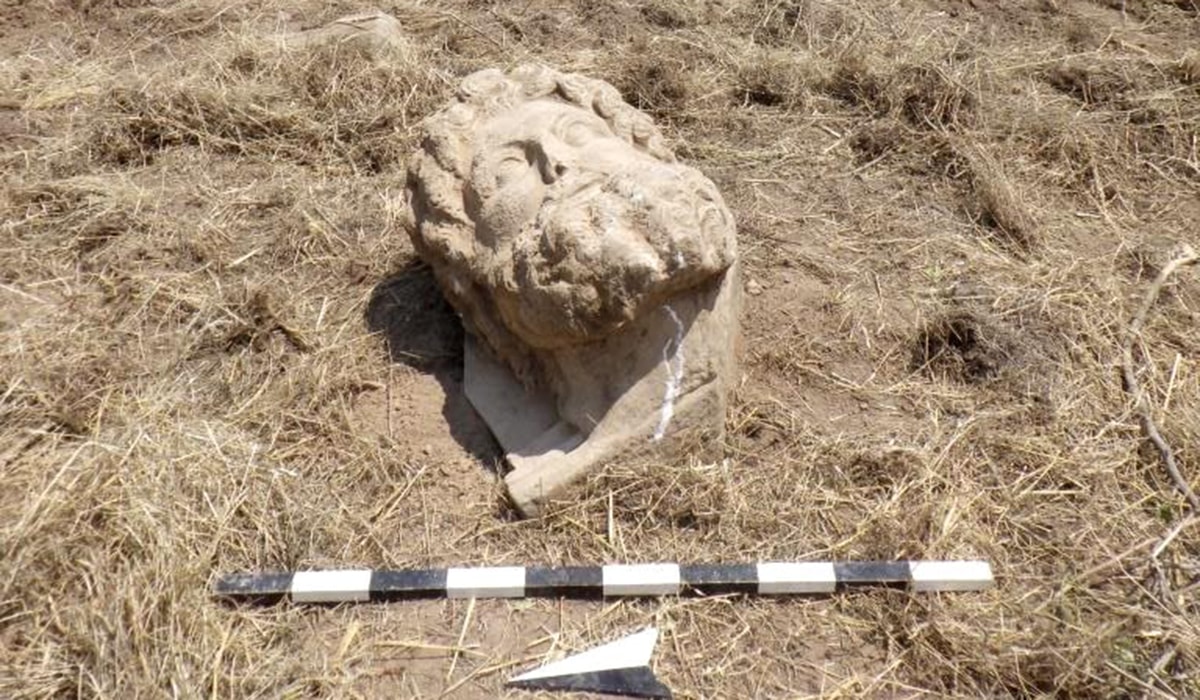
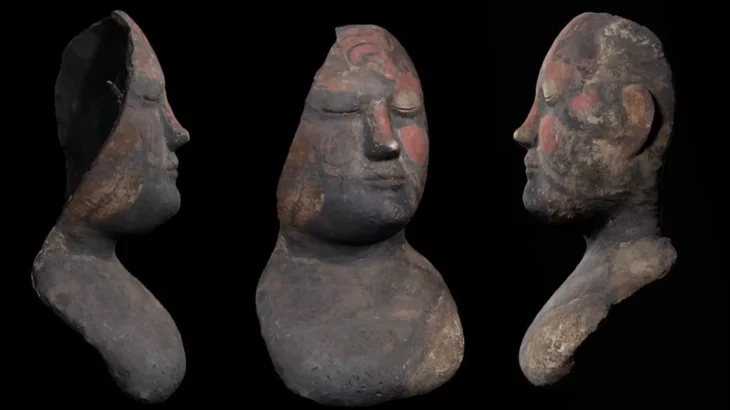
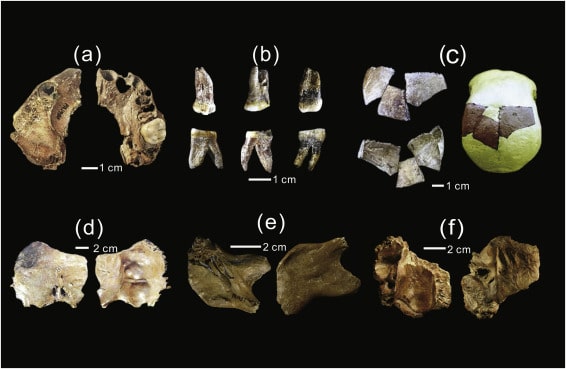
A marble ‘Zeus head’ was found in the ancient city of Aphrodisias, located within the borders of the Geyre neighborhood in the Karacasu district of Aydın province in western Türkiye.
The artifact found during excavations in the ancient city of Aphrodisias was announced by Mehmet Nuri Ersoy, Minister of Culture and Tourism of Türkiye.
Mehmet Nuri Ersoy, Minister of Culture and Tourism, in his post with the note ‘A unique discovery in Aphrodisias’, said, ‘The marble head, which reunited with the light of day after centuries, exhibits the splendor of Zeus, the most powerful and important god in Greek mythology.’
The bearded colossal marble head, carved in relief as an architectural console or part of a console, was found inverted near the surface in an area 50 meters west of the Temple of Aphrodite.
