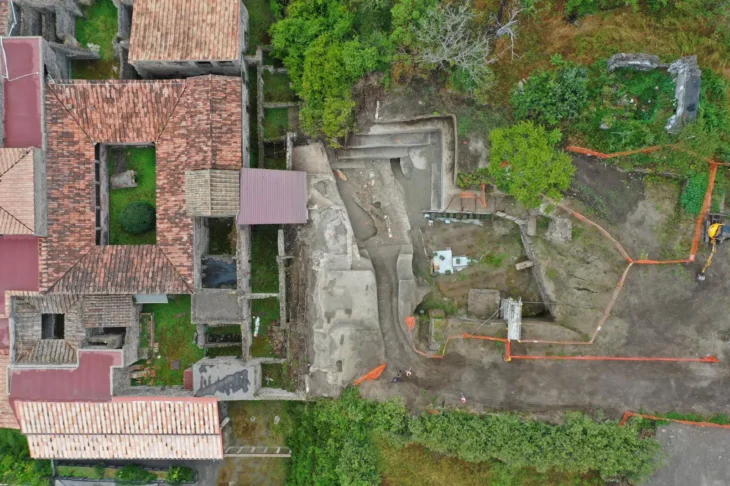
Experts suggest that markings on a stone pillar at the 12,000-year-old Göbeklitepe archaeological site in Türkiye probably represent the oldest solar calendar in history, having been established as a memorial to a catastrophic comet strike.
According to a recent study from the University of Edinburgh, the markings at the location might be a record of an astronomical event that marked a significant turning point in human civilization.
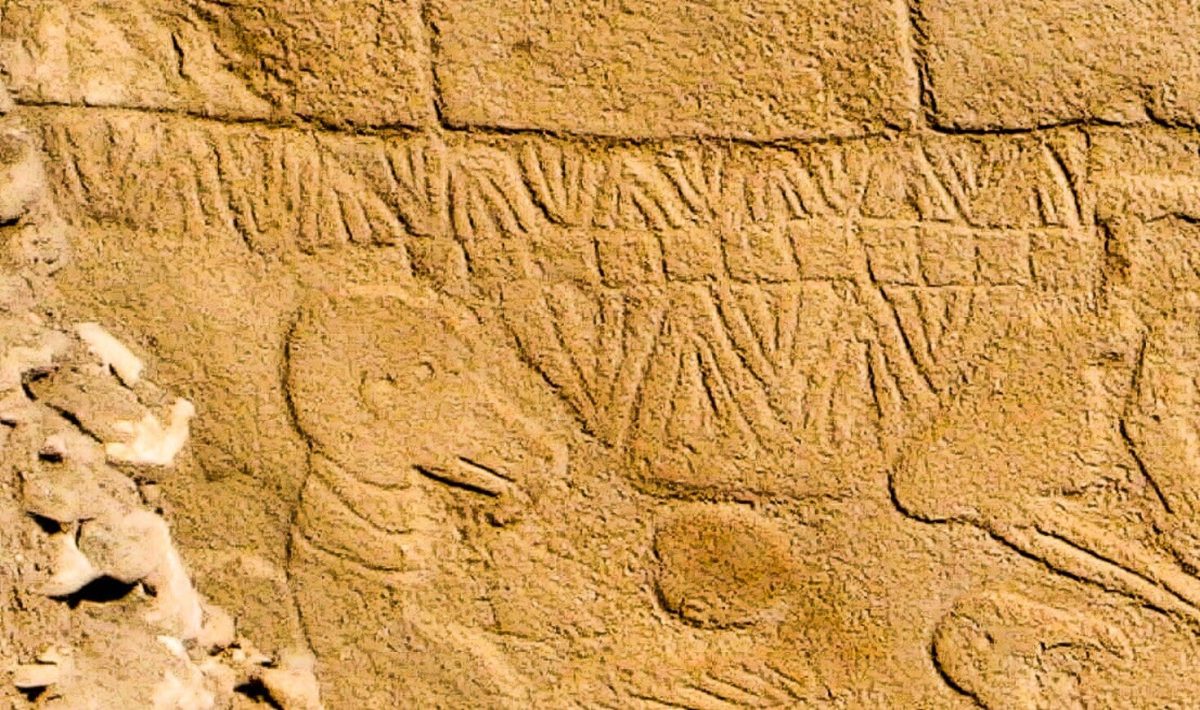
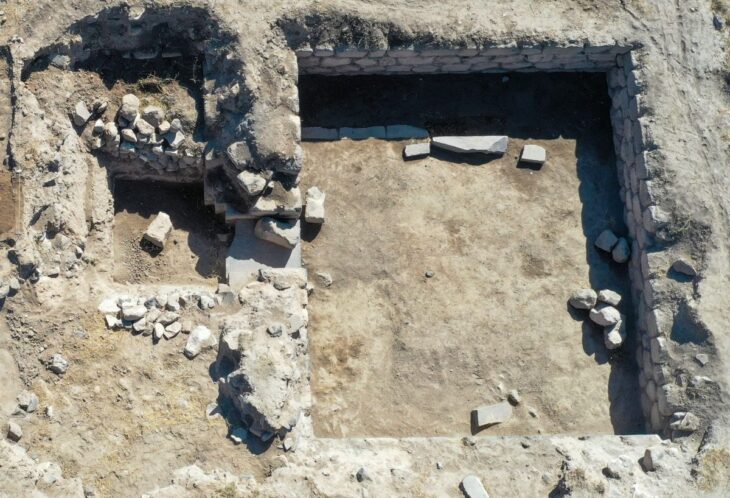
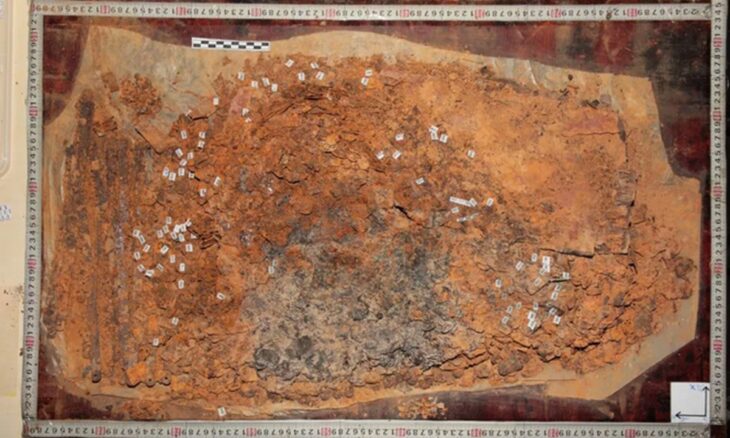
Southeast Türkiye’s Göbeklitepe is well-known for its array of enormous, T-shaped stone pillars adorned with animal and abstract symbol carvings. According to recent analysis, some of these carvings might have functioned as a kind of calendar that tracked important celestial events and marked the positions of the sun, moon, and stars.