The 66-centimeter-high marble head underwent preliminary cleaning and conservation to remove heavily solidified soil deposits.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
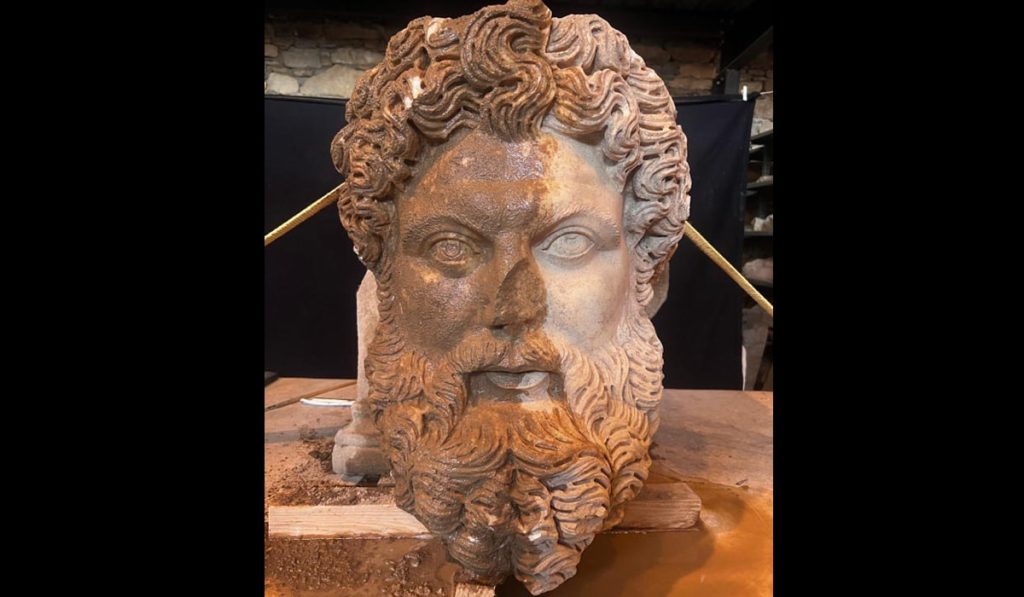

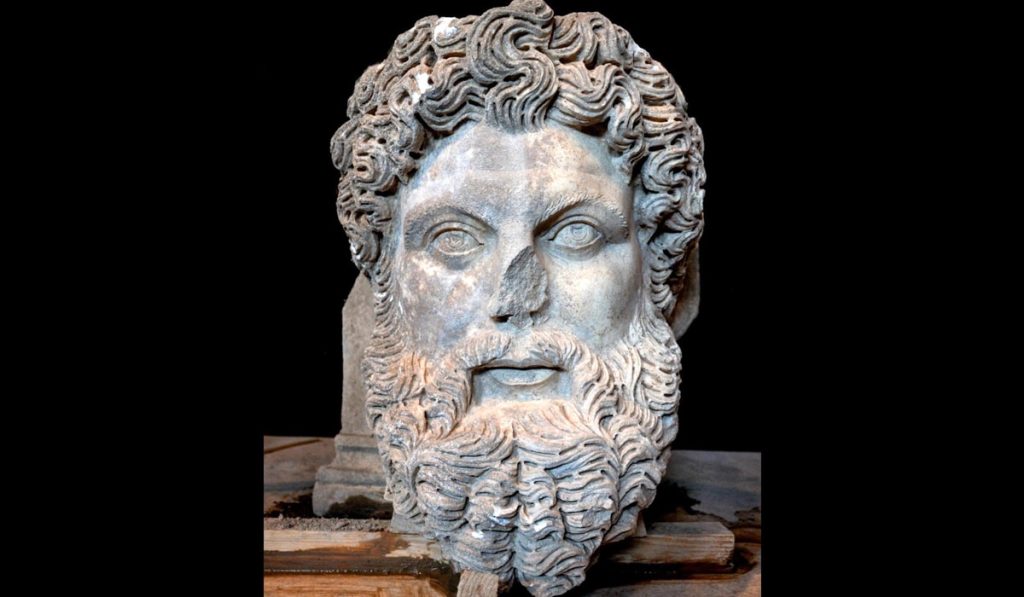
Made from a single block of medium-grained Aphrodisas marble, the head has been dated by archaeologists to the 2nd-3rd century AD.
“As if he were a breathing God…”
The Ministry of Culture and Tourism made the following statement: “The magnificent drill work on the hair and beard belongs to a top Aphrodisias sculpture workshop. The sophisticated depiction of the powerful divine image gives the head a powerful effect.
The delicate technique borrowed from portrait sculpture is used here to give the classical image of Zeus a more realistic, contemporary effect, as if he were a breathing god.
The head is an exceptional find of the highest quality and historical significance.”

Situated in the upper valley of the Morsynus River in southwest Turkey, the site is comprised of two parts: the northeastern marble quarries and the archaeological site of Aphrodisias. The city was constructed a century after the Aphrodite temple, which dates to the third century BC. Aphrodisias’s marble quarries and the sculptures created by its sculptors were the source of its wealth. Temples, a theater, an agora, and two bath complexes are among the major civic buildings that surround the city’s streets.
One of the main reasons Aphrodisias rose to prominence as a premier hub for the production of marble sculpture was the close proximity of the marble quarries to the city. City sculptors were well-known across the Roman Empire. They were renowned for their virtuoso portrait sculptures as well as their statues of gods and Dionysian figures in the Hellenistic style.
Aphrodisian sculptors were highly sought after in the major empire centers, such as Sardis, Stratonikeia, Laodikeia, Constantinople, and Rome, for their marble portrait busts and statues of emperors, governors, and philosophers in the late antiquity (4th–6th centuries AD). They were the most skilled marble statue carvers of the time. Because of the methods employed, the caliber of the regional artistic design, and the creation of sophisticated portrait sculpture, Aphrodisias occupied a special place in the Roman world.