This finding suggests that prehistoric humans utilized these engravings to document their observations of the universe, possibly signifying a primitive lunisolar calendar that combined solar and lunar cycles to predict the passage of time.
A fresh analysis of V-shaped symbols carved onto pillars at the site has found that each V could represent a single day. This interpretation allowed researchers to count a solar calendar of 365 days on one of the pillars, consisting of 12 lunar months plus 11 extra days.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
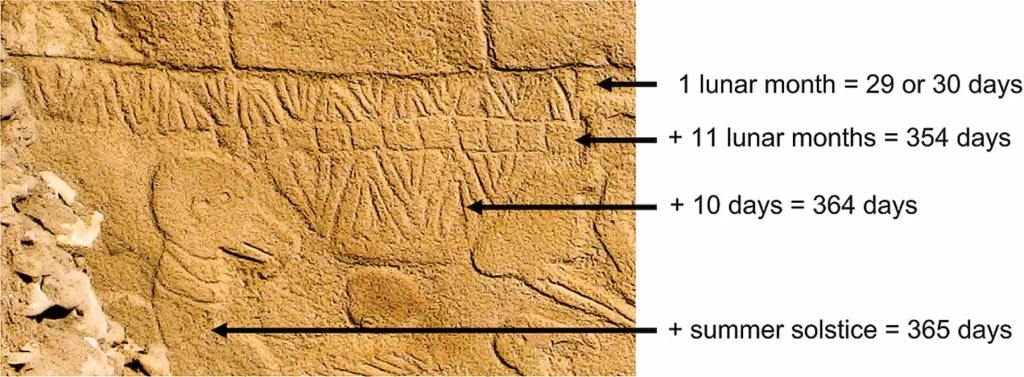
The summer solstice manifests as a distinct, unique day, symbolized by a V hung around the neck of a creature resembling a bird and believed to symbolize the summer solstice constellation at the time. Other statues nearby, possibly representing deities, have been found with similar V-markings at their necks.
More than a millennium before other known instances of lunisolar calendars, Göbekli Tepe may have had a highly developed calendar. This challenges our understanding into question the accuracy with which early humans were able to track celestial cycles and other astronomical phenomena.
Scientists believe that these carvings at Göbekli Tepe may commemorate a comet impact that occurred around 10,850 BCE, nearly 13,000 years ago. The comet strike is believed to have triggered a mini-ice age lasting over 1,200 years, which caused the extinction of many large animals. This event might also have led to changes in lifestyle and agriculture, paving the way for the rise of civilization in the Fertile Crescent of Western Asia.
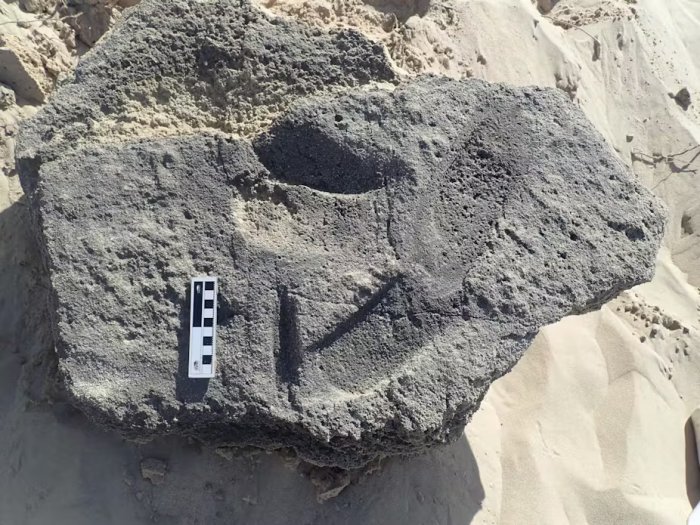
It is thought that the Taurid meteor stream is the source of the comet fragments that struck Earth, and this is depicted on another pillar at Göbekli Tepe. Further proof of the ancient people’s astronomical knowledge comes from this 27-day stream that seemed to originate from the constellations of Aquarius and Pisces.
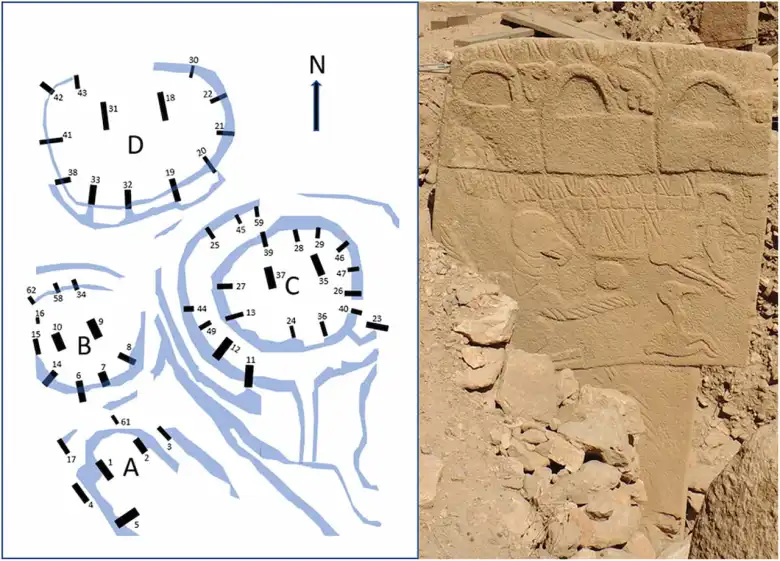
This discovery suggests that ancient people recorded dates using precession, the wobble of Earth’s axis affecting constellation movement, at least 10,000 years before Hipparchus of Ancient Greece documented it in 150 BC.
These carvings held significance for the people of Göbeklitepe for millennia, hinting that the impact event may have triggered a new cult or religion that influenced the development of civilization.
Dr Martin Sweatman of the University of Edinburgh’s School of Engineering, who led the research, said: “It appears the inhabitants of Göbekli Tepe were keen observers of the sky, which is to be expected given their world had been devastated by a comet strike. This event might have triggered civilization by initiating a new religion and by motivating developments in agriculture to cope with the cold climate. Possibly, their attempts to record what they saw are the first steps towards the development of writing millennia later.